Which Of The Following Is Polynomial
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
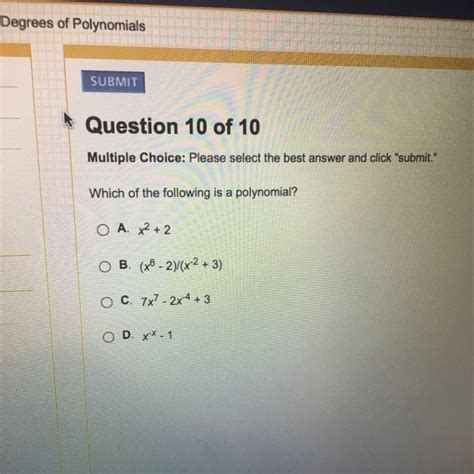
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Polynomial? A Comprehensive Guide
Polynomials are fundamental algebraic objects that appear throughout mathematics and its applications. Understanding what constitutes a polynomial and what doesn't is crucial for success in algebra, calculus, and beyond. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the definition of polynomials, explore various examples and non-examples, and equip you with the knowledge to confidently identify polynomials in any context.
Defining a Polynomial
A polynomial is a mathematical expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients. The key characteristics defining a polynomial are:
- Exponents must be non-negative integers: This means the powers of the variables can only be 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Fractional or negative exponents are not allowed.
- Coefficients can be real or complex numbers: The numbers multiplying the variables can be any real number (like 2, -5, π) or complex number (like 2+3i).
- Variables are raised to whole number powers: The variables themselves (typically represented by letters like x, y, z) are raised to whole number powers (integers greater than or equal to zero).
- Finite number of terms: A polynomial consists of a finite (limited) number of terms. Each term is a product of a coefficient and a variable raised to a non-negative integer power.
Let's break this down with examples.
Examples of Polynomials
Here are several examples illustrating the characteristics of polynomials:
- 3x² + 5x - 7: This is a polynomial in one variable (x). The exponents are 2, 1, and 0 (implicitly in the constant term -7). The coefficients are 3, 5, and -7.
- 2xy² + 4x - 6y + 1: This is a polynomial in two variables (x and y). The exponents are non-negative integers.
- 5: This is a constant polynomial (a polynomial of degree 0). It can be considered as 5x⁰.
- x⁴ - 2x³ + x² - 5x + 10: This is a polynomial in one variable (x). It's a quartic polynomial (degree 4).
- 7a³b²c + 2ab - 3c⁴ + 9: This is a polynomial in three variables (a, b, and c).
Non-Examples of Polynomials
Understanding what isn't a polynomial is equally important. Here are some expressions that fail to meet the criteria of a polynomial:
- 3x⁻² + 5x - 7: This is not a polynomial because the exponent -2 is negative.
- √x + 2: This is not a polynomial because the exponent on x is ½ (a fraction), which is not a non-negative integer.
- 1/x + 5: This is equivalent to x⁻¹ + 5, which has a negative exponent and therefore is not a polynomial.
- 2ˣ + 4: This is not a polynomial because the variable x is in the exponent. Polynomials have variables only in the base, not in the exponent.
- sin(x) + 2x: Trigonometric functions like sin(x) are not allowed in polynomials.
- |x| + 1: Absolute value functions are not polynomials.
- (x²+1)/(x-1): This expression involves division by a variable, which is not permitted in polynomials.
Degree of a Polynomial
The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable appearing in the polynomial. For polynomials in multiple variables, the degree is the highest sum of exponents in any single term.
Examples:
- 3x² + 5x - 7: Degree 2 (quadratic)
- 2xy² + 4x - 6y + 1: Degree 3 (the term 2xy² has a sum of exponents 1+2=3)
- 5: Degree 0 (constant)
- x⁴ - 2x³ + x² - 5x + 10: Degree 4 (quartic)
- 7a³b²c + 2ab - 3c⁴ + 9: Degree 6 (the term 7a³b²c has a sum of exponents 3+2+1=6)
Operations with Polynomials
Polynomials can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided (with some limitations).
- Addition/Subtraction: Combine like terms (terms with the same variables raised to the same powers).
- Multiplication: Use the distributive property (FOIL method for binomials) to multiply each term in one polynomial by each term in the other.
- Division: Polynomial long division or synthetic division can be used to divide polynomials. The result may be a quotient polynomial and a remainder polynomial.
Applications of Polynomials
Polynomials have widespread applications in various fields:
- Modeling real-world phenomena: Polynomials can model curves, trajectories, and other relationships in physics, engineering, and economics.
- Computer graphics: Polynomials are used in creating curves and surfaces in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer graphics.
- Numerical analysis: Polynomials are used to approximate functions and solve equations.
- Signal processing: Polynomials are used in digital signal processing to design filters and other signal processing algorithms.
- Cryptography: Polynomials play a significant role in various cryptographic techniques.
Identifying Polynomials: A Step-by-Step Approach
To determine if an expression is a polynomial, follow these steps:
- Check the exponents: Are all exponents non-negative integers? If any exponent is negative, fractional, or a variable, the expression is not a polynomial.
- Examine the coefficients: Are the coefficients real or complex numbers? This condition is generally satisfied.
- Count the terms: Is the number of terms finite? Infinite sums are not polynomials.
- Check for disallowed functions: Does the expression contain any trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan), logarithmic functions (log), exponential functions (eˣ), absolute value functions, or other non-algebraic functions? If so, it's not a polynomial.
- Verify the operations: Are the only operations used addition, subtraction, and multiplication? Division by a variable is not allowed.
By systematically applying these steps, you can accurately identify whether a given mathematical expression qualifies as a polynomial.
Conclusion
Understanding polynomials is crucial for success in mathematics and its applications. This comprehensive guide provided a detailed explanation of what defines a polynomial, explored numerous examples and non-examples, discussed the degree of a polynomial, and outlined a step-by-step approach to identifying them. By mastering these concepts, you’ll be well-equipped to handle polynomial operations and appreciate their vast applications across various scientific and technical fields. Remember that the key characteristics—non-negative integer exponents, real or complex coefficients, and a finite number of terms—are the defining features that distinguish a polynomial from other mathematical expressions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Movement Of Earth Around The Sun Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Ph Of A Neutral Solution
Mar 17, 2025
-
Did The Ussr Imiss The Great Depression
Mar 17, 2025
-
Choose The Components Of A Respiratory Membrane
Mar 17, 2025
-
Dendrite Is To Axon As Is To
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Polynomial . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
