What Element Has 4 Protons And 5 Neutrons
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
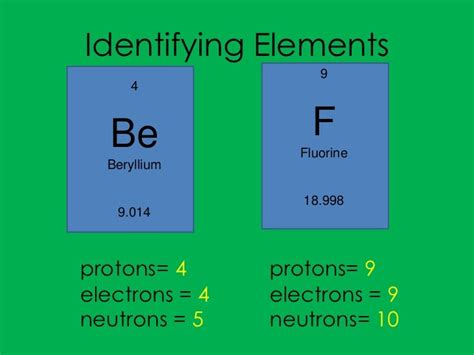
Table of Contents
What Element Has 4 Protons and 5 Neutrons? Unveiling the Mystery of Beryllium-9
The question, "What element has 4 protons and 5 neutrons?" leads us on a fascinating journey into the world of atomic structure and isotopes. The answer isn't immediately obvious, requiring a basic understanding of atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. Let's delve into the specifics to unravel the mystery.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
To understand what element possesses 4 protons and 5 neutrons, we must first grasp the fundamental components of an atom:
- Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and determines its chemical properties.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also found in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its chemical behavior.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. Electrons participate in chemical bonding and determine an atom's reactivity.
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. This number uniquely identifies each element on the periodic table. For instance, hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1 (1 proton), helium (He) has an atomic number of 2 (2 protons), and so on.
The mass number of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. It represents the atom's total mass, with protons and neutrons contributing approximately one atomic mass unit (amu) each. Electrons have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Count
Now, here's where things get interesting. While the number of protons defines an element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same atomic number (same number of protons) but different mass numbers (different numbers of neutrons).
Isotopes of the same element exhibit similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons, dictating their reactivity. However, they may differ slightly in physical properties due to their varying mass. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, meaning they undergo decay over time.
Identifying the Element: Beryllium-9
Returning to our original question, an element with 4 protons is beryllium (Be), as its atomic number is 4. This means every beryllium atom has 4 protons in its nucleus.
However, the question also specifies 5 neutrons. This indicates a specific isotope of beryllium. The mass number of this isotope is 4 (protons) + 5 (neutrons) = 9. Therefore, the element with 4 protons and 5 neutrons is Beryllium-9 (⁹Be).
Properties of Beryllium-9
Beryllium-9 is the most common and stable isotope of beryllium, making up approximately 100% of naturally occurring beryllium. Let's examine some of its key characteristics:
Physical Properties:
- Solid at room temperature: Beryllium is a grayish-white, strong, lightweight metal.
- High melting point: It has a relatively high melting point, indicating strong metallic bonding.
- High thermal conductivity: Beryllium efficiently conducts heat.
- High modulus of elasticity: It possesses exceptional stiffness and strength-to-weight ratio.
- Toxicity: Beryllium and its compounds are toxic, posing health risks if inhaled or ingested.
Chemical Properties:
- Relatively unreactive: Beryllium exhibits amphoteric behavior, meaning it can react with both acids and bases. However, it is relatively unreactive compared to other alkali earth metals.
- Forms compounds: Beryllium readily forms compounds with various elements, showcasing a range of oxidation states.
- Strong metallic bonding: The strong metallic bonding in beryllium contributes to its high melting point and other physical properties.
Applications of Beryllium and its Isotopes
Beryllium's unique properties make it valuable in various applications:
- Aerospace: Due to its lightweight yet strong nature, beryllium finds use in aircraft and spacecraft components, reducing weight and improving performance.
- Nuclear reactors: Beryllium's ability to moderate neutrons makes it a vital material in nuclear reactors.
- X-ray technology: Beryllium's transparency to X-rays makes it suitable for X-ray windows in medical and scientific instruments.
- Electronics: Its high thermal conductivity makes it useful in electronic devices to manage heat dissipation.
- Military applications: Its strength and light weight are advantageous in military applications.
While Beryllium-9 is the most common isotope, other beryllium isotopes exist, albeit with shorter half-lives and varying applications in research and specific scientific fields. For instance, Beryllium-7, a radioactive isotope, finds use in certain medical imaging techniques and environmental studies.
Further Exploration: Isotopic Abundance and Nuclear Reactions
The abundance of different isotopes within a sample of an element is crucial. Isotopic abundance refers to the relative proportion of each isotope present in a naturally occurring sample. In the case of beryllium, ⁹Be accounts for almost all naturally occurring beryllium, with trace amounts of other isotopes.
Nuclear reactions can alter the number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus, leading to the formation of different isotopes or even entirely new elements. These reactions are essential in various fields, including nuclear energy generation, medical treatments (radiotherapy), and scientific research. Understanding these reactions provides a more profound comprehension of the behavior of elements and their isotopes.
Conclusion: The Significance of Beryllium-9
The element with 4 protons and 5 neutrons is Beryllium-9 (⁹Be), a stable and abundant isotope of beryllium. Its unique combination of properties – strength, lightness, and high thermal conductivity – makes it a valuable material in a wide range of applications, from aerospace to nuclear technology. Understanding atomic structure, isotopes, and nuclear reactions provides valuable insight into the nature of matter and the behavior of elements, highlighting the importance of Beryllium-9 within this broader scientific context. Further research into the properties and applications of Beryllium and its isotopes continues to reveal new possibilities and advances in various fields of science and technology. The study of isotopes, such as Beryllium-9, underscores the complexity and diversity within the seemingly simple world of elements, emphasizing the intricate relationships between protons, neutrons, and the resulting properties and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Rubbing Alcohol Homogeneous Or Heterogeneous
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is Equivalent Fraction Of 4 5
Apr 02, 2025
-
Organelle Where Cellular Respiration Takes Place
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Number Is 45 Of 60
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Oxygen A Solid Liquid Or A Gas
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Element Has 4 Protons And 5 Neutrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
