X 3 2x 2 X 4
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
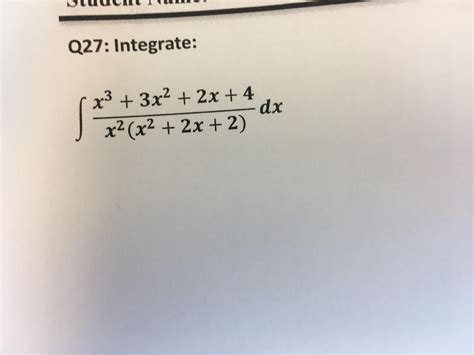
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into x³ + 2x² + x⁴
The seemingly simple algebraic expression, x³ + 2x² + x⁴, holds a surprising depth of mathematical concepts within its compact form. This article will explore this expression, examining its various facets, from basic polynomial manipulation to more advanced applications in calculus and beyond. We'll uncover its secrets and reveal its significance in the broader world of mathematics.
Understanding the Basics: Polynomials and Their Properties
Before we delve into the specifics of x³ + 2x² + x⁴, let's establish a solid foundation in polynomial algebra. A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables (like 'x' in our case) and coefficients, combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Each term in a polynomial is a product of a coefficient and a variable raised to a non-negative integer power.
Key Terminology:
- Degree: The highest power of the variable in the polynomial. In x³ + 2x² + x⁴, the degree is 4.
- Coefficient: The numerical factor of each term. In our expression, the coefficients are 1, 2, and 1.
- Terms: The individual parts of a polynomial separated by plus or minus signs. Our expression has three terms: x³, 2x², and x⁴.
- Constant Term: A term with no variable (a power of 0). Our expression does not have a constant term.
Rearranging and Simplifying: Putting the Polynomial in Standard Form
Mathematicians typically prefer to present polynomials in standard form, which involves arranging the terms in descending order of their powers. Our expression, x³ + 2x² + x⁴, isn't in standard form. Let's rearrange it:
x⁴ + x³ + 2x²
This seemingly small change improves readability and facilitates further mathematical operations.
Analyzing the Polynomial: Roots, Factors, and Graphing
Understanding the roots (or zeros) of a polynomial is crucial. Roots are the values of 'x' that make the polynomial equal to zero. Finding the roots of a quartic polynomial (degree 4) like ours can be more challenging than simpler polynomials. While there are formulas for solving cubic and quadratic equations, solving quartic equations often involves numerical methods or advanced techniques.
Factors and Factorization:
A crucial aspect of polynomial analysis is factorization. Factorization involves expressing the polynomial as a product of simpler expressions. For our polynomial, x⁴ + x³ + 2x², finding factors might involve techniques like grouping or using the rational root theorem (if rational roots exist).
Graphing the Polynomial:
Visualizing the polynomial through its graph can provide valuable insights into its behavior. The graph will reveal the roots (x-intercepts), local maxima and minima, and the overall shape of the function. While sketching by hand can be challenging for a quartic polynomial, using graphing software or calculators will provide an accurate representation.
Calculus and the Polynomial: Derivatives and Integrals
Calculus introduces powerful tools for analyzing functions like our polynomial. The derivative reveals the slope of the curve at any given point, indicating increasing or decreasing behavior. The second derivative provides information about the concavity (curvature) of the curve.
First Derivative:
The first derivative of x⁴ + x³ + 2x² is 4x³ + 3x² + 4x. Setting this to zero and solving helps find critical points (potential local maxima or minima).
Second Derivative:
The second derivative, 12x² + 6x + 4, helps determine the concavity at these critical points and assists in classifying them as maxima or minima.
Integration:
Integrating the polynomial allows us to calculate the area under the curve. The indefinite integral of x⁴ + x³ + 2x² is (1/5)x⁵ + (1/4)x⁴ + (2/3)x³ + C, where C is the constant of integration. Definite integrals, with specified limits, provide the exact area between those limits.
Applications in Various Fields
The seemingly abstract concept of a polynomial like x⁴ + x³ + 2x² has practical applications in various fields:
- Engineering: Polynomials are used to model various phenomena, such as the trajectory of projectiles, the stress on a beam, or the flow of fluids.
- Physics: They describe the movement of objects under the influence of forces or the behavior of waves.
- Computer Science: Polynomials form the basis of many algorithms and are essential in areas like numerical analysis and computer graphics.
- Economics: They are used in modeling economic growth, demand curves, and other economic relationships.
- Statistics: Polynomials play a vital role in regression analysis, allowing the creation of curves that best fit data sets.
Advanced Topics and Further Exploration
The study of polynomials extends far beyond the scope of this introductory analysis. More advanced concepts include:
- Complex Roots: Polynomials can have complex roots (involving imaginary numbers).
- Numerical Methods: Techniques like Newton-Raphson iteration are employed to approximate roots when exact solutions are difficult to find.
- Partial Fraction Decomposition: This method is used to break down rational functions (fractions of polynomials) into simpler forms for easier integration.
- Polynomial Interpolation: This technique allows the creation of a polynomial that passes through a given set of points.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Polynomials
The expression x³ + 2x² + x⁴, although seemingly simple, serves as a gateway to a rich and vast mathematical landscape. Its exploration touches upon fundamental concepts in algebra, calculus, and their various applications. Understanding polynomials is not just about manipulating symbols; it's about understanding the underlying mathematical principles that govern numerous natural phenomena and technological advancements. This deep dive into the seemingly simple polynomial provides a foundational understanding for further explorations into the captivating world of mathematics. The ongoing exploration of polynomials and their properties will continue to yield new insights and applications for years to come. The continued study of these fundamental concepts remains essential for advancements in many fields of science and technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What 2 Elements Make Up Water
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Genetic Identity Of Human Males Is Known By The
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Figure Has 6 Faces 12 Edges And 8 Vertices
Mar 25, 2025
-
Resolution Of A Printer Is Measured In
Mar 25, 2025
-
Most Stable Measure Of Central Tendency
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 2x 2 X 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
