Which Of The Following Reactions Is A Double Displacement Reaction
News Leon
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
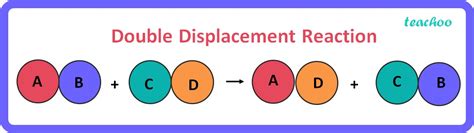
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Reactions is a Double Displacement Reaction? A Comprehensive Guide
Double displacement reactions, also known as double replacement reactions or metathesis reactions, are a fundamental concept in chemistry. Understanding how to identify these reactions is crucial for mastering stoichiometry, predicting products, and understanding chemical reactivity. This article will provide a detailed explanation of double displacement reactions, explore various examples, and help you confidently determine which reactions fall under this category.
Understanding Double Displacement Reactions
A double displacement reaction occurs when two compounds exchange ions or atoms to form two new compounds. The general form of the reaction can be represented as:
AB + CD → AD + CB
where A and C are cations (positively charged ions) and B and D are anions (negatively charged ions). Crucially, the cations and anions switch partners. This exchange results in the formation of two new ionic compounds.
Key Characteristics of Double Displacement Reactions:
- Ion Exchange: The defining feature is the exchange of ions between the reactants.
- Formation of Precipitates, Gases, or Water: Many double displacement reactions lead to the formation of a precipitate (an insoluble solid), a gas, or water. The formation of one of these products drives the reaction forward. If none of these are formed, the reaction may not proceed significantly.
- No Change in Oxidation States: Double displacement reactions are typically not redox reactions; the oxidation states of the atoms remain unchanged.
Identifying Double Displacement Reactions: A Step-by-Step Approach
To determine if a given reaction is a double displacement reaction, follow these steps:
- Identify the Reactants: Determine the chemical formulas of the reactants.
- Identify the Ions: Break down the reactants into their constituent ions.
- Predict the Products: Mentally switch the cations and anions to predict the products. Use your knowledge of ionic charges to ensure the products are electrically neutral.
- Check for Solubility: Use a solubility chart or your knowledge of solubility rules to determine if any of the products are insoluble (form a precipitate). Consider whether a gas is produced or if water is formed.
- Balance the Equation: Ensure the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides of the equation.
Examples of Double Displacement Reactions
Let's examine several examples to illustrate the concept and the application of the identification steps:
Example 1: Precipitation Reaction
Consider the reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO₃) and sodium chloride (NaCl):
AgNO₃(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO₃(aq)
- Reactants: Silver nitrate (AgNO₃) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Ions: Ag⁺, NO₃⁻, Na⁺, Cl⁻.
- Products: Silver chloride (AgCl) and sodium nitrate (NaNO₃).
- Solubility: Silver chloride (AgCl) is insoluble and forms a precipitate. Sodium nitrate (NaNO₃) is soluble.
- Balanced Equation: The equation is already balanced.
This is a classic double displacement reaction resulting in a precipitate.
Example 2: Neutralization Reaction
Neutralization reactions between acids and bases are a common type of double displacement reaction. For instance, the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
- Reactants: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Ions: H⁺, Cl⁻, Na⁺, OH⁻.
- Products: Sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H₂O).
- Solubility: Both sodium chloride and water are soluble. The driving force here is water formation.
- Balanced Equation: The equation is already balanced.
This reaction forms water, another indicator of a double displacement reaction.
Example 3: Gas-Forming Reaction
The reaction between sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) produces carbon dioxide gas:
Na₂CO₃(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
- Reactants: Sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Ions: 2Na⁺, CO₃²⁻, H⁺, Cl⁻.
- Products: Sodium chloride (NaCl), water (H₂O), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Solubility: Sodium chloride is soluble; water is liquid, and carbon dioxide is a gas. The release of CO₂ gas drives this reaction forward.
- Balanced Equation: The equation is balanced.
Gas evolution is a strong indicator of a double displacement reaction.
Distinguishing Double Displacement from Other Reaction Types
It's essential to differentiate double displacement reactions from other types of chemical reactions:
- Single Displacement Reactions: In these reactions, one element replaces another in a compound. For example: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl₂(aq) + H₂(g). Notice the absence of ion exchange; zinc replaces hydrogen.
- Combination Reactions (Synthesis Reactions): Two or more substances combine to form a single product. Example: 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2H₂O(l).
- Decomposition Reactions: A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. Example: 2H₂O₂(l) → 2H₂O(l) + O₂(g).
- Combustion Reactions: A substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, often producing heat and light. Example: CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l).
Advanced Considerations and Exceptions
While the general principles outlined above are applicable to most double displacement reactions, there are exceptions and nuances to consider:
- Weak Electrolytes: Reactions involving weak acids or bases may not proceed to completion, as the ions are not fully dissociated in solution.
- Complex Ion Formation: Some double displacement reactions involve the formation of complex ions, adding complexity to the product prediction.
- Equilibrium: Many double displacement reactions are reversible and reach an equilibrium state, rather than going to completion.
Practical Applications of Double Displacement Reactions
Double displacement reactions have numerous applications in various fields:
- Chemical Synthesis: Used to prepare a wide range of inorganic and organic compounds.
- Water Treatment: Used to remove impurities from water through precipitation reactions.
- Medicine: Used in drug synthesis and delivery.
- Analytical Chemistry: Used in qualitative and quantitative analysis of substances.
Conclusion
Identifying double displacement reactions requires a systematic approach that involves recognizing the exchange of ions between reactants and the formation of products such as precipitates, gases, or water. By mastering the key characteristics and applying the step-by-step identification process, you can confidently classify reactions and deepen your understanding of chemical reactivity. This knowledge forms a crucial foundation for further studies in chemistry and related fields. Remember to always consider solubility rules and the driving force behind the reaction to accurately predict and understand the products formed.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All Isosceles Right Triangles Are Similar
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Long Are Blood Vessels In The Human Body
Apr 04, 2025
-
Select All The Differences Between Gymnosperms And Angiosperms
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is True About Isotopes
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Red Blood Cell Placed In A Hypotonic Solution
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Reactions Is A Double Displacement Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
