Balance Equation C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
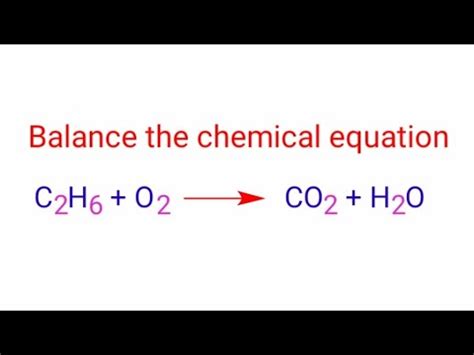
Table of Contents
Balancing the Combustion Equation: C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
The complete combustion of ethane (C₂H₆), a common alkane, with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) is a fundamental chemical reaction with significant implications in various fields, from understanding energy production to assessing environmental impact. This article delves deep into the intricacies of balancing the chemical equation for this reaction, exploring the underlying principles, various balancing methods, and the importance of stoichiometry in accurately representing the reaction.
Understanding the Combustion Reaction
Before diving into the balancing process, let's establish a firm understanding of what's happening at a molecular level. Ethane (C₂H₆), a colorless and odorless gas, reacts with oxygen (O₂) in a highly exothermic reaction—meaning it releases a significant amount of heat. This reaction is the basis of many combustion engines and industrial processes. The products of complete combustion are carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). Incomplete combustion, however, can produce carbon monoxide (CO) and other harmful byproducts. We'll focus solely on the complete combustion scenario in this article.
The unbalanced equation representing this reaction is:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
This equation simply states that ethane and oxygen react to form carbon dioxide and water. However, it doesn't accurately reflect the relative amounts of each substance involved. To accurately represent the reaction, we need to balance the equation.
The Importance of Balanced Equations
A balanced chemical equation adheres to the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. The total mass of the reactants (the substances on the left side of the arrow) must equal the total mass of the products (the substances on the right side of the arrow). This means that the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. An unbalanced equation doesn't satisfy this crucial principle and thus fails to accurately represent the reaction.
Balancing the equation ensures that:
- Stoichiometric ratios are established: This allows us to determine the precise molar ratios of reactants and products involved.
- Accurate calculations are possible: We can accurately calculate the amounts of reactants needed and the amounts of products formed.
- A complete picture of the reaction is provided: A balanced equation offers a comprehensive and accurate representation of the chemical transformation.
Methods for Balancing the Equation
Several methods can be used to balance the combustion equation for ethane. We will explore two common approaches:
1. The Inspection Method (Trial and Error)
This method involves systematically adjusting the coefficients (the numbers placed in front of the chemical formulas) until the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation. It's a trial-and-error process, but with practice, it becomes efficient.
Let's balance the equation using the inspection method:
-
Balance Carbon (C): We have 2 carbon atoms on the left (in C₂H₆) and 1 on the right (in CO₂). To balance carbon, we place a coefficient of 2 in front of CO₂:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + H₂O
-
Balance Hydrogen (H): We have 6 hydrogen atoms on the left (in C₂H₆) and 2 on the right (in H₂O). To balance hydrogen, we place a coefficient of 3 in front of H₂O:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
-
Balance Oxygen (O): Now, let's count the oxygen atoms. On the right, we have 4 oxygen atoms from 2CO₂ (2 x 2 = 4) and 3 oxygen atoms from 3H₂O (3 x 1 = 3), totaling 7 oxygen atoms. On the left, we have 2 oxygen atoms (in O₂). To balance oxygen, we need a coefficient of 7/2 in front of O₂:
C₂H₆ + (7/2)O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
However, fractional coefficients are generally avoided in balanced equations. To eliminate the fraction, we multiply the entire equation by 2:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
This is the balanced equation for the complete combustion of ethane. Notice that the number of atoms of each element is now equal on both sides of the equation.
2. The Algebraic Method
The algebraic method is a more systematic approach, particularly useful for complex reactions. It involves assigning variables to the coefficients and setting up a system of algebraic equations based on the conservation of atoms.
Let's assign variables to the coefficients:
aC₂H₆ + bO₂ → cCO₂ + dH₂O
Now, we can set up equations based on the conservation of each element:
- Carbon (C): 2a = c
- Hydrogen (H): 6a = 2d
- Oxygen (O): 2b = 2c + d
We can solve this system of equations. Let's arbitrarily set a = 1 (we can choose any non-zero value for one of the variables). Then:
- c = 2a = 2
- d = 3a = 3
- 2b = 2(2) + 3 = 7 => b = 7/2
Again, we get a fractional coefficient (b = 7/2). Multiplying the entire equation by 2 to eliminate the fraction, we obtain the same balanced equation as before:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
Stoichiometric Calculations and Applications
The balanced equation provides the foundation for performing stoichiometric calculations. Stoichiometry deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. For instance, the balanced equation tells us that:
- 2 moles of ethane react with 7 moles of oxygen.
- 4 moles of carbon dioxide and 6 moles of water are produced.
This information is crucial in various applications:
- Energy Production: Understanding the stoichiometry of ethane combustion is vital in designing and optimizing combustion engines and power plants. It helps determine the optimal fuel-to-air ratio for maximum energy output and minimal pollution.
- Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes rely on the combustion of hydrocarbons like ethane. Accurate stoichiometric calculations are essential for efficient process control and yield maximization.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Knowing the stoichiometric ratios helps estimate the amount of greenhouse gases (CO₂) produced during ethane combustion, allowing for better environmental impact assessments and the development of cleaner energy technologies.
Incomplete Combustion: A Deviation from the Balanced Equation
It's important to note that the balanced equation we derived represents complete combustion. In reality, incomplete combustion can occur, particularly under conditions of limited oxygen supply. Incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide (CO) and/or soot (carbon particles) along with CO₂ and H₂O. The balanced equation for incomplete combustion is more complex and depends on the specific conditions. For example, a possible equation for incomplete combustion could be:
2C₂H₆ + 5O₂ → 4CO + 6H₂O
This equation shows that less oxygen leads to the formation of carbon monoxide instead of carbon dioxide. Carbon monoxide is a highly toxic gas, highlighting the importance of ensuring sufficient oxygen supply during combustion processes.
Conclusion
Balancing the chemical equation for the combustion of ethane, C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O, is a fundamental exercise in stoichiometry. The balanced equation, 2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O, provides a crucial quantitative description of this important reaction, allowing for accurate calculations and a deeper understanding of the process. The balanced equation's applications extend to various fields, including energy production, industrial processes, and environmental impact assessment. Understanding both complete and incomplete combustion scenarios is vital for optimizing processes and mitigating environmental risks associated with hydrocarbon combustion.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Projectile Is Fired Horizontally From A Gun
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Europe Is Called The Peninsula Of Peninsulas
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Mineralocorticoid
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Benefit Of Insurance
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Happens To The Plant Cell In A Hypertonic Solution
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Balance Equation C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
