Which Of The Following Has The Shortest Wavelength
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
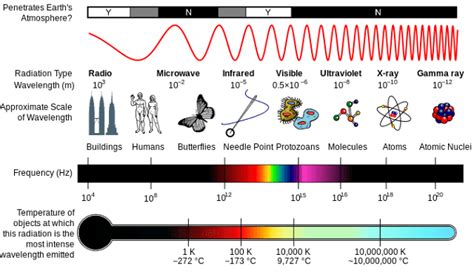
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Has the Shortest Wavelength? A Deep Dive into the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The question, "Which of the following has the shortest wavelength?" requires context. Wavelength is a property of waves, and the answer depends entirely on what types of waves are being compared. The most common comparison involves the electromagnetic spectrum, a vast range of electromagnetic radiation spanning an incredible range of wavelengths and frequencies. This article will delve into the electromagnetic spectrum, exploring the characteristics of its various components and ultimately determining which part boasts the shortest wavelengths.
Understanding Wavelength and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Before we can determine which type of electromagnetic radiation possesses the shortest wavelength, we need to understand these fundamental concepts:
What is Wavelength?
Wavelength (λ) is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave. It's usually measured in meters (m), but depending on the type of wave, smaller units like nanometers (nm), micrometers (µm), or angstroms (Å) are often more practical. A shorter wavelength signifies a higher frequency and, correspondingly, higher energy.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Colorful Range
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, organized by wavelength and frequency. These types include:
-
Radio waves: These have the longest wavelengths, ranging from millimeters to kilometers. They are used in communication technologies, broadcasting, and radar.
-
Microwaves: With wavelengths from millimeters to centimeters, microwaves are used in microwave ovens, radar, and satellite communication.
-
Infrared (IR) radiation: These have wavelengths longer than visible light, ranging from about 700 nanometers to 1 millimeter. We experience infrared radiation as heat. Many remote controls use infrared light.
-
Visible light: This is the only portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. It ranges from approximately 400 nanometers (violet) to 700 nanometers (red). The colors of the rainbow represent different wavelengths within this narrow band.
-
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: With wavelengths shorter than visible light, ranging from 10 to 400 nanometers, UV radiation is responsible for sunburns and can cause damage to living cells. It is also used in sterilization techniques.
-
X-rays: These have extremely short wavelengths, ranging from 0.01 to 10 nanometers. X-rays are highly energetic and can penetrate soft tissues, making them valuable in medical imaging.
-
Gamma rays: These possess the shortest wavelengths, ranging from less than 0.01 nanometers to less than a picometer. Gamma rays are the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, and they are produced by nuclear reactions and radioactive decay. They are also used in cancer treatment.
Comparing Wavelengths: The Quest for the Shortest
Now that we have a grasp of the electromagnetic spectrum, we can readily answer the question of which type of electromagnetic radiation has the shortest wavelength. The clear winner is gamma rays. Their wavelengths are incredibly short, significantly shorter than X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, visible light, infrared radiation, microwaves, and radio waves. This short wavelength corresponds to their exceptionally high energy and penetrating power.
Why Gamma Rays Have the Shortest Wavelength
The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to its frequency and directly proportional to its energy. Gamma rays have the highest frequency and energy within the electromagnetic spectrum. This high energy arises from their origins: nuclear processes, such as radioactive decay and nuclear fusion, release immense amounts of energy, which is manifested as gamma rays with incredibly short wavelengths.
Practical Applications and Implications
The extremely short wavelengths of gamma rays have significant implications across various scientific fields:
-
Medical Applications: While highly energetic and potentially dangerous, gamma rays are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancerous cells. The short wavelengths allow for precise targeting, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
-
Astronomy: Gamma-ray astronomy provides invaluable insights into the most energetic events in the universe, such as supernovae and active galactic nuclei. Observing gamma rays helps scientists understand the processes behind these powerful celestial phenomena.
-
Material Science: Gamma rays are used in various material science techniques, such as gamma-ray spectroscopy, to analyze the composition and structure of materials. Their high penetrating power allows them to interact with matter deeply, revealing valuable information.
-
Sterilization: Gamma radiation is also used to sterilize medical equipment and food products. Its high energy effectively kills microorganisms and pathogens, ensuring sterility and safety.
Further Exploration of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
While gamma rays hold the title for shortest wavelength, understanding the entire electromagnetic spectrum is crucial. Each part of the spectrum interacts with matter differently, leading to unique properties and applications. Exploring these interactions reveals fascinating insights into the nature of light and matter. The following are a few areas of further exploration:
-
The Relationship between Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy: A deeper understanding of the mathematical relationships between these properties is crucial for comprehending the behavior of electromagnetic radiation. The fundamental equation relating these factors is often expressed as: c = λν, where 'c' is the speed of light, 'λ' is the wavelength, and 'ν' is the frequency.
-
Interaction of Electromagnetic Radiation with Matter: Different types of electromagnetic radiation interact with matter differently. For example, X-rays can penetrate soft tissues, while visible light is reflected or absorbed. Understanding these interactions is essential for various applications, such as medical imaging and spectroscopy.
-
Technological Advancements and Applications: Continuous advancements in technology lead to innovative applications of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Exploring the latest technological advancements helps us grasp the potential of these diverse forms of radiation.
Conclusion: Gamma Rays Reign Supreme
In conclusion, when comparing the various forms of electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays unequivocally have the shortest wavelengths. Their exceptionally high energy and short wavelengths make them crucial for numerous applications in medicine, astronomy, and material science. While each part of the electromagnetic spectrum plays a vital role, the dominance of gamma rays in terms of wavelength is undeniable. Understanding the unique properties of each part of the spectrum provides a profound appreciation for the remarkable diversity and power of electromagnetic radiation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Ends Of A Long Bone Are Called The
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Catalyst Speeds Up A Chemical Reaction By
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Vertical Angle Of An Isosceles Triangle Is 100 Degree
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes Ingestion
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 16 Of 40
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Has The Shortest Wavelength . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
