Which Of The Following Antibodies Is A Pentamer
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
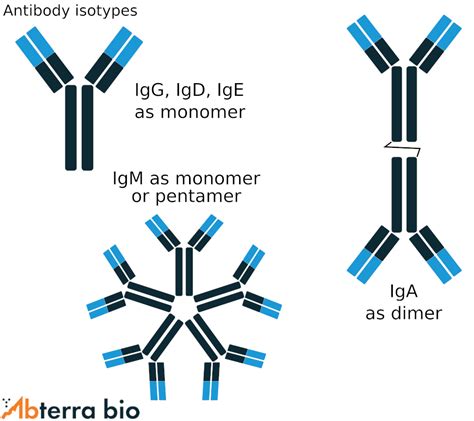
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Antibodies is a Pentamer? Understanding Immunoglobulin Structure and Function
The question, "Which of the following antibodies is a pentamer?" points to a fundamental aspect of immunology: the structure and function of antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig). Understanding the different classes of immunoglobulins and their structural variations is crucial for comprehending the complex workings of the immune system. This article will delve into the intricacies of antibody structure, focusing specifically on the pentameric structure of IgM, and exploring its implications for immune response.
Antibody Structure: A Building Block of Immunity
Antibodies are glycoproteins produced by plasma cells (differentiated B cells) that play a central role in adaptive immunity. Their primary function is to recognize and bind to specific antigens – foreign substances like bacteria, viruses, toxins, and even self-antigens in the case of autoimmune disorders. This binding initiates a cascade of events leading to the neutralization or elimination of the threat.
The basic structural unit of an antibody is a monomer, composed of four polypeptide chains:
- Two identical heavy chains (H chains): These chains are larger and determine the antibody isotype (IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgD).
- Two identical light chains (L chains): These chains are smaller and are of two types: kappa (κ) and lambda (λ).
These chains are connected by disulfide bonds, forming a Y-shaped molecule. Each arm of the Y contains a variable region (Fab region) responsible for antigen binding, and the stem of the Y contains a constant region (Fc region) responsible for effector functions.
Variable and Constant Regions: Specificity and Effector Functions
The variable region (Fab) is highly diverse, allowing antibodies to bind a vast array of antigens with remarkable specificity. This diversity arises from V(D)J recombination, a complex genetic process that shuffles and recombines gene segments during B cell development, creating a vast repertoire of unique antibody sequences. This region's hypervariable loops, known as complementarity-determining regions (CDRs), directly contact the antigen.
The constant region (Fc) is relatively conserved within an isotype. This region interacts with various immune cells and proteins, initiating effector functions such as:
- Opsonization: Coating the antigen, making it more easily recognized and phagocytosed by macrophages and neutrophils.
- Complement activation: Triggering the complement cascade, a series of enzymatic reactions leading to lysis of the pathogen.
- Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC): Recruiting natural killer (NK) cells to destroy antibody-coated cells.
IgM: The Pentameric Antibody
Among the five major isotypes (IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgD), IgM is unique in its pentameric structure. This means that five basic antibody monomers are joined together by a joining (J) chain polypeptide, forming a large, star-shaped molecule. This structure has significant implications for its function.
The Significance of the Pentameric Structure
The pentameric structure of IgM contributes to its high avidity, even though individual monomers might have relatively low affinity for their target antigen. Avidity refers to the overall strength of binding between an antibody and its antigen, taking into account the number of binding sites and their individual affinities. The ten antigen-binding sites of IgM provide a significantly higher avidity than the two sites of a monomeric antibody. This high avidity is crucial for effectively neutralizing pathogens, particularly in the early stages of an immune response.
IgM is typically the first antibody produced during an infection. Its pentameric structure allows for rapid and efficient binding to pathogens, helping to control the infection until more specialized antibody isotypes, such as IgG, are produced. This early response is vital in preventing the spread of infection.
IgM's Role in the Immune Response
The large size and structure of IgM also influence its effector functions. It is particularly effective at activating the complement system, leading to the lysis of pathogens. The multiple Fc regions in the pentamer provide numerous binding sites for complement proteins, enhancing the overall effectiveness of complement activation. This contributes significantly to the rapid elimination of pathogens during the early immune response.
However, the large size of IgM limits its ability to penetrate tissues. Its primary location is in the blood and lymph, making it more effective against pathogens in these fluid compartments. This contrasts with IgG, which can more effectively penetrate tissues and provide long-lasting protection.
Other Antibody Isotypes: A Comparative Overview
Understanding the pentameric nature of IgM becomes clearer when compared to the other immunoglobulin isotypes:
-
IgG: The most abundant antibody isotype in serum. It exists as a monomer and is responsible for long-term immunity, opsonization, complement activation, and ADCC. Its ability to cross the placenta provides passive immunity to the developing fetus.
-
IgA: Primarily found in mucosal secretions (tears, saliva, mucus) and breast milk. It exists mainly as a dimer (two monomers joined together), providing protection against pathogens at mucosal surfaces.
-
IgE: Involved in allergic reactions and defense against parasitic infections. It binds to mast cells and basophils, triggering the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators upon antigen binding. It exists as a monomer.
-
IgD: Its function is less well-understood compared to other isotypes. It's primarily found on the surface of naive B cells and may play a role in B cell activation and differentiation. It is a monomer.
Clinical Significance of IgM and its Pentameric Structure
The unique properties of IgM, particularly its pentameric structure, have significant clinical implications:
-
Diagnosis of infections: The presence of IgM antibodies in serum often indicates a recent infection, as IgM is typically the first antibody produced. IgM antibody tests are commonly used to diagnose acute infections like rubella, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasmosis.
-
Autoimmune diseases: The high avidity of IgM can contribute to autoimmune diseases by effectively binding to self-antigens and triggering autoimmune responses. However, IgM's role in autoimmunity is complex and not fully understood.
-
Immunodeficiencies: Deficiencies in IgM production can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, highlighting the importance of IgM in immune defense.
Conclusion: The Importance of Antibody Structure in Immunity
The question of which antibody is a pentamer unequivocally points to IgM. This unique structural feature plays a crucial role in the initial stages of the immune response, providing rapid and effective protection against pathogens. Its high avidity and ability to activate the complement system are vital for controlling infections until other antibody isotypes take over for long-term immunity. Understanding the structural and functional diversity of antibodies, particularly the distinct properties of IgM, is essential for comprehending the intricacies of the immune system and its role in health and disease. Further research into the precise mechanisms of IgM action continues to enhance our understanding of immune responses and develop more effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. The pentameric structure of IgM is not merely a structural curiosity; it is a key element in the dynamic and complex process of defending the body against disease. The study of immunoglobulins, and IgM in particular, remains a vibrant and essential area of immunological research.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Bone Does Not Articulate With Any Other Bone
Mar 19, 2025
-
Square Root Of 3 Divided By 3
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Undergoes Solvolysis In Methanol Most Rapidly
Mar 19, 2025
-
In Circle T What Is The Value Of X
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Horizontal Force Of Magnitude 35 0 N Pushes
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Antibodies Is A Pentamer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
