An External User Of Accounting Information
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
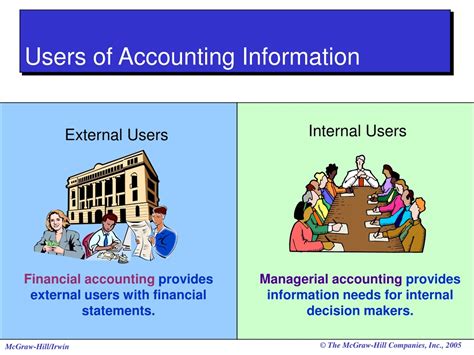
Table of Contents
The External User of Accounting Information: A Deep Dive
Accounting information isn't just for internal use; it's a vital resource for a wide range of external users who make crucial decisions based on a company's financial health and performance. Understanding who these external users are, what information they need, and how they utilize it is crucial for both businesses and accounting professionals. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse world of external users of accounting information, detailing their specific needs and the implications of accurate and timely financial reporting.
Who are the External Users of Accounting Information?
External users are individuals or entities outside a company who rely on its financial statements and other accounting data for various purposes. This group encompasses a broad spectrum of stakeholders, each with unique information requirements. Let's examine some of the key players:
1. Investors: The Cornerstone of External Use
Investors, both current and potential, form the largest and arguably most important group of external users. They scrutinize financial statements to assess a company's profitability, liquidity, and solvency before making investment decisions. Their needs are multifaceted:
-
Shareholders: Existing shareholders use financial information to evaluate the company's performance and determine whether to hold, buy more, or sell their shares. They look for indicators of growth, profitability, and dividend potential.
-
Potential Investors: Prospective investors rely heavily on financial statements to assess the risk and return profile of an investment. They carefully analyze key ratios, trends, and financial health indicators to make informed investment choices.
-
Creditors and Lenders: These stakeholders are interested in a company's ability to repay its debts. They use financial information to assess creditworthiness, including debt-to-equity ratios, cash flow statements, and overall financial stability.
2. Creditors and Lenders: Assessing Creditworthiness
Creditors and lenders (banks, financial institutions, and bondholders) use accounting information to gauge a company's creditworthiness before extending loans or credit. They focus on aspects such as:
-
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio indicates the proportion of debt financing compared to equity financing. A higher ratio suggests higher financial risk.
-
Cash Flow Statement: This statement provides insight into a company's cash inflows and outflows, indicating its ability to meet its debt obligations.
-
Profitability Ratios: These ratios demonstrate a company's ability to generate profits, which contributes to its ability to repay debt.
3. Government and Regulatory Bodies: Ensuring Compliance
Government agencies and regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US use accounting information to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Their concerns include:
-
Tax Compliance: Accurate accounting information is crucial for determining the correct amount of taxes owed.
-
Financial Reporting Compliance: Regulatory bodies monitor financial reporting to ensure accuracy, transparency, and adherence to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
-
Fraud Detection: Government agencies may use accounting data to detect and investigate potential instances of financial fraud.
4. Customers: Evaluating Long-Term Stability
While less directly involved than investors or creditors, customers benefit from a company's financial stability. Their interest lies in the long-term viability of the business:
-
Product Availability: A financially sound company is more likely to continue producing and supplying goods or services.
-
Reputation and Trust: Financial stability influences a customer's perception of a company's reliability and trustworthiness.
5. Suppliers: Assessing Credit Risk
Suppliers evaluate a company's financial health to assess the credit risk associated with providing goods or services on credit. They use accounting information to:
-
Determine Credit Limits: Financial statements help determine appropriate credit limits to minimize the risk of non-payment.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Suppliers may use financial data to negotiate favorable payment terms.
6. Employees: Evaluating Job Security and Compensation
Employees use accounting information, particularly in large companies, to assess job security and potential for salary increases. Key aspects include:
-
Company Performance: Strong financial performance often translates to higher job security and better compensation opportunities.
-
Pension Plans: Financial health directly impacts the sustainability of employee pension plans.
7. Competitors: Benchmarking and Strategic Planning
Competitors use publicly available accounting information to benchmark their own performance against that of their rivals. This data helps in:
-
Strategic Planning: Understanding a competitor's financial strength and weaknesses informs strategic planning and market positioning.
-
Market Share Analysis: Financial data can provide insights into a competitor's market share and growth trajectory.
The Types of Information Used by External Users
External users typically access a range of financial information, including:
-
Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
-
Income Statement: Shows a company's revenues, expenses, and profits over a period of time.
-
Cash Flow Statement: Tracks the movement of cash both into and out of a company over a period of time.
-
Statement of Changes in Equity: Details the changes in a company's equity over a period of time.
-
Notes to the Financial Statements: These provide additional information and explanations to the main financial statements, clarifying accounting policies and significant transactions.
-
Financial Ratio Analysis: This involves calculating various ratios from the financial statements to gain insights into profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency.
The Importance of Accurate and Timely Financial Reporting
The accuracy and timeliness of accounting information are paramount for external users. Inaccurate or delayed information can lead to:
-
Poor Investment Decisions: Investors may make incorrect investment decisions based on flawed data, resulting in financial losses.
-
Erroneous Credit Decisions: Lenders may extend credit to companies that are not creditworthy, leading to defaults and losses.
-
Inefficient Resource Allocation: Government agencies may allocate resources inefficiently based on inaccurate financial reporting.
-
Damaged Reputation: A company with a history of inaccurate financial reporting may suffer reputational damage, affecting its ability to attract investors and customers.
Ethical Considerations and the Role of Auditors
The ethical implications of accounting information are significant. Independent auditors play a critical role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. They provide an objective assessment of the financial health of a company, adding a layer of credibility for external users. Any instances of fraudulent or misleading financial reporting can have severe consequences for all stakeholders involved.
The Future of External Use of Accounting Information
With the increasing use of technology and data analytics, the way external users access and interpret accounting information is evolving rapidly. This includes:
-
XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): XBRL is a standard for electronic business reporting, making financial data more accessible and easily analyzed.
-
Data Visualization Tools: These tools allow users to visualize complex financial data more effectively, enhancing understanding and decision-making.
-
Predictive Analytics: Advanced analytics are being used to predict future financial performance based on historical accounting data.
Conclusion: A Crucial Link in the Business Ecosystem
External users of accounting information play a critical role in the business ecosystem. Their decisions, based on the accuracy and timeliness of financial reporting, significantly impact the success and sustainability of businesses. Ensuring the quality and integrity of accounting information is therefore not only crucial for the companies themselves but also essential for maintaining a robust and transparent market economy. The continued evolution of technology and analytical techniques will further enhance the way external users leverage this information, making accurate and ethical accounting practices more vital than ever before.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Dendrites Differ From Axons In That Dendrites
Mar 20, 2025
-
Find The Lettered Angles In Each Of The Following Figures
Mar 20, 2025
-
Labelled Diagram Of A Reflex Arc
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Kingdom Includes Only Multicellular Heterotrophs
Mar 20, 2025
-
A Cylinder With A Movable Piston
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An External User Of Accounting Information . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
