Which Of The Following Is A False Statement
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
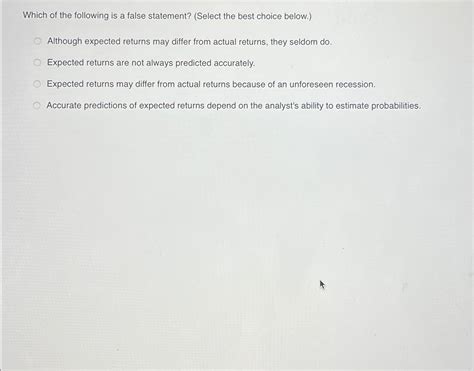
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a False Statement? A Deep Dive into Identifying Falsity
Identifying false statements is a crucial skill, applicable across various aspects of life, from everyday conversations to critical academic analysis. This seemingly simple task often requires a nuanced understanding of logic, context, and the subtle art of discerning truth from falsehood. This comprehensive guide will delve into the complexities of identifying false statements, exploring different approaches, common pitfalls, and providing practical examples to sharpen your skills.
Understanding the Nature of False Statements
Before we dissect how to identify false statements, it's crucial to understand what constitutes a false statement. A false statement, simply put, is a claim that does not accurately reflect reality. This seemingly straightforward definition can become surprisingly complex when considering several factors:
1. Factual vs. Opinion:
Distinguishing between factual claims and opinions is paramount. A factual claim can be verified or falsified through evidence. For example, "The Earth is round" is a factual claim supported by overwhelming scientific evidence. An opinion, on the other hand, expresses a personal belief or judgment and is not inherently true or false. "Pineapple belongs on pizza" is an opinion; there's no objective truth to it. It's crucial to focus on factual claims when assessing the truthfulness of a statement.
2. Context Matters:
The context in which a statement is made significantly impacts its truthfulness. A statement might be true in one context but false in another. For example, "It's cold outside" is true in a snowy winter but false on a sunny summer day. Always consider the surrounding information and circumstances when evaluating the veracity of a claim.
3. Ambiguity and Vagueness:
Ambiguous or vague statements can be difficult to assess as true or false. For example, "The weather is nice" is subjective and lacks precision. Clearly defined statements are much easier to evaluate.
4. Implicit Assumptions:
Statements often contain implicit assumptions – unstated beliefs that underpin the claim. Identifying these assumptions is crucial. For example, the statement "He's a successful businessman" assumes a specific definition of success. One person might consider wealth success while another prioritizes work-life balance. Uncovering these assumptions allows for a more accurate evaluation.
Strategies for Identifying False Statements
Identifying false statements involves employing a combination of critical thinking skills and logical reasoning. Here are several effective strategies:
1. Examine the Evidence:
This is perhaps the most fundamental approach. Does the statement align with verifiable evidence? Look for supporting data, credible sources, and factual backing. If the statement lacks credible evidence or contradicts established facts, it's likely false.
2. Check for Logical Fallacies:
Logical fallacies are errors in reasoning that undermine the validity of an argument. Familiarizing yourself with common fallacies (e.g., ad hominem, straw man, slippery slope) will help you identify weak or deceptive arguments. A statement built upon a logical fallacy is inherently suspect.
3. Consider the Source:
The credibility and reliability of the source significantly impact the trustworthiness of a statement. Is the source known for accuracy and objectivity? Does the source have a potential bias or vested interest? Skepticism is warranted when dealing with unreliable sources.
4. Look for Contradictions:
Does the statement contradict itself or other known facts? Internal inconsistencies are a strong indicator of falsehood. If parts of the statement clash, it raises serious doubts about its truthfulness.
5. Employ Reverse Engineering:
Try to disprove the statement. If you can easily find counter-evidence or demonstrate its impossibility, it's likely false. This approach encourages a critical and skeptical mindset.
Common Pitfalls in Identifying False Statements
Even with the strategies outlined above, several common pitfalls can hinder your ability to accurately identify false statements.
1. Confirmation Bias:
This cognitive bias leads us to favor information confirming our existing beliefs while disregarding contradictory evidence. Be aware of your own biases and actively seek out opposing viewpoints to avoid skewed judgment.
2. Emotional Reasoning:
Allowing emotions to cloud judgment can lead to misinterpretations. Maintain objectivity and focus on the factual evidence rather than emotional responses.
3. Overreliance on Authority:
Blindly accepting a statement solely because it's made by an authority figure is dangerous. Even experts can be wrong. Always critically evaluate the reasoning behind any claim, regardless of the source.
Practical Examples: Analyzing False Statements
Let's examine some examples to solidify these concepts:
Example 1: "All birds can fly."
This statement is false. While many birds can fly, some, like penguins and ostriches, are flightless. This highlights the importance of avoiding generalizations.
Example 2: "The sun rises in the west."
This statement is unequivocally false. This is a simple factual error easily disproven by observation.
Example 3: "Eating chocolate causes acne."
This statement is debatable. While some studies suggest a correlation, there's no conclusive scientific evidence proving a direct causal link. The statement is likely an oversimplification or a misinterpretation of scientific findings.
Example 4: "The capital of France is Berlin."
This statement is false. The capital of France is Paris. This is a clear factual inaccuracy.
Example 5: "Vaccination causes autism."
This statement is categorically false. Extensive scientific research has debunked this claim, yet it persists due to misinformation and conspiracy theories. This example highlights the importance of relying on credible scientific evidence over unsubstantiated claims.
Conclusion: Cultivating Critical Thinking
Identifying false statements is not merely an academic exercise. It's a crucial life skill essential for navigating the complex flow of information in today's world. By understanding the nature of falsehood, employing effective strategies, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can significantly enhance your ability to discern truth from deception. Develop a mindset of critical inquiry, actively seek out diverse perspectives, and cultivate a healthy skepticism to navigate the world of information with confidence and accuracy. This ability will not only improve your understanding of the world but also empower you to make informed decisions based on sound judgment and reliable information. Remember to always question, investigate, and verify before accepting any statement as truth. The pursuit of truth is a continuous journey, and sharpening your skills in identifying false statements is a critical step along the way.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Minutes Are There In One Day
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Sphere Has How Many Vertex
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Ne
Mar 15, 2025
-
Tool Used To Detect Electric Charge
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In A Single Molecule Of H2o
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A False Statement . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
