In Circle T What Is The Value Of X
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
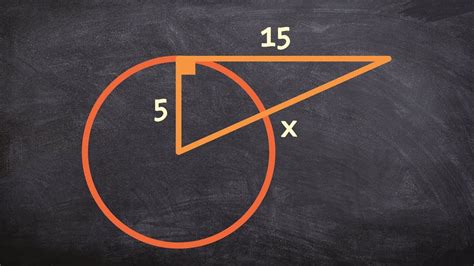
Table of Contents
In Circle T, What is the Value of x? A Comprehensive Guide to Circle Theorems and Problem Solving
Determining the value of 'x' within a circle, given specific conditions, often involves applying various circle theorems. This article delves into common scenarios, providing a step-by-step approach to solving problems related to angles, chords, tangents, and secants within a circle. We’ll cover various theorems and illustrate their applications with numerous examples, equipping you with the skills to confidently tackle similar problems. This guide focuses on the practical application of these theorems, aiming to build your problem-solving skills rather than simply stating the theorems themselves.
Understanding Circle Theorems: The Foundation for Solving 'x'
Before jumping into solving for 'x', let's revisit some fundamental circle theorems that form the basis of our problem-solving strategies. These theorems govern the relationships between angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants within a circle. A solid understanding of these theorems is crucial for accurately determining the value of 'x' in various scenarios.
1. The Inscribed Angle Theorem
This theorem states that an inscribed angle (an angle whose vertex lies on the circle and whose sides are chords) is half the measure of its intercepted arc (the arc contained within the angle).
Example: If an inscribed angle measures 30 degrees, its intercepted arc measures 60 degrees.
2. The Central Angle Theorem
A central angle (an angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle) has a measure equal to its intercepted arc.
Example: If a central angle measures 70 degrees, its intercepted arc also measures 70 degrees.
3. The Angles in a Cyclic Quadrilateral Theorem
A cyclic quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon whose vertices lie on a circle. In a cyclic quadrilateral, the opposite angles are supplementary (their sum is 180 degrees).
Example: If two opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are 75 and 105 degrees, the theorem is satisfied (75 + 105 = 180).
4. The Tangent-Secant Theorem
When a tangent and a secant are drawn to a circle from an external point, the square of the length of the tangent segment is equal to the product of the lengths of the secant segment and its external segment.
Example: Let's say the length of the tangent segment is 't', the length of the external segment of the secant is 'a', and the length of the entire secant segment is 'a+b'. Then, the theorem states: t² = a(a+b).
5. The Intersecting Chords Theorem
When two chords intersect inside a circle, the product of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the segments of the other chord.
Example: If two chords intersect, dividing one into segments of length 'a' and 'b', and the other into segments of length 'c' and 'd', then the theorem states: a * b = c * d.
Solving for 'x': Practical Examples
Now, let's apply these theorems to solve for 'x' in different scenarios within circle T. We'll tackle various complexities, building your understanding step by step.
Example 1: Inscribed Angle and Intercepted Arc
Imagine a circle with an inscribed angle 'x' intercepting an arc of 100 degrees. Using the inscribed angle theorem, we know:
x = (1/2) * 100 degrees x = 50 degrees
Example 2: Cyclic Quadrilateral
Consider a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD inscribed in circle T. We know angle A = 70 degrees and angle C = x. Since opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary:
70 + x = 180 degrees x = 110 degrees
Example 3: Intersecting Chords
Two chords intersect inside circle T. One chord is divided into segments of length 6 and 8, while the other chord is divided into segments of length 4 and 'x'. Applying the intersecting chords theorem:
6 * 8 = 4 * x 48 = 4x x = 12
Example 4: Tangent and Secant
A tangent segment of length 10 is drawn to circle T from an external point. A secant is also drawn from the same point, with its external segment having length 4 and the internal segment having length 'x'. Applying the tangent-secant theorem:
10² = 4(4+x) 100 = 16 + 4x 84 = 4x x = 21
Example 5: Combination of Theorems
This example involves a more complex scenario requiring the application of multiple theorems. Suppose we have a circle with an inscribed angle 'x', a central angle 'y', and a chord subtending both angles. If the measure of the arc subtended by the central angle is 120 degrees, and the inscribed angle is 'x', we know:
y = 120 degrees (Central Angle Theorem) x = y/2 = 120/2 = 60 degrees (Inscribed Angle Theorem)
Therefore, x = 60 degrees. This illustrates how multiple theorems can be used in conjunction to solve for an unknown angle.
Advanced Problem Solving Strategies
Solving for 'x' can become significantly more challenging with more complex geometrical setups. Here are some advanced strategies:
-
Auxiliary Lines: Sometimes, drawing auxiliary lines (lines added to the diagram to create additional relationships) can simplify the problem, allowing you to apply known theorems more effectively.
-
Breaking Down Complex Shapes: Complex figures can be broken down into simpler shapes (triangles, quadrilaterals, etc.) to isolate and solve for individual angles or segments before using these values to find 'x'.
-
Using Algebra: Algebraic equations are often necessary to solve for 'x', especially when multiple theorems are involved or when the problem involves more than one unknown.
-
Systematic Approach: Follow a systematic approach. Identify the known angles and segments, note the relationships between them (using circle theorems), and construct equations to solve for 'x'.
Conclusion: Mastering the Value of 'x' in Circle T
Finding the value of 'x' within a circle is a fundamental skill in geometry. Mastering circle theorems and applying them strategically—through practice and understanding the relationships between angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants—is key. Remember to utilize advanced strategies like auxiliary lines and algebraic equations to solve more complex problems. The more practice you dedicate to solving these problems, the more intuitive and proficient you will become in unraveling the mysteries of circle geometry. Remember, solving for ‘x’ is not just about the answer; it's about understanding the underlying principles and applying them to diverse geometric situations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Naoh Was Added To A 7 75
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Does Fish Heart Have
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is 90 Degree Celsius In Fahrenheit
Mar 20, 2025
-
Vitamin A Is Necessary For The Synthesis Of Rhodopsin
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Role Of Nad In Cellular Respiration
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In Circle T What Is The Value Of X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
