Copper And Nitric Acid Balanced Equation
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
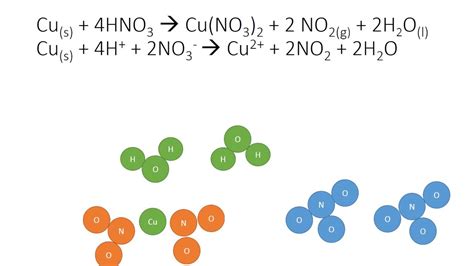
Table of Contents
Copper and Nitric Acid: A Deep Dive into the Balanced Equation and its Implications
The reaction between copper (Cu) and nitric acid (HNO₃) is a classic example of a redox reaction, captivating both students and seasoned chemists alike. This seemingly simple reaction yields fascinating results, showcasing the diverse oxidation states of nitrogen and the vibrant colors of copper's nitrate compounds. Understanding the balanced equation for this reaction is crucial to grasping the underlying chemistry and predicting the products formed under varying conditions. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of the copper and nitric acid reaction, exploring the balanced equations, the factors influencing the reaction, and its broader applications.
Understanding the Reaction: Redox at Play
The reaction between copper and nitric acid is a redox reaction, meaning it involves both reduction and oxidation processes occurring simultaneously. Copper, a transition metal, readily loses electrons (oxidation), while the nitrogen in nitric acid gains electrons (reduction). The specific products formed depend largely on the concentration of the nitric acid.
Dilute Nitric Acid Reaction
When copper reacts with dilute nitric acid, the primary reduction product is nitrogen monoxide (NO), a colorless gas that readily oxidizes to brown nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) in the presence of air. The balanced equation for this reaction is:
3Cu(s) + 8HNO₃(aq) → 3Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4H₂O(l)
Let's break down this equation:
- 3Cu(s): Three moles of solid copper are oxidized.
- 8HNO₃(aq): Eight moles of aqueous nitric acid act as both the oxidizing agent and the source of nitrate ions.
- 3Cu(NO₃)₂(aq): Three moles of aqueous copper(II) nitrate are formed, a soluble salt resulting in a characteristic blue-green solution.
- 2NO(g): Two moles of gaseous nitrogen monoxide are produced, a colorless gas that quickly turns brown due to its oxidation to NO₂.
- 4H₂O(l): Four moles of liquid water are formed as a byproduct.
This reaction is characterized by the evolution of a colorless gas (NO), which quickly turns brown in air due to its oxidation to NO₂. The solution turns a distinctive blue-green due to the formation of copper(II) nitrate.
Concentrated Nitric Acid Reaction
The reaction with concentrated nitric acid differs significantly. In this case, nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) is the primary reduction product. The balanced equation for this reaction is:
Cu(s) + 4HNO₃(aq) → Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2NO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
Here's a breakdown:
- Cu(s): One mole of solid copper is oxidized.
- 4HNO₃(aq): Four moles of aqueous nitric acid act as the oxidizing agent.
- Cu(NO₃)₂(aq): One mole of aqueous copper(II) nitrate is formed, resulting in the same blue-green solution.
- 2NO₂(g): Two moles of gaseous nitrogen dioxide are produced, a reddish-brown gas with a pungent odor. This is a key distinction from the dilute acid reaction.
- 2H₂O(l): Two moles of liquid water are formed.
The concentrated nitric acid reaction is easily distinguished by the evolution of reddish-brown fumes of NO₂. The solution still turns blue-green due to the copper(II) nitrate.
Factors Influencing the Reaction
Several factors influence the reaction between copper and nitric acid:
- Concentration of Nitric Acid: As we've seen, the concentration directly affects the reduction product of nitrogen: NO from dilute acid and NO₂ from concentrated acid.
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature generally accelerates the reaction rate.
- Surface Area of Copper: A larger surface area of copper (e.g., using copper powder instead of a solid piece) increases the reaction rate due to increased contact with the acid.
- Presence of other substances: The presence of other substances in the solution can either catalyze or inhibit the reaction.
Observations and Safety Precautions
Performing this experiment requires careful attention to safety:
- Fume Hood: Always conduct this reaction in a well-ventilated fume hood to avoid inhaling toxic nitrogen oxides. NO₂ is particularly harmful.
- Protective Gear: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and a lab coat.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of the reaction waste according to established laboratory procedures. Copper(II) nitrate solutions are mildly toxic and should not be released into the environment.
Applications and Significance
The reaction between copper and nitric acid has several important applications:
- Synthesis of Copper(II) Nitrate: This reaction serves as a common method for synthesizing copper(II) nitrate, a valuable chemical used in various applications, including as a catalyst and in electroplating.
- Analytical Chemistry: The reaction can be used in quantitative analysis to determine the concentration of copper in a sample.
- Etching and Cleaning: Nitric acid is often used in etching and cleaning processes for copper surfaces in various industries.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Deeper Concepts
The reaction between copper and nitric acid provides an excellent platform to explore several advanced chemical concepts:
- Redox Potentials: Understanding the standard reduction potentials of copper and the nitrogen species involved helps predict the spontaneity and products of the reaction.
- Reaction Kinetics: Studying the rate of reaction under different conditions allows for an investigation of reaction kinetics, including activation energy and rate constants.
- Equilibrium: While the reactions primarily proceed to completion, investigating the equilibrium aspects can provide valuable insights.
Conclusion: A Reaction Rich in Chemistry
The reaction between copper and nitric acid is a fascinating example of a redox reaction that highlights the versatility of both copper and nitrogen. Understanding the balanced equations, the factors affecting the reaction, and the safety precautions is crucial for anyone working with these chemicals. This reaction serves as a valuable tool in various fields, and its study enhances a deeper understanding of fundamental chemical principles. This comprehensive exploration should provide a solid foundation for further study and experimentation. Remember to always prioritize safety when conducting chemical experiments.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Two Subatomic Particles Found In The Nucleus
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Monomer Of Cellulose
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Sequence Is Correct
Mar 22, 2025
-
No Mans Sky 1 2 6 24 120
Mar 22, 2025
-
Number Of Electrons In A 2p Orbital
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Copper And Nitric Acid Balanced Equation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
