1 Sinx 1 Sinx Secx Tanx 2
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
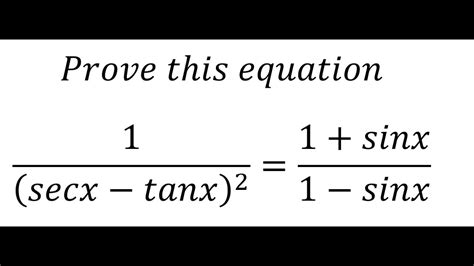
Table of Contents
Decoding the Trigonometric Expression: 1 - sinx - sinx secx tanx = 2
This article delves into the trigonometric equation 1 - sinx - sinx secx tanx = 2, exploring its simplification, solutions, and the underlying trigonometric identities crucial for its resolution. We'll not only solve the equation but also illuminate the mathematical reasoning and techniques involved, making it accessible to a wide range of readers, from high school students to advanced learners. This in-depth analysis will cover various aspects, including:
Understanding the Components: A Trigonometric Primer
Before tackling the equation directly, let's review the fundamental trigonometric functions and identities involved:
- sinx: The sine of x, representing the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
- cosx: The cosine of x, representing the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
- tanx: The tangent of x, representing the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right-angled triangle, or equivalently, sinx/cosx.
- secx: The secant of x, the reciprocal of cosx (1/cosx).
- cscx: The cosecant of x, the reciprocal of sinx (1/sinx).
- cotx: The cotangent of x, the reciprocal of tanx (cosx/sinx).
Key Trigonometric Identities: These identities are crucial for simplifying and solving trigonometric equations. Some important ones include:
- sin²x + cos²x = 1: This Pythagorean identity forms the basis of many trigonometric manipulations.
- 1 + tan²x = sec²x: Derived from the Pythagorean identity.
- 1 + cot²x = csc²x: Another Pythagorean identity variant.
Simplifying the Equation: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Let's analyze the given equation: 1 - sinx - sinx secx tanx = 2
Our primary goal is to simplify the equation by expressing it in terms of sine and cosine, leveraging the fundamental trigonometric identities.
-
Rewrite in terms of sine and cosine: Replace secx with (1/cosx) and tanx with (sinx/cosx). The equation becomes:
1 - sinx - sinx * (1/cosx) * (sinx/cosx) = 2
-
Simplify the expression: Combine the terms involving sinx and cosx:
1 - sinx - (sin²x/cos²x) = 2
-
Rearrange the equation: Move all terms to one side to create a standard equation:
-1 - sinx - (sin²x/cos²x) = 0
-
Find a common denominator: To combine the terms more effectively, let's find a common denominator:
(-cos²x - sinx cos²x - sin²x) / cos²x = 0
-
Utilize the Pythagorean identity: Remember that sin²x + cos²x = 1. We can use this to substitute for cos²x:
(-(1 - sin²x) - sinx(1 - sin²x) - sin²x) / cos²x = 0
-
Expand and simplify: Expand the expression and collect like terms:
(-1 + sin²x - sinx + sin³x - sin²x) / cos²x = 0
-
Further simplification: The sin²x terms cancel out:
(-1 - sinx + sin³x) / cos²x = 0
Solving the Equation: Finding the Solutions
Now that we have simplified the equation, we need to solve for x. Notice that the equation is satisfied only if the numerator is equal to zero, since the denominator cannot be zero (as that would lead to division by zero). Therefore, we solve:
-1 - sinx + sin³x = 0
This is a cubic equation in sinx. Let's substitute y = sinx:
y³ - y - 1 = 0
Solving cubic equations can be complex. Numerical methods (like Newton-Raphson) or graphical methods are often employed for finding approximate solutions. Analytical solutions using Cardano's method are possible but lengthy and complex.
Approximate Solutions: Using numerical methods or a graphing calculator, we find approximate solutions for y (and therefore sinx):
- y ≈ 1.3247
- y ≈ -0.6624 + 0.5623i
- y ≈ -0.6624 - 0.5623i
Since the sine function's range is [-1, 1], only the real solution within this range is relevant. However, even the real solution (approximately 1.3247) lies outside the range of sinx, implying that there are no real solutions for x in the given equation. The complex solutions indicate that the equation has solutions within the complex plane, but these are beyond the scope of typical trigonometric problem-solving.
Analyzing the Results and Implications
The lack of real solutions highlights an important aspect of trigonometric equations: not all trigonometric equations have solutions within the real number domain. The original equation, after simplification, leads to a cubic equation that doesn't yield real solutions for sinx within its acceptable range.
This analysis demonstrates the importance of:
- Careful simplification: Incorrect simplification can lead to erroneous results.
- Understanding the domain and range: Recognizing the constraints on trigonometric functions is crucial.
- Appropriate solution techniques: Choosing the right method to solve the resulting equation is essential.
Expanding on Trigonometric Equation Solving Techniques
Solving trigonometric equations often involves a variety of techniques beyond the specific example demonstrated above. Here's a brief overview:
- Factoring: If the equation can be factored, it simplifies the solution process considerably.
- Using trigonometric identities: Mastering trigonometric identities is paramount for simplifying and solving equations.
- Quadratic formula: If the equation reduces to a quadratic in a trigonometric function, the quadratic formula provides a direct solution.
- Substitution: Substituting variables can simplify complex equations.
- Graphical methods: Plotting the functions can visually identify approximate solutions.
- Numerical methods: For equations that are difficult to solve analytically, numerical methods provide approximate solutions.
Conclusion: A Deep Dive into Trigonometric Problem Solving
This exploration of the equation 1 - sinx - sinx secx tanx = 2 demonstrates a structured approach to solving complex trigonometric problems. By systematically simplifying the equation, utilizing key identities, and applying appropriate solution techniques, we arrived at a conclusion regarding the solvability within the real number domain. Understanding the underlying principles and applying various mathematical tools is vital for success in trigonometry and related fields. This detailed analysis serves as a valuable resource for students and anyone interested in furthering their understanding of trigonometric equation solving. Remember to always check your work, verify solutions, and consider the domain and range of trigonometric functions when solving trigonometric equations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
One Atomic Mass Unit Is Equal To
Mar 25, 2025
-
Acetic Acid Reacts With Sodium Hydroxide
Mar 25, 2025
-
Two Opposite Charges Separated By A Small Distance
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Light Years To The Moon
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Correct Order Of Phases In Cellular Respiration
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 Sinx 1 Sinx Secx Tanx 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
