Ca Oh 2 Hcl Balanced Equation
News Leon
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
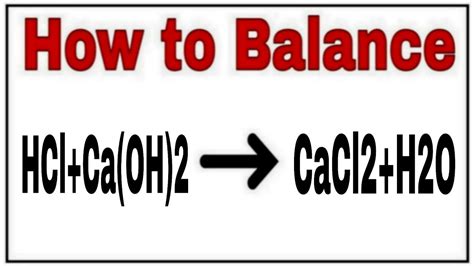
Table of Contents
The Balanced Equation: Ca(OH)₂ + HCl and its Implications
The reaction between calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂, and hydrochloric acid, HCl, is a classic example of a neutralization reaction in chemistry. Understanding this reaction, its balanced equation, and its implications is crucial for various applications, from understanding basic chemical principles to practical uses in industry and everyday life. This article delves deep into the Ca(OH)₂ + HCl reaction, exploring its balanced equation, stoichiometry, applications, and safety considerations.
Understanding the Reactants
Before diving into the reaction itself, let's understand the individual components:
Calcium Hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂
Calcium hydroxide, also known as slaked lime or hydrated lime, is a white, crystalline powder. It's a strong base, meaning it readily dissociates in water to release hydroxide ions (OH⁻), increasing the solution's pH. Its strong basic nature makes it useful in various applications, discussed later. It is relatively insoluble in water, meaning only a limited amount dissolves to form a saturated solution. The solubility of Ca(OH)₂ increases slightly with decreasing temperature.
Hydrochloric Acid, HCl
Hydrochloric acid is a strong, highly corrosive acid. It is a colorless, pungent-smelling liquid. In aqueous solution, it completely dissociates into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻). The high concentration of H⁺ ions makes it highly acidic, with a low pH. HCl is a common reagent in many chemical processes and is also found in the stomach as gastric acid, aiding digestion.
The Balanced Chemical Equation
The reaction between calcium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid is a neutralization reaction, where an acid reacts with a base to produce salt and water. The unbalanced equation is:
Ca(OH)₂ + HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O
This equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms of each element isn't equal on both sides. To balance it, we need to adjust the coefficients to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides. The balanced equation is:
Ca(OH)₂ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + 2H₂O
This balanced equation shows that one molecule of calcium hydroxide reacts with two molecules of hydrochloric acid to produce one molecule of calcium chloride and two molecules of water. This ratio is crucial for stoichiometric calculations, which we'll discuss later.
Stoichiometry and Calculations
Stoichiometry is the quantitative relationship between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Using the balanced equation, we can perform various calculations, such as determining the amount of product formed from a given amount of reactant or vice versa.
For example:
-
Determining the moles of HCl needed to react completely with a given amount of Ca(OH)₂: If we have 'x' moles of Ca(OH)₂, we would need 2x moles of HCl based on the stoichiometric ratio (1:2) in the balanced equation.
-
Calculating the mass of CaCl₂ produced: Knowing the moles of Ca(OH)₂ used and the molar mass of CaCl₂, we can calculate the theoretical yield of CaCl₂ using the stoichiometric ratio.
-
Limiting Reactant Determination: If we have unequal molar amounts of Ca(OH)₂ and HCl, one reactant will be completely consumed before the other. This reactant is called the limiting reactant, and it dictates the amount of product formed.
These calculations are fundamental in chemistry and are vital in various applications, including industrial processes and laboratory experiments.
Applications of the Ca(OH)₂ + HCl Reaction
The neutralization reaction between Ca(OH)₂ and HCl has numerous applications:
1. Acid-Base Titrations:
This reaction is frequently used in acid-base titrations. Titration is a quantitative analytical technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution (in this case, either HCl or Ca(OH)₂) using a solution of known concentration. The equivalence point, where the moles of acid and base are equal, is determined using an indicator that changes color at a specific pH.
2. Wastewater Treatment:
Calcium hydroxide is used to neutralize acidic wastewater from industrial processes before it's released into the environment. The reaction effectively neutralizes the acidity, reducing the environmental impact.
3. Chemical Synthesis:
Calcium chloride (CaCl₂), a product of this reaction, is widely used as a desiccant (drying agent), in road de-icing, and in various other chemical processes. The controlled reaction between Ca(OH)₂ and HCl can be utilized to synthesize CaCl₂ with high purity.
4. Agriculture:
Calcium hydroxide is used to adjust the pH of soil in agriculture. It can neutralize acidic soils, making them more suitable for plant growth. The reaction with acidic components in the soil helps to optimize soil conditions.
5. Food and Beverage Industry:
Calcium hydroxide has limited use in food and beverage processing, primarily as a pH adjuster or in some specific food preservation techniques.
Safety Precautions
When handling calcium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid, it's crucial to prioritize safety:
-
Hydrochloric Acid: HCl is highly corrosive and can cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat. Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhalation of fumes.
-
Calcium Hydroxide: Although less hazardous than HCl, Ca(OH)₂ can irritate skin and eyes. Wear appropriate PPE when handling it. Avoid inhalation of dust.
-
Neutralization Reaction: The neutralization reaction itself can be exothermic (releases heat), particularly when using concentrated solutions. Add the acid to the base slowly and carefully to avoid splashing and excessive heat generation. Always work under proper ventilation to prevent the build-up of heat and potentially dangerous gases.
-
Waste Disposal: Dispose of the reaction mixture properly according to local regulations.
Conclusion
The reaction between Ca(OH)₂ and HCl, represented by the balanced equation Ca(OH)₂ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + 2H₂O, is a fundamental chemical reaction with far-reaching applications. Understanding its stoichiometry, applications, and safety aspects is essential for students, researchers, and professionals in various fields. From quantitative analysis in titrations to wastewater treatment and industrial chemical synthesis, this reaction plays a vital role in many processes. Always prioritize safety when handling these chemicals and follow proper laboratory procedures. Remember that this reaction represents a simplified model; the actual behavior of the system might be more complex due to factors like temperature, concentrations, and presence of other substances. Further exploration into the kinetics and thermodynamics of the reaction provides deeper insights into this fundamental process. The practical applications highlighted are just a few examples; many other industrial and scientific processes rely on the principles demonstrated by this seemingly simple chemical reaction. The importance of accurate stoichiometric calculations and a profound understanding of safety procedures are crucial for successful outcomes in all these applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Opposite Of Brilliant
Apr 01, 2025
-
Does Accumulated Depreciation Have A Credit Balance
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Element Has 4 Protons And 5 Neutrons
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Does Radius Decrease Across A Period
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Krebs Cycle Takes Place In
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ca Oh 2 Hcl Balanced Equation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
