Difference Between Ac & Dc Motor
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
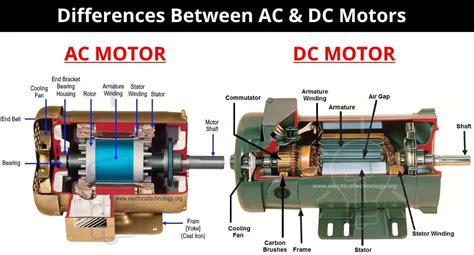
Table of Contents
AC vs. DC Motors: A Comprehensive Comparison
The world of electric motors is vast and varied, but two types stand out above the rest: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) motors. Understanding the key differences between these two is crucial for anyone involved in engineering, maintenance, or simply curious about the mechanics behind electric power. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core distinctions, exploring their construction, operation, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
Fundamental Differences: AC vs. DC Power Supply
The most fundamental difference lies in the type of power supply they utilize. As their names suggest:
-
AC motors operate on alternating current, where the direction of current flow reverses periodically. This cyclical change is typically 50 or 60 times per second (Hertz), depending on the regional power grid.
-
DC motors run on direct current, where the current flows consistently in one direction.
This seemingly simple difference has profound implications on the motor's design, operation, and overall characteristics.
Construction and Working Principles
While both motor types achieve rotational motion through electromagnetic interaction, their internal constructions differ significantly:
AC Motor Construction and Operation
AC motors are generally more robust and require less maintenance due to their simpler construction. They come in several types, each with unique characteristics:
-
Induction Motors: These are the most common type of AC motor. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. A rotating magnetic field is created in the stator (stationary part) by the AC supply, inducing a current in the rotor (rotating part). This induced current interacts with the stator's magnetic field, causing the rotor to turn. They are further categorized into Squirrel Cage and Wound Rotor types, with differences in rotor construction and starting characteristics.
-
Synchronous Motors: These motors run at a constant speed synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply. They require an external DC source for excitation of the rotor's field winding. Synchronous motors offer precise speed control, making them suitable for applications requiring high accuracy.
-
Single-phase vs. Three-phase: AC motors can be single-phase or three-phase, depending on the number of phases in the power supply. Three-phase motors are more powerful, efficient, and have smoother operation compared to their single-phase counterparts.
DC Motor Construction and Operation
DC motors, while generally more complex than AC motors, offer more precise speed control and higher starting torque. Key components include:
-
Commutator: This is a crucial part of a DC motor, acting as a mechanical switch. It reverses the current direction in the rotor windings to maintain the torque and rotational direction. This switching mechanism introduces maintenance concerns, as commutators can wear out over time.
-
Brushes: These are electrically conductive components that make contact with the commutator, facilitating the current flow to the rotor windings. Like commutators, brushes are subject to wear and tear.
-
Field Windings: These windings, located in the stator, generate the magnetic field that interacts with the rotor's current to produce torque. The arrangement of field windings can influence the motor's characteristics. Different configurations (series, shunt, compound) affect speed regulation, torque characteristics, and starting capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages: AC vs. DC
Choosing between an AC and DC motor depends heavily on the specific application. Let's break down their advantages and disadvantages:
AC Motor Advantages:
- Simplicity and Robustness: Generally simpler construction, leading to lower cost and higher reliability.
- Lower Maintenance: Fewer moving parts compared to DC motors, reducing maintenance needs and extending lifespan.
- Widely Available: Power readily available from the grid, making them ubiquitous in industrial and residential applications.
- Higher Efficiency at High Loads: In many cases, AC motors are more efficient when operating under heavy loads.
AC Motor Disadvantages:
- Less Precise Speed Control: Achieving precise speed control requires sophisticated techniques and often involves additional components.
- Higher Starting Current: Can draw significantly higher current during startup, potentially impacting the power supply.
- Lower Starting Torque: Generally offer lower starting torque compared to DC motors. This can be a limitation in some applications requiring high initial torque.
DC Motor Advantages:
- Precise Speed Control: Offers superior speed control capabilities, easily adjustable through varying the voltage or field current.
- High Starting Torque: Provides higher starting torque, suitable for applications requiring significant initial force.
- Better Efficiency at Low Loads: In certain applications, DC motors can exhibit better efficiency at lower loads.
DC Motor Disadvantages:
- Higher Maintenance: The commutator and brushes require regular maintenance and replacement, leading to higher lifecycle costs.
- Complex Construction: More complex internal structure, potentially leading to increased manufacturing costs.
- Higher Cost: Generally more expensive than comparable AC motors.
- More Susceptible to Electrical Noise: The commutator can generate electrical noise, potentially affecting sensitive electronics.
Applications: Where Each Motor Excels
The choice between AC and DC motors is highly application-dependent. Let's explore where each shines:
AC Motor Applications:
- Industrial Applications: Fans, pumps, compressors, conveyors, and other industrial machinery.
- Household Appliances: Refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and many more.
- Power Tools: Drills, saws, and other power tools (often using AC induction motors).
- Electric Vehicles (Increasingly): Induction motors are becoming more prevalent in electric vehicles due to their high efficiency and durability.
DC Motor Applications:
- Robotics: Precise control and high torque make them ideal for robotic actuators.
- Electric Vehicles (Traditionally): Historically dominant in electric vehicles, though AC induction motors are gaining ground.
- Automotive Applications: Power windows, seat adjustments, and other auxiliary systems.
- Computer Peripherals: Disk drives, printers, and other devices requiring precise control.
- Traction Motors (in some trains): DC motors, particularly those with regenerative braking capabilities, are still used in some train applications.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The landscape of electric motors is constantly evolving. Several key trends are shaping the future of both AC and DC motor technology:
-
Permanent Magnet Motors: Both AC and DC motors are increasingly employing permanent magnets, offering higher efficiency and potentially smaller size.
-
Brushless DC Motors: These motors eliminate the need for brushes and commutators, leading to longer lifespan and reduced maintenance. They combine the advantages of both AC and DC motors, providing precise control with higher efficiency and durability.
-
Advanced Control Systems: Sophisticated control systems are enhancing the performance and efficiency of both AC and DC motors, allowing for more precise speed and torque control.
-
Power Electronics: Advances in power electronics are facilitating more efficient conversion and control of electrical power, optimizing the operation of both AC and DC motors.
Conclusion
The choice between an AC and DC motor hinges on a careful consideration of the specific application requirements. Factors like speed control precision, starting torque needs, maintenance costs, and efficiency under various load conditions all play a vital role in the decision-making process. While AC motors often dominate in high-power, robust applications, DC motors excel where precise control and high starting torque are paramount. The ongoing advancements in motor technology are continuously blurring the lines between these two categories, offering increasingly sophisticated and efficient solutions for a wide range of applications. Understanding the nuances of each technology empowers engineers and consumers alike to make informed choices, leading to optimal performance and efficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Log X Log X 3 1
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Molecular Geometry For Bf3
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Subatomic Particle With A Positive Charge Is The
Mar 19, 2025
-
Select All Of The Statements Which Are True About Rainforests
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Differences Between Political Parties And Interest Groups
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Ac & Dc Motor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
