Difference Between Associative And Commutative Property
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
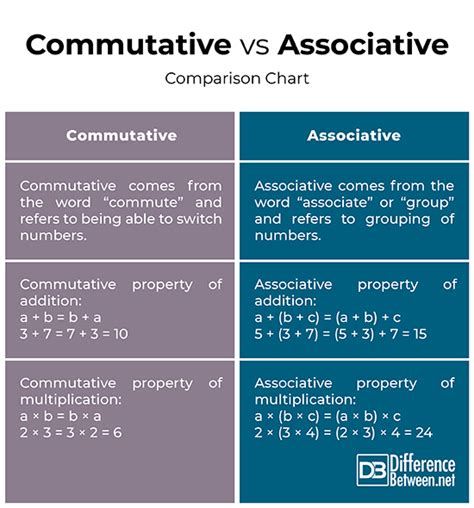
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Subtle Differences: Associative vs. Commutative Properties
Mathematics, at its core, is built upon fundamental principles that govern how numbers and operations interact. Among these foundational concepts, the associative and commutative properties stand out, often causing confusion due to their similarities. While both properties deal with the order of operations, they do so in distinct ways. Understanding these differences is crucial for mastering arithmetic, algebra, and even more advanced mathematical concepts. This article will delve deep into the nuances of the associative and commutative properties, clarifying their definitions, illustrating their applications, and highlighting the key distinctions that set them apart.
Understanding the Commutative Property
The commutative property, in essence, states that the order of operands doesn't affect the outcome of certain operations. This means that you can swap the numbers around, and the answer remains the same. This property applies primarily to addition and multiplication.
Commutative Property of Addition:
The commutative property of addition states that for any two numbers, a and b:
a + b = b + a
Example:
5 + 3 = 8 and 3 + 5 = 8. The order of addition doesn't change the sum.
This principle extends to more than two numbers. For instance:
2 + 4 + 6 = 12 and 6 + 2 + 4 = 12. The sum remains constant irrespective of the arrangement.
Commutative Property of Multiplication:
Similarly, the commutative property of multiplication states that for any two numbers, a and b:
a * b = b * a
Example:
4 * 7 = 28 and 7 * 4 = 28. The product remains unchanged despite altering the order of factors.
Again, this principle extends to multiple numbers:
2 * 3 * 5 = 30 and 5 * 2 * 3 = 30. The product remains consistent.
Where the Commutative Property Doesn't Apply:
Crucially, the commutative property does not hold true for all mathematical operations. It fails to apply to:
- Subtraction: 5 - 3 ≠ 3 - 5.
- Division: 10 / 2 ≠ 2 / 10.
- Exponentiation: 2³ ≠ 3²
This limitation is an important distinction to keep in mind when applying mathematical principles.
Delving into the Associative Property
Unlike the commutative property, which deals with the order of operands, the associative property concerns the grouping of operands within an expression involving the same operation. It states that the way numbers are grouped in an operation does not change the final result. This property primarily applies to addition and multiplication.
Associative Property of Addition:
The associative property of addition states that for any three numbers, a, b, and c:
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
Example:
(2 + 3) + 4 = 9 and 2 + (3 + 4) = 9. Regardless of how we group the numbers, the sum remains the same.
This property allows us to add numbers in any convenient grouping, simplifying complex calculations.
Associative Property of Multiplication:
Similarly, the associative property of multiplication states that for any three numbers, a, b, and c:
(a * b) * c = a * (b * c)
Example:
(2 * 5) * 3 = 30 and 2 * (5 * 3) = 30. The product remains the same irrespective of the grouping.
This is particularly helpful when dealing with larger multiplications.
Limitations of the Associative Property:
Like the commutative property, the associative property does not apply universally. It does not hold for:
- Subtraction: (5 - 3) - 1 ≠ 5 - (3 - 1).
- Division: (12 / 3) / 2 ≠ 12 / (3 / 2).
- Exponentiation: (2²)³ ≠ 2⁽²³⁾.
Key Differences: A Comparative Analysis
The following table summarizes the key differences between the commutative and associative properties:
| Feature | Commutative Property | Associative Property |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Order of operands | Grouping of operands |
| Applies to | Addition and multiplication | Addition and multiplication |
| Does not apply to | Subtraction, division, exponentiation, etc. | Subtraction, division, exponentiation, etc. |
| Illustrative Equation (Addition) | a + b = b + a | (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) |
| Illustrative Equation (Multiplication) | a * b = b * a | (a * b) * c = a * (b * c) |
| Impact | Changes the order of numbers in the operation | Changes the grouping of numbers in the operation |
| Real-World Analogy (Commutative) | Putting on socks and shoes; the order doesn't matter | |
| Real-World Analogy (Associative) | Adding ingredients to a cake; the order doesn't matter as long as all ingredients are added |
Practical Applications and Examples
These properties are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they are fundamental tools used extensively in various mathematical fields and practical applications.
1. Simplifying Calculations: The associative and commutative properties allow us to rearrange and regroup numbers to simplify complex calculations. For instance, when adding a series of numbers, it's often easier to group compatible numbers together. Similarly, when multiplying, grouping numbers that result in easy calculations can significantly speed up the process.
2. Algebra and Equation Solving: In algebra, these properties are crucial for manipulating equations and solving for unknowns. They allow us to rearrange terms and simplify expressions without altering the underlying mathematical truth.
3. Matrix Operations: In linear algebra, the associative and commutative properties (where applicable) simplify matrix operations such as addition and multiplication.
4. Programming and Computer Science: These properties are essential in computer science and programming for optimizing algorithms and improving the efficiency of code.
5. Everyday Life: While we may not consciously apply them, these properties are implicitly used in many aspects of daily life. Consider the task of packing a suitcase – the order in which items are placed generally doesn't matter (commutative), and grouping similar items together (associative) often makes packing more efficient.
Advanced Considerations: Beyond Basic Arithmetic
While this article primarily focuses on the application of these properties to basic arithmetic, their significance extends to more complex mathematical structures. For example:
-
Abstract Algebra: The associative and commutative properties are defining characteristics of algebraic structures such as groups, rings, and fields. In these abstract settings, the properties are generalized beyond numbers to encompass other mathematical objects.
-
Vector Spaces: In linear algebra, vector addition is both commutative and associative. This is crucial for many properties of vector spaces and their applications in physics and engineering.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
The associative and commutative properties, although seemingly simple, are fundamental building blocks of mathematics. Understanding their differences—that commutativity focuses on order, while associativity focuses on grouping—is vital for mastering arithmetic operations, simplifying complex calculations, and progressing to more advanced mathematical concepts. By grasping these nuances and appreciating their limitations, you solidify your foundation in mathematics and enhance your ability to solve a wide range of problems efficiently and accurately. Remember that while these properties offer valuable tools for simplification and manipulation, it's crucial to always verify their applicability to the specific operation at hand. Their consistent and correct application ensures accuracy and efficiency in mathematical processes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Layer Of The Skin Does Not Contain Blood Vessels
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Does Xenon Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Light Years Is Pluto From Earth
Mar 21, 2025
-
Sequence Is True For The Lytic Cycle Of A Virus
Mar 21, 2025
-
Does Protists Have Membrane Bound Organelles
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Associative And Commutative Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
