Which Of The Following Events Does Not Occur During Prophase
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
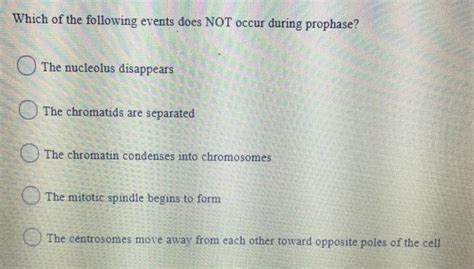
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Events Does Not Occur During Prophase? A Deep Dive into Cell Division
Prophase, the first stage of mitosis and meiosis, is a critical period of cellular restructuring and preparation for chromosome segregation. Understanding what doesn't happen during prophase is just as crucial as knowing what does happen, as it helps solidify our understanding of the entire cell division process. This comprehensive article will explore the key events of prophase and definitively identify the processes that are absent during this crucial phase.
Key Events of Prophase: Setting the Stage for Chromosome Segregation
Before we delve into what doesn't occur, let's solidify our understanding of what does happen during prophase. This phase is characterized by several dramatic changes within the cell nucleus:
1. Chromosome Condensation: From Chromatin to Visible Chromosomes
The most visually striking event of prophase is the condensation of chromatin. Chromatin, the diffuse, uncondensed form of DNA, undergoes a remarkable transformation, coiling and compacting into visible, rod-shaped structures – the chromosomes. This condensation is essential for the efficient segregation of chromosomes during later stages of cell division. The tightly packed structure prevents entanglement and breakage of the long DNA strands.
2. Nuclear Envelope Breakdown: Opening the Gateway
The nuclear envelope, the membrane that encloses the nucleus, begins to break down during prophase. This fragmentation allows the chromosomes to freely move within the cytoplasm, preparing for their alignment along the metaphase plate. The disassembly of the nuclear lamina, a protein network underlying the nuclear membrane, is a crucial aspect of this process.
3. Centrosome Movement and Spindle Formation: Building the Machinery
In animal cells, the centrosomes, the microtubule-organizing centers, duplicate early in the cell cycle and begin migrating to opposite poles of the cell during prophase. These centrosomes are critical for the formation of the mitotic spindle, a complex network of microtubules that will later guide the separation of chromosomes. The spindle fibers begin to grow from the centrosomes, extending towards the center of the cell. While plant cells lack centrosomes, they still form a spindle apparatus, although the mechanism is slightly different.
4. Nucleolus Disassembly: Quieting the Ribosome Factory
The nucleolus, a prominent structure within the nucleus responsible for ribosome biogenesis, disassembles during prophase. This disassembly reflects the temporary halt in protein synthesis as the cell prioritizes the complex process of chromosome segregation. The components of the nucleolus are dispersed throughout the cytoplasm and will reassemble later in the cell cycle.
Events That Do Not Occur During Prophase: Clarifying the Timeline
Now, let's address the central question: what processes are notably absent during prophase? Several crucial events are deferred to later stages of mitosis or meiosis.
1. Chromosome Alignment at the Metaphase Plate: A Later Arrangement
Chromosomes do not align along the metaphase plate during prophase. The metaphase plate, an imaginary plane equidistant from the two poles of the cell, is the site where chromosomes will align precisely in the subsequent metaphase stage. The spindle fibers are still forming and extending during prophase; the precise alignment of chromosomes requires the fully developed spindle apparatus.
2. Sister Chromatid Separation: A Precisely Timed Event
Sister chromatids do not separate during prophase. Sister chromatids, identical copies of a chromosome, are held together by the cohesin protein complex. Their separation is a tightly regulated process that occurs during anaphase, ensuring accurate chromosome distribution to daughter cells. Premature separation would lead to chromosomal instability and genetic errors.
3. Cytokinesis: The Cell Division Finale
Cytokinesis, the physical division of the cytoplasm to produce two daughter cells, does not occur during prophase. Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division, occurring after the chromosomes have been properly segregated. Prophase focuses entirely on the preparation for chromosome separation, and cytokinesis is a distinct process that follows the completion of mitosis or meiosis.
4. DNA Replication: A Preceding Event
DNA replication is a process that occurs before prophase, during the S phase (synthesis phase) of the cell cycle. Prophase begins only after the DNA has been faithfully replicated, providing two identical copies of each chromosome, ready for segregation. DNA replication during prophase would be redundant and potentially detrimental, leading to errors in the distribution of genetic material.
5. Crossing Over (in Mitosis): A Meiotic Specialty
While crossing over is a crucial event in meiosis I prophase, it does not occur in mitosis. Crossing over, a process where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, increases genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms. Mitosis, on the other hand, is a process of asexual reproduction, aiming for identical daughter cells, therefore crossing over isn't necessary nor does it occur.
Understanding the Sequential Nature of Cell Division: A Holistic Perspective
The distinct stages of cell division, including prophase, are not isolated events but rather a precisely orchestrated sequence of events. Each stage plays a specific and essential role in the faithful transmission of genetic material from one generation of cells to the next. Understanding what doesn't occur during prophase emphasizes the temporal organization and intricate regulation of the cell cycle. The absence of events like chromosome alignment, sister chromatid separation, and cytokinesis highlights the preparation that prophase provides for the subsequent stages of cell division. This sequential nature ensures that the process of cell division is accurate and efficient. Errors in this orchestration can lead to severe consequences, such as genetic abnormalities and uncontrolled cell growth.
Prophase: A Critical Foundation for Accurate Cell Division
In conclusion, prophase is a dynamic and essential stage in both mitosis and meiosis. While marked by significant cellular changes, including chromosome condensation, nuclear envelope breakdown, and spindle formation, it’s crucial to recognize what doesn't happen during this phase. The absence of events like chromosome alignment, sister chromatid separation, cytokinesis, and DNA replication emphasizes the carefully regulated and sequential nature of the cell cycle. This clear understanding of both the occurrences and absences during prophase is fundamental to comprehending the intricacies of cell division and its crucial role in growth, development, and reproduction. The precise timing and execution of each stage ensure the accurate transmission of genetic information and the maintenance of genome integrity, underscoring the importance of this fundamental biological process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Charge Of Uniform Linear Density
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Polynomial
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is Boiling Water A Physical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is A Webcam An Input Or Output Device
Mar 17, 2025
-
Word For A Person Who Uses Big Words
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Events Does Not Occur During Prophase . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
