Which Of The Following Is A Function Of The Ribosome
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
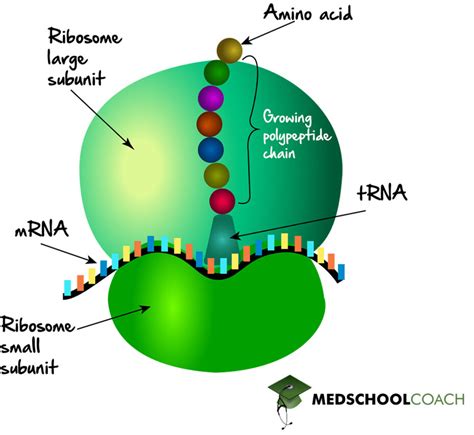
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Function of the Ribosome? Protein Synthesis and Beyond
The ribosome, a cellular structure found in all known living organisms except for some viruses, plays a pivotal role in the life of a cell. While often simplified in introductory biology courses as the "protein synthesis machine," the ribosome's functions are far more nuanced and complex than that singular description implies. Understanding the ribosome's multifaceted role requires delving into the intricate mechanisms of protein synthesis, as well as appreciating its involvement in other cellular processes, including aspects of gene regulation and even ribosomal diseases.
The Core Function: Protein Synthesis – A Detailed Look
The most fundamental function of the ribosome is undoubtedly protein synthesis, or translation. This crucial process converts the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) into a polypeptide chain, the building block of proteins. Let's break down this complex process step-by-step:
1. Initiation: Setting the Stage
Translation initiation begins with the assembly of the ribosomal subunits around the mRNA molecule. This involves several key players:
- Initiator tRNA: This special tRNA molecule, carrying the amino acid methionine (Met), binds to the mRNA's start codon (AUG).
- Small ribosomal subunit (30S in prokaryotes, 40S in eukaryotes): This subunit binds to the mRNA and the initiator tRNA, forming the initiation complex.
- Large ribosomal subunit (50S in prokaryotes, 60S in eukaryotes): This subunit joins the complex, creating a complete ribosome ready for peptide bond formation.
- Initiation factors: These proteins facilitate the assembly of the initiation complex, ensuring accurate initiation.
2. Elongation: Building the Polypeptide Chain
Once the initiation complex is formed, the ribosome moves along the mRNA, reading the codons (three-nucleotide sequences) sequentially. For each codon, a corresponding tRNA molecule, carrying a specific amino acid, enters the ribosome's A (aminoacyl) site.
- Codon Recognition: The tRNA's anticodon (complementary to the mRNA codon) base-pairs with the codon in the A site.
- Peptide Bond Formation: A peptide bond is formed between the amino acid in the A site and the growing polypeptide chain attached to the tRNA in the P (peptidyl) site.
- Translocation: The ribosome moves one codon along the mRNA, shifting the tRNA in the A site to the P site and the tRNA in the P site to the E (exit) site. The tRNA in the E site then exits the ribosome.
This elongation cycle repeats until a stop codon is encountered.
3. Termination: The End of the Line
Stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) signal the end of translation. They don't code for an amino acid; instead, they trigger the recruitment of release factors, proteins that promote the release of the completed polypeptide chain from the ribosome. The ribosomal subunits then dissociate, ready to initiate another round of translation.
Beyond Protein Synthesis: Other Ribosomal Functions
While protein synthesis is the ribosome's primary function, emerging research suggests a broader role in cellular processes:
1. Ribosome Biogenesis: A Complex Orchestration
The ribosome itself is a complex molecular machine, composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and numerous ribosomal proteins. The assembly of these components, known as ribosome biogenesis, is a highly regulated and intricate process involving numerous enzymes and other factors. Errors in ribosome biogenesis can lead to various cellular defects.
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) as a Catalytic Component
rRNA is not just a structural component of the ribosome; it is also a ribozyme, an RNA molecule with catalytic activity. The peptidyl transferase activity, responsible for forming peptide bonds during translation, resides within the rRNA, highlighting the catalytic power of RNA.
3. Gene Regulation: A Surprising Role
Ribosomes aren't just passive participants in gene expression; they can also influence it. The abundance and activity of ribosomes can affect the rate of translation of specific mRNAs. Furthermore, some ribosome-associated factors can directly influence mRNA stability or translation initiation, thereby influencing gene expression at a translational level.
4. Ribosome-Associated Quality Control
Ribosomes are involved in quality control mechanisms. Errors during translation, such as premature termination or the incorporation of incorrect amino acids, can trigger mechanisms that lead to the degradation of faulty proteins or the termination of translation. These quality control processes are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
5. Ribosomal Diseases: A Growing Area of Research
Disruptions in ribosome biogenesis, structure, or function can lead to a range of human diseases, collectively known as ribosomopathies. These diseases often manifest in diverse ways, reflecting the ribosome's critical role in multiple cellular processes. Examples include Diamond-Blackfan anemia, Treacher Collins syndrome, and others. Research in this field is actively expanding our understanding of ribosome function and its connection to human health.
The Ribosome: A Dynamic and Essential Cellular Component
The ribosome, far from being a simple protein synthesis machine, is a remarkably complex and dynamic structure with a central role in numerous cellular processes. Its functions extend beyond the well-established role in translation to include ribosome biogenesis, gene regulation, quality control, and other emerging roles still under investigation. Understanding the intricacies of ribosome function is crucial not only for comprehending fundamental biological processes but also for developing therapies for ribosome-related diseases. The continuing research in this field promises to further illuminate the complexities of this essential cellular organelle and its multifaceted contributions to life. The sophistication of its mechanisms and the variety of its functions underscore its importance as a central player in cellular life and a target for future therapeutic interventions. The impact of even minor disruptions to ribosomal function highlights the critical need to further understand this essential molecular machine and its pervasive influence on cellular health and disease. Future research will undoubtedly continue to unveil even more subtle and intricate aspects of ribosome biology, enriching our understanding of this remarkable cellular component.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Site Of Lipid Synthesis
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Argon
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Polysaccharides
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Far Can Light Travel In One Second
Mar 23, 2025
-
Epithelial Tissues Bottom Layer Of Cells Rests On A
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Function Of The Ribosome . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
