Area Of An 8 Inch Circle
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
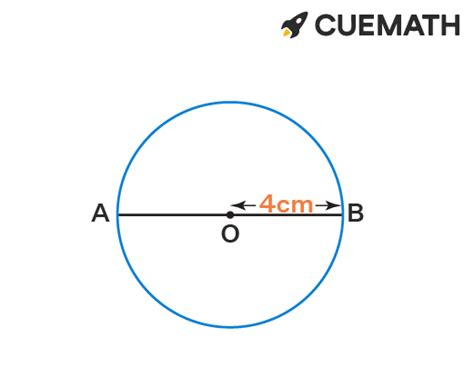
Table of Contents
Calculating the Area of an 8-Inch Circle: A Comprehensive Guide
The area of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry with widespread applications in various fields, from engineering and architecture to everyday life. This comprehensive guide will delve into the calculation of the area of an 8-inch circle, exploring the underlying formula, practical applications, and potential challenges in real-world scenarios. We'll also discuss related concepts and provide examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Formula: πr²
The area of any circle is calculated using the formula A = πr², where:
- A represents the area of the circle.
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
- r represents the radius of the circle, which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
In our case, we have an 8-inch circle. This means the diameter (the distance across the circle through the center) is 8 inches. To use the formula, we need the radius. The radius is half the diameter, so:
r = diameter / 2 = 8 inches / 2 = 4 inches
Calculating the Area: Step-by-Step
Now that we have the radius, we can plug it into the formula:
A = πr² = π * (4 inches)² = π * 16 square inches
Using the approximation of π ≈ 3.14159, we get:
A ≈ 3.14159 * 16 square inches ≈ 50.26544 square inches
Therefore, the area of an 8-inch circle is approximately 50.27 square inches. We typically round to two decimal places for practical purposes.
Understanding Square Inches
It's crucial to understand the unit of measurement: square inches. This signifies that the area is measured in two dimensions – length and width. Imagine dividing the circle into tiny squares, each measuring one inch by one inch. The total number of these squares needed to cover the circle's surface is approximately 50.27.
Practical Applications of Circle Area Calculation
The ability to calculate the area of a circle has countless practical applications:
1. Engineering and Design:
- Pipe Sizing: Determining the cross-sectional area of pipes is vital in fluid dynamics calculations for applications like water flow, gas transmission, and oil pipelines.
- Circular Structures: Architects and engineers need to calculate the area of circular structures like domes, columns, and foundations for accurate material estimations and structural stability assessments.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing processes, calculating circular areas is crucial for determining material usage in creating components like discs, plates, and wheels.
2. Everyday Life:
- Gardening: Calculating the area of a circular garden bed helps in determining the amount of soil, fertilizer, or mulch needed.
- Baking: Knowing the area of a circular baking pan helps in adjusting baking times and ingredient quantities.
- Home Improvement: Calculating the area of a circular rug or tabletop helps in selecting appropriate sizes for a space.
3. Science and Research:
- Physics: Circle area calculations are fundamental in physics concepts like projectile motion and circular motion.
- Biology: In biology, calculating areas of circular structures like cells or microorganisms can be important in research.
- Astronomy: The area of celestial objects is relevant in astronomy for understanding their properties and luminosity.
Beyond the Basic Calculation: Dealing with Real-World Scenarios
While the formula A = πr² provides the theoretical area, real-world applications often introduce complexities:
1. Irregular Shapes:
In reality, perfectly circular shapes are rare. Many objects are only approximately circular. In such cases, advanced techniques like numerical integration or approximations using polygons might be necessary for accurate area determination.
2. Measurement Errors:
Measuring the diameter or radius of a circle perfectly is challenging. Any measurement error will directly affect the calculated area. Understanding and mitigating measurement errors through precision instruments and multiple measurements is crucial for obtaining reliable results.
3. Material Waste and Efficiency:
In manufacturing and construction, calculating the area accurately is crucial for minimizing material waste. Efficient material utilization is important for cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
4. Combining Areas:
Often, projects involve multiple circles or combinations of circles and other shapes. The ability to calculate individual areas and then sum them up or subtract them as needed, is essential.
Exploring Related Concepts: Circumference and Diameter
The area of a circle is closely related to its circumference and diameter.
-
Circumference (C): The circumference is the distance around the circle. It's calculated using the formula C = 2πr or C = πd, where 'd' is the diameter. For an 8-inch circle, the circumference is approximately 25.13 inches.
-
Diameter (d): The diameter is twice the radius. It's the longest distance across the circle, passing through the center.
Understanding the relationships between area, circumference, and diameter allows for a more comprehensive understanding of circular geometry. Often, one can be derived from the other, making calculations more efficient.
Advanced Applications: Integrating Circle Area into Complex Problems
The calculation of the area of a circle is often just one step in solving a larger problem. Consider these examples:
-
Calculating the volume of a cylinder: The area of the circular base is multiplied by the height to determine the volume.
-
Determining the area of a sector: A sector is a portion of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc. Its area is a fraction of the total circle's area, determined by the angle of the sector.
-
Finding the area of a ring (annulus): The area of a ring is found by subtracting the area of the inner circle from the area of the outer circle.
These examples highlight how calculating the area of a circle serves as a building block for solving more complex geometric problems.
Conclusion: Mastering Circle Area Calculations
Mastering the calculation of the area of a circle is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. While the basic formula, A = πr², is straightforward, understanding its implications in real-world scenarios requires careful consideration of measurement errors, irregular shapes, and the integration of circle area into more complex geometric problems. By appreciating these nuances, one can confidently apply this essential geometric principle across various disciplines and everyday situations. Remember, accuracy and precision are paramount, especially when dealing with practical applications where material usage, efficiency, and safety are crucial factors. Continuous practice and a deep understanding of the underlying principles will solidify your mastery of this important concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Conjugate Base Of Hso4
Mar 19, 2025
-
55 Miles Per Hour To Meters Per Second
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Twinkling Of Stars Is Caused By
Mar 19, 2025
-
Literary Elements In The Road Not Taken
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Does Mg Have
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of An 8 Inch Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
