Who Said Atoms Of Different Elements Are Different
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
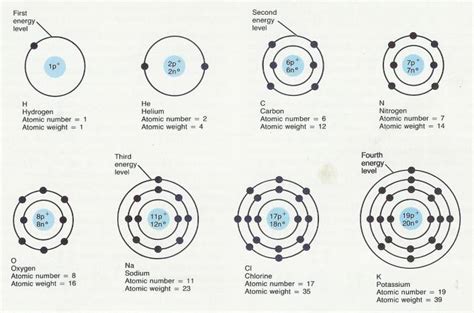
Table of Contents
Who Said Atoms of Different Elements Are Different? Unraveling the Atomic Theory
The statement that atoms of different elements are different is a cornerstone of modern chemistry and physics. It's a seemingly simple concept, but understanding its history and the scientific journey that led to its acceptance reveals a fascinating story of intellectual evolution and groundbreaking experimentation. This wasn't a single "eureka" moment, but rather a culmination of centuries of thought and observation, building upon the work of numerous scientists. Let's delve into the historical context and the key figures who contributed to this pivotal understanding.
From Philosophical Speculation to Scientific Inquiry: The Early Days
The idea of matter being composed of fundamental, indivisible particles dates back to ancient Greece. Philosophers like Leucippus and Democritus, in the 5th century BC, proposed the concept of atomos, meaning "indivisible." However, their ideas were largely philosophical musings, lacking the experimental evidence needed for scientific acceptance. These early atomists didn't differentiate between atoms of different elements; their focus was on the existence of atoms themselves, not their properties or diversity.
The Rise of Alchemy and the Seeds of Modern Chemistry
For centuries after the ancient Greeks, alchemical practices dominated the study of matter. While often shrouded in mysticism and secrecy, alchemy laid some groundwork for future chemical discoveries. Alchemists, through their tireless experimentation, observed transformations of substances, although their interpretations were often far from accurate. Their experiments, however, unknowingly highlighted the existence of different types of matter, implicitly suggesting the possibility of different atomic constituents.
Dalton's Atomic Theory: A Landmark Contribution
The true scientific revolution regarding atomic theory began with John Dalton in the early 19th century. His work, published in 1803 and detailed further in his book A New System of Chemical Philosophy, marked a significant turning point. Dalton wasn't the first to propose atoms, but his contribution lay in proposing a comprehensive atomic theory based on experimental observations, particularly concerning the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions.
Key Postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory:
- All matter is made of atoms: This echoed the ancient Greek philosophers, but with a stronger scientific basis.
- Atoms are indivisible and indestructible: This postulate, while later proven incorrect with the discovery of subatomic particles, was crucial to Dalton's framework.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties: This was a key innovation. Dalton explicitly stated that atoms of the same element are identical, implying that differences in chemical properties stem from differences in their atoms.
- Atoms of different elements differ in mass and other properties: This is the central point of our discussion. Dalton's assertion that atoms of different elements possess distinct properties solidified the concept of elemental diversity at the atomic level. This differentiation was based on observed differences in the ratios of elements combining to form compounds.
- Atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds: This explained the law of definite proportions – a compound always contains the same proportion of elements by mass.
- Atoms can be rearranged in chemical reactions, but they are neither created nor destroyed: This was a direct consequence of the conservation of mass.
Dalton's atomic theory provided a clear, quantitative framework for understanding chemical reactions. His careful experimental work and rigorous analysis allowed him to establish the fundamental differences between atoms of different elements, moving beyond mere speculation to a robust scientific model. Therefore, while the ancient Greeks contemplated the existence of atoms, it was Dalton who definitively proposed that these atoms differed based on element.
Beyond Dalton: Further Refinements and Discoveries
While Dalton's theory was groundbreaking, it wasn't without limitations. The discovery of isotopes, atoms of the same element with different masses, showed that not all atoms of the same element are identical. However, the core concept that atoms of different elements possess inherently different properties remained intact.
J.J. Thomson's discovery of the electron in 1897 shattered Dalton's notion of indivisible atoms. His plum pudding model, while flawed, showed that atoms had internal structure. Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1909 further revolutionized atomic understanding, revealing the nucleus and leading to the nuclear model of the atom. These discoveries didn't negate Dalton's fundamental contribution, but refined our understanding of the atomic structure underlying the differences between elements.
The Periodic Table: A Visual Representation of Atomic Diversity
Dmitri Mendeleev's periodic table, published in 1869, provided a powerful visual representation of the differences between elements. By arranging elements in order of increasing atomic weight, Mendeleev observed recurring patterns in their properties. This periodic arrangement directly reflected the underlying diversity of atomic structure, providing compelling evidence for the distinct nature of atoms from different elements.
The periodic table remains a cornerstone of chemistry, highlighting the relationships and differences between elements based on their atomic structure and properties. Its existence and predictive power further validated the concept that atoms of different elements are inherently different.
Modern Understanding: Atomic Number and Electronic Configuration
Today, we understand that the fundamental difference between atoms of different elements lies in their atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus. This number uniquely defines an element and determines its chemical properties. The arrangement of electrons in electron shells (electronic configuration) further contributes to the distinct chemical behavior of different elements.
The differences in atomic number and electronic configuration explain the observed differences in chemical reactivity, bonding behavior, and other properties. These differences are fundamental and are the basis for the entire field of chemistry.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Scientific Inquiry
The statement that atoms of different elements are different isn't simply a fact; it's a culmination of centuries of scientific investigation. From the philosophical musings of ancient Greece to the sophisticated models of modern physics, the journey to understanding atomic diversity is a testament to the power of human curiosity and the relentless pursuit of scientific knowledge. While Dalton's theory has been refined and expanded upon, his groundbreaking work in establishing the inherent differences between atoms of different elements remains a pivotal contribution to the history of science. His assertion remains a fundamental principle upon which our understanding of the physical world is built. The ongoing exploration of atomic structure and behavior continues to enrich and expand our understanding of the universe around us, a journey that began with the simple, yet profound, idea that atoms of different elements are fundamentally different.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Area Of An 8 Inch Circle
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Iron
Mar 19, 2025
-
Python Check If A String Is A Number
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Length Of Line Segment Pq
Mar 19, 2025
-
Homologous Chromosomes Separate During Which Phase Of Meiosis
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Who Said Atoms Of Different Elements Are Different . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
