Which Of The Following Compounds Is Ionic
News Leon
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
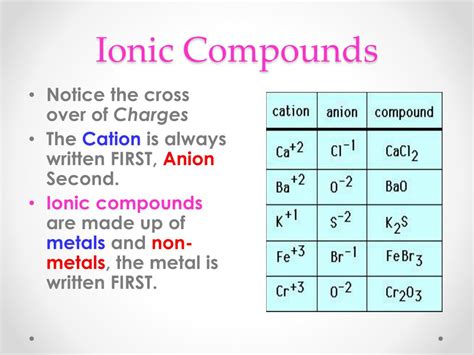
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Compounds is Ionic? A Deep Dive into Chemical Bonding
Determining whether a compound is ionic or covalent is a fundamental concept in chemistry. Understanding the differences between these bond types is crucial for predicting a compound's properties, such as melting point, solubility, and conductivity. This article will delve deep into the principles of ionic and covalent bonding, providing you with the tools to identify ionic compounds effectively. We'll explore electronegativity, the octet rule, and the characteristics that distinguish ionic from covalent compounds. By the end, you'll be able to confidently analyze a chemical formula and determine its bonding nature.
Understanding Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Before we dive into identifying ionic compounds, let's establish a firm understanding of the fundamental differences between ionic and covalent bonds.
Ionic Bonds: A Transfer of Electrons
Ionic bonds form through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. This occurs when one atom donates one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion (cation), while the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion (anion). This transfer of electrons usually happens between a metal and a non-metal. Metals tend to have low electronegativity and readily lose electrons, while non-metals have high electronegativity and readily gain electrons.
Key Characteristics of Ionic Compounds:
- High melting and boiling points: The strong electrostatic forces between ions require a significant amount of energy to overcome.
- Crystalline structure: Ions are arranged in a highly ordered, three-dimensional lattice structure.
- Brittle: The rigid structure is easily disrupted when subjected to stress, leading to fracturing.
- Conductivity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water, as the ions become mobile.
- Solubility: Many ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water, due to the interaction between the ions and the polar solvent molecules.
Covalent Bonds: A Sharing of Electrons
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, usually fulfilling the octet rule (eight electrons in the outermost shell). This type of bonding typically occurs between non-metal atoms. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, creating a bond.
Key Characteristics of Covalent Compounds:
- Lower melting and boiling points: The intermolecular forces (forces between molecules) are generally weaker than the electrostatic forces in ionic compounds.
- Various physical states: Covalent compounds can exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature.
- Generally non-conductive: Covalent compounds typically do not conduct electricity because they lack free-moving charged particles.
- Solubility: Solubility varies greatly depending on the polarity of the molecule and the solvent.
Electronegativity: A Key Determinant
Electronegativity is a crucial factor in determining the type of bond that forms between two atoms. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. A large difference in electronegativity between two atoms indicates an ionic bond, while a small difference suggests a covalent bond.
The Pauling Electronegativity Scale: This scale provides numerical values for electronegativity, with fluorine (the most electronegative element) assigned a value of 4.0.
General Rules of Thumb:
- ΔEN > 1.7: Generally considered ionic.
- 0.5 < ΔEN < 1.7: Generally considered polar covalent.
- ΔEN < 0.5: Generally considered nonpolar covalent.
(ΔEN represents the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms.)
Identifying Ionic Compounds: A Practical Approach
Let's apply these concepts to identify ionic compounds. When presented with a chemical formula, consider the following:
- Identify the elements: Determine which elements are present in the compound.
- Classify the elements: Classify each element as a metal or a non-metal. Metals are typically found on the left side of the periodic table, while non-metals are on the right.
- Consider electronegativity: Consult a periodic table or electronegativity chart to determine the electronegativity values of the elements. Calculate the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN).
- Analyze the ΔEN: Use the guidelines mentioned above to determine the bond type. A large ΔEN (generally > 1.7) strongly suggests an ionic bond.
- Look for characteristic properties: If the compound exhibits properties consistent with ionic compounds (high melting point, crystalline structure, conductivity when molten or dissolved), this further supports the identification.
Examples: Is it Ionic or Covalent?
Let's examine some examples to solidify our understanding.
Example 1: NaCl (Sodium Chloride)
- Sodium (Na) is a metal; Chlorine (Cl) is a non-metal.
- The electronegativity difference is large (ΔEN ≈ 2.1).
- NaCl exhibits high melting point, crystalline structure, and conducts electricity when molten.
- Conclusion: NaCl is an ionic compound.
Example 2: H₂O (Water)
- Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O) are both non-metals.
- The electronegativity difference is moderate (ΔEN ≈ 1.4).
- H₂O has a relatively low melting point and does not conduct electricity.
- Conclusion: H₂O is a polar covalent compound.
Example 3: CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide)
- Carbon (C) and Oxygen (O) are both non-metals.
- The electronegativity difference is small (ΔEN ≈ 1.0).
- CO₂ is a gas at room temperature and does not conduct electricity.
- Conclusion: CO₂ is a nonpolar covalent compound.
Example 4: MgO (Magnesium Oxide)
- Magnesium (Mg) is a metal, Oxygen (O) is a non-metal.
- The electronegativity difference is large (ΔEN ≈ 2.1)
- MgO exhibits a high melting point and crystalline structure.
- Conclusion: MgO is an ionic compound.
Example 5: CH₄ (Methane)
- Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) are both nonmetals.
- The electronegativity difference is small (ΔEN ≈ 0.4).
- CH₄ is a gas at room temperature and does not conduct electricity.
- Conclusion: CH₄ is a nonpolar covalent compound.
Beyond Simple Binary Compounds
The principles discussed apply to more complex compounds as well. When dealing with compounds containing polyatomic ions (ions composed of more than one atom, such as sulfate (SO₄²⁻) or ammonium (NH₄⁺)), remember that these ions behave as single charged entities in determining the overall ionic or covalent nature of the compound. For instance, ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) is an ionic compound because the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) interacts ionically with the chloride ion (Cl⁻).
Exceptions and Grey Areas
While the electronegativity difference provides a helpful guideline, it's important to acknowledge that there are exceptions and grey areas. Some compounds exhibit properties intermediate between purely ionic and purely covalent. These are often described as having polar covalent bonds, where the electrons are shared unequally, resulting in a partial positive and partial negative charge within the molecule.
Conclusion: Mastering the Identification of Ionic Compounds
Identifying ionic compounds involves understanding the fundamental principles of chemical bonding, especially the role of electronegativity. By systematically analyzing the elements present, their classification (metal or non-metal), and the electronegativity difference, you can effectively determine whether a compound is primarily ionic or covalent. Remember to consider the characteristic properties of each type of compound to further support your identification. While exceptions exist, the principles outlined here provide a robust framework for accurately classifying a wide range of chemical compounds. Consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the periodic table will significantly enhance your ability to confidently identify ionic compounds.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Evaporation Is A Physical Change
Mar 31, 2025
-
Do Gram Positive Bacteria Have Porins
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Compounds Is Most Soluble In Water
Mar 31, 2025
-
Part Of The Brain That Controls Breathing And Heartbeat
Mar 31, 2025
-
This Pair Of Structures Anchors The Spindle
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Compounds Is Ionic . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
