Which Of The Following Are Disaccharides
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
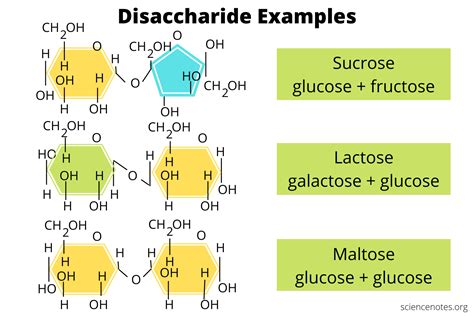
Table of Contents
Which of the Following are Disaccharides? A Comprehensive Guide
Disaccharides, a crucial class of carbohydrates, play a vital role in various biological processes. Understanding their structure, properties, and functions is essential for comprehending metabolism, nutrition, and related fields. This article delves deep into the world of disaccharides, clarifying their definition, providing examples, and differentiating them from other carbohydrate types. We will also explore their significance in human biology and beyond.
Understanding Disaccharides: The Basics
Before we identify specific disaccharides, let's establish a firm understanding of what defines this class of carbohydrates. Disaccharides are a type of carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides (simple sugars) undergo a dehydration reaction. This reaction involves the removal of a water molecule (H₂O) as a glycosidic bond forms, linking the two monosaccharides together. The glycosidic bond is a crucial characteristic of disaccharides, defining their chemical structure and influencing their properties.
The monosaccharides involved in disaccharide formation can be the same or different, leading to a diverse range of disaccharides with varying properties. The type of monosaccharides and the position of the glycosidic linkage significantly impact the disaccharide's chemical and physical attributes such as sweetness, solubility, and digestibility.
Key Characteristics of Disaccharides
- Composition: Two monosaccharide units joined by a glycosidic bond.
- Molecular Weight: Relatively larger than monosaccharides but smaller than polysaccharides.
- Solubility: Generally soluble in water, though solubility can vary based on the constituent monosaccharides and the bond type.
- Sweetness: Possess a sweet taste, although the degree of sweetness differs among various disaccharides.
- Digestibility: Can be broken down into monosaccharides by enzymes in the digestive system, enabling absorption and utilization by the body.
Common Examples of Disaccharides: A Detailed Look
Several common disaccharides are frequently encountered in our diet and biological systems. Let's examine some key examples:
1. Sucrose (Table Sugar): A Widely Used Disaccharide
Sucrose is perhaps the most familiar disaccharide. Commonly known as table sugar, it's widely used as a sweetener in foods and beverages. Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of:
- Glucose: An aldohexose (a six-carbon aldehyde sugar).
- Fructose: A ketohexose (a six-carbon ketone sugar).
The glucose and fructose units are linked by an α(1→2) glycosidic bond. This specific linkage is crucial, dictating sucrose's properties and how it is metabolized.
2. Lactose (Milk Sugar): Essential for Mammalian Development
Lactose, also known as milk sugar, is found naturally in milk and dairy products. It's an essential nutrient for mammalian infants, providing energy for growth and development. Lactose is a disaccharide composed of:
- Glucose: An aldohexose.
- Galactose: An aldohexose, an epimer of glucose (differing only in the orientation of a hydroxyl group).
Lactose is linked by a β(1→4) glycosidic bond. The presence of galactose, distinct from glucose, distinguishes lactose from other disaccharides. Many adults experience lactose intolerance, lacking the enzyme lactase needed to digest lactose efficiently.
3. Maltose (Malt Sugar): A Product of Starch Digestion
Maltose, also known as malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed by the breakdown of starch. It's often used in brewing and food processing. Maltose comprises two glucose units linked by an α(1→4) glycosidic bond. This linkage differs from that in lactose, influencing its properties and how the body processes it.
4. Cellobiose: A Building Block of Cellulose
Cellobiose is a disaccharide that's not directly found in nature in significant quantities. It's a product of cellulose breakdown. Cellulose, a major structural component of plant cell walls, is a polymer of glucose units linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds. Cellobiose is a repeating unit in this polymer. While it's a disaccharide, its β(1→4) linkage renders it indigestible for humans, as we lack the necessary enzymes to break this specific bond.
Differentiating Disaccharides from Other Carbohydrates
Understanding the differences between disaccharides and other carbohydrate types is vital. Here's a comparison:
Disaccharides vs. Monosaccharides
- Monosaccharides: The simplest form of carbohydrates; single sugar units (e.g., glucose, fructose, galactose). They are the building blocks of disaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond. They are hydrolyzed (broken down) into monosaccharides during digestion.
Disaccharides vs. Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides: Complex carbohydrates; long chains of monosaccharides linked together (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose). They have much higher molecular weights compared to disaccharides.
- Disaccharides: Relatively smaller and simpler than polysaccharides. They are often intermediates in the digestion of polysaccharides.
The Importance of Disaccharides in Human Biology and Nutrition
Disaccharides play significant roles in human biology and nutrition. Their functions include:
- Energy Source: They provide energy after being digested into monosaccharides. Glucose, a product of disaccharide breakdown, is the primary energy source for the body.
- Dietary Component: Disaccharides are found in various foods and beverages, contributing to our overall carbohydrate intake.
- Metabolic Intermediates: They act as intermediates in various metabolic pathways.
- Prebiotics: Some disaccharides can act as prebiotics, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Identifying Disaccharides: Practical Applications and Examples
Now, let's tackle the core question directly: how to identify disaccharides. The process often involves chemical analysis, such as:
- Hydrolysis: Breaking down the disaccharide into its constituent monosaccharides using acid or enzymes. The resulting monosaccharides can then be identified using chromatography or other analytical techniques.
- Specific enzymatic assays: Using enzymes specific to certain disaccharides to detect their presence. For instance, lactase can be used to detect lactose.
- Spectroscopic methods: Techniques like infrared spectroscopy or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) can be used to analyze the chemical structure of the disaccharide.
Example: Consider a solution containing an unknown carbohydrate. After undergoing hydrolysis, you find that it yields only glucose molecules. This suggests that the original carbohydrate is likely maltose. If the hydrolysis yields both glucose and galactose, it indicates lactose.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Overview of Disaccharides
This comprehensive overview has explored the essential characteristics of disaccharides, providing examples and comparisons with other carbohydrate types. Disaccharides are critical for human health and play significant roles in biological processes. Understanding their structure, properties, and functions is essential for comprehending metabolism, nutrition, and other related aspects of biology and biochemistry. Through chemical analysis and understanding their constituent monosaccharides and the type of glycosidic linkage, we can accurately identify disaccharides in various biological and dietary contexts. The significance of disaccharides in human health and nutrition cannot be overstated, highlighting the importance of further research and education in this crucial area of biochemistry and food science. Remember, while this article provides a detailed explanation, always consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized advice about your diet and nutritional needs.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 Is The Only Even Prime Number
Apr 02, 2025
-
Distance Between Earth And Moon In Light Years
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Chemically Inert Unreactive
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Standard Unit For Measuring Volume Is
Apr 02, 2025
-
Materials Like Rubber That Resist The Flow Of E
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Disaccharides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
