What Figure Has 6 Faces 12 Edges And 8 Vertices
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 4 min read
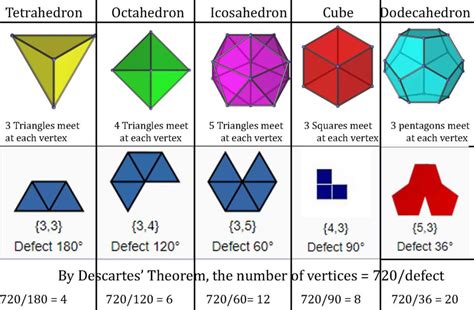
Table of Contents
What Figure Has 6 Faces, 12 Edges, and 8 Vertices? Unveiling the Cube
The question, "What figure has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices?" immediately brings to mind a specific three-dimensional shape: the cube. However, understanding why this is the answer requires delving into the fascinating world of geometry, specifically polyhedra and their properties. This article will explore the characteristics of a cube, delve into the mathematical principles behind its structure, and examine its importance in various fields.
Understanding Geometric Terminology
Before we solidify the answer, let's clarify the key terms:
- Faces: The flat surfaces of a three-dimensional shape. Think of them as the sides of the object.
- Edges: The line segments where two faces meet. These are the lines you see forming the boundaries of the faces.
- Vertices: The points where three or more edges meet. These are the "corners" of the shape.
These three elements – faces, edges, and vertices – are fundamental to describing and classifying three-dimensional shapes, also known as polyhedra. A polyhedron is a solid geometric figure with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices.
The Cube: A Perfect Example
A cube is a regular hexahedron, meaning it's a polyhedron with six faces. Crucially, all these faces are congruent squares. This regularity leads to the specific counts of edges and vertices: twelve edges and eight vertices.
Let's visualize:
- Faces: Imagine a cardboard box. It has six faces: a top and bottom, and four sides.
- Edges: These are the lines where the faces connect. Count them: four around the top, four around the bottom, and four connecting the top and bottom. That's twelve edges.
- Vertices: The eight corners of the box are the vertices. Each vertex is where three faces and three edges meet.
Therefore, a cube perfectly fits the description: 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices.
Euler's Formula: A Mathematical Relationship
The relationship between the number of faces (F), edges (E), and vertices (V) of any convex polyhedron is described by Euler's formula:
V - E + F = 2
Let's test this with the cube:
- V (Vertices) = 8
- E (Edges) = 12
- F (Faces) = 6
8 - 12 + 6 = 2
The formula holds true! This fundamental relationship provides a powerful tool for verifying the properties of various polyhedra. It's not just limited to cubes; it applies to a vast range of three-dimensional shapes, including tetrahedra, octahedra, dodecahedra, and icosahedra.
Beyond the Cube: Exploring Other Polyhedra
While the cube is the most readily identifiable shape with 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices, it's essential to acknowledge that other, less regular, polyhedra could theoretically possess the same characteristics. However, these would not be regular polyhedra like the cube where all faces are congruent and all angles are equal. The regularity of the cube is key to its unique properties.
Consider, for example, a distorted cube – imagine a cube that has been squeezed or stretched unevenly. While the number of faces, edges, and vertices might remain the same, the shape and the properties of the faces would no longer be identical. This highlights that the regularity of the cube's structure is a critical aspect of its definition.
The Importance of Cubes in Various Fields
The cube's simple yet elegant structure makes it incredibly significant across diverse fields:
1. Mathematics and Geometry:
- Foundation of Solid Geometry: Cubes serve as a fundamental building block in understanding three-dimensional geometry. Their properties are used to teach concepts like volume, surface area, and spatial reasoning.
- Tessellations: Cubes can perfectly tessellate (tile) three-dimensional space, meaning they can fill space without any gaps. This property has implications in crystallography and materials science.
2. Engineering and Architecture:
- Structural Design: The cube's stability and strength make it a preferred shape in various engineering applications, including building construction and designing mechanical components.
- Packaging: Cubical boxes are highly efficient for packaging and shipping goods, optimizing space and simplifying logistics.
3. Computer Graphics and Game Development:
- 3D Modeling: Cubes form the basis for many 3D models, serving as primitive shapes that can be manipulated and combined to create complex structures.
- Game Engines: Cubes are frequently used as foundational elements in game development, representing objects, environments, and collision detection.
4. Chemistry and Physics:
- Crystal Structures: The arrangement of atoms in some crystalline structures resembles cubic lattices, influencing their physical properties.
- Modeling molecules: Simple molecules can be represented using cube-like structures.
5. Art and Design:
- Sculpture and Architecture: The cube's clean lines and geometric simplicity are often incorporated into artistic works, conveying a sense of order and structure.
- Graphic Design: The cube is a powerful visual element used in logos, branding, and other design applications.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous Cube
The answer to the question, "What figure has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices?" is definitively the cube. This seemingly simple shape holds profound mathematical significance and practical applications in numerous fields. Its properties, governed by Euler's formula and its inherent regularity, make it a cornerstone of geometry and a versatile building block for various applications across science, engineering, and art. Understanding the cube goes beyond simply memorizing its characteristics; it's about appreciating its fundamental role in our understanding of the three-dimensional world. The cube's ubiquity serves as a testament to its enduring importance and its remarkable influence on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Explain The Role Of Health In Human Capital Formation
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Function Of Trna Is To
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Components Are Necessary For Photosynthesis To Occur
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Primary Excretory Route For Water Soluble Vitamins
Mar 28, 2025
-
Formula Standard Deviation For Grouped Data
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Figure Has 6 Faces 12 Edges And 8 Vertices . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
