What Is 90 Degree Celsius In Fahrenheit
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
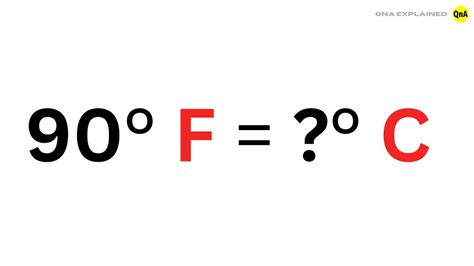
Table of Contents
What is 90 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit? A Comprehensive Guide
Converting temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a common task, especially for those who work with both systems or travel internationally. While many online converters exist, understanding the conversion process itself is crucial for better comprehension and application in various contexts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the conversion of 90 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, explore the history of these temperature scales, and provide useful tips and applications.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Before we jump into the conversion, let's briefly review the two temperature scales:
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is a metric unit based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Zero degrees Celsius (0°C) represents the freezing point of water, while 100 degrees Celsius (100°C) represents its boiling point. This linear scale is widely used globally, particularly in scientific contexts and most countries worldwide.
Fahrenheit (°F): Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, this scale uses different reference points. 32 degrees Fahrenheit (32°F) marks the freezing point of water, and 212 degrees Fahrenheit (212°F) marks its boiling point. This scale remains prevalent in the United States and a few other countries.
The Conversion Formula: Celsius to Fahrenheit
The conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit utilizes a simple yet effective formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Where:
- °F represents the temperature in Fahrenheit.
- °C represents the temperature in Celsius.
Calculating 90 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit
Now, let's apply the formula to convert 90 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit:
°F = (90°C × 9/5) + 32
°F = (162) + 32
°F = 194
Therefore, 90 degrees Celsius is equal to 194 degrees Fahrenheit.
Practical Applications of Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversions
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is invaluable in various situations:
Cooking and Baking:
Many international recipes use Celsius, while others utilize Fahrenheit. Understanding the conversion is vital for accurate temperature control, ensuring consistent and successful results in the kitchen. For example, a recipe calling for 90°C might require you to adjust your oven to 194°F.
Scientific Experiments and Research:
Scientific experiments often involve precise temperature measurements. Researchers frequently need to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit to maintain consistency across different studies and publications. Many scientific instruments allow for readings in both scales, but understanding the conversion provides a crucial backup.
Meteorology and Weather Forecasting:
Weather reports can be presented in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the region. The ability to quickly convert allows for better understanding and comparison of weather conditions across different locations. Knowing that a high of 90°C is a scorching 194°F is a practical example.
Healthcare and Medicine:
Temperature plays a critical role in healthcare. Medical devices often display temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, but knowing the conversion is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. For instance, a high fever in Celsius would need to be converted to Fahrenheit for easier understanding by a healthcare professional.
International Travel:
Traveling internationally exposes you to different temperature scales. Understanding the conversion is vital for packing appropriate clothing, preparing for outdoor activities, and interpreting weather forecasts.
Industrial Processes:
Many industrial processes, such as manufacturing and chemical engineering, rely on precise temperature control. The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is critical for maintaining optimal conditions and preventing equipment malfunctions.
A Deeper Dive into Temperature Scales: History and Context
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales have distinct histories and unique characteristics:
The Celsius Scale (Originally Centigrade):
The Celsius scale, initially known as the centigrade scale, was developed by Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer. In 1742, he proposed a scale where 0°C represented the boiling point of water and 100°C represented its freezing point – the opposite of what we use today! This was later reversed to its current form, reflecting the more intuitive progression from freezing to boiling.
The Fahrenheit Scale:
The Fahrenheit scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist. His original scale used the freezing point of a brine solution (a mixture of water, ice, and ammonium chloride) as 0°F, and the freezing point of water as 32°F. This was later modified to the current standard, with 32°F as the freezing point and 212°F as the boiling point of water. The choice of these specific points is less clearly defined than with Celsius and involved experiments with specific substances.
Other Temperature Scales:
It's important to note that Celsius and Fahrenheit are not the only temperature scales. Other scales, such as Kelvin and Rankine, are used in various scientific and engineering applications. The Kelvin scale, for instance, is an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero – the theoretical lowest possible temperature.
Tips for Accurate Conversions:
- Utilize Online Converters: While understanding the formula is crucial, online converters provide a convenient and quick way to perform conversions. Several reliable tools are available.
- Double-Check Your Calculations: Always double-check your calculations to avoid errors, especially when dealing with critical applications.
- Understand the Context: Consider the context when interpreting temperature readings. A comfortable room temperature of 20°C (68°F) feels very different from a hot summer day of 30°C (86°F) or a scorching 90°C (194°F).
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature and its Impact
The conversion itself is just the first step. Understanding the implications of temperature in various contexts, from weather patterns to human physiology, is equally important. High temperatures, like 90°C, represent extreme conditions that pose various risks, including heat stroke and material damage. Similarly, understanding the lower end of the temperature scales is crucial for aspects such as frost prevention and winter preparedness.
Conclusion:
Converting 90 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit is a straightforward process, as demonstrated by the formula provided. However, the broader context – the history, applications, and implications of these temperature scales – offers a more complete understanding. Whether you're cooking, conducting research, or simply interpreting a weather report, the ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill with numerous practical applications. Mastering this conversion and understanding the principles behind it enhances your understanding of the world around you.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Words Meaning English To English With 2 Meanings
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Term For The Removal Of Metabolic Waste
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Time Of Day Is The Coldest
Mar 20, 2025
-
A Solution Contains Dissolved Substances Called
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Does Freedom Mean To Me Essay
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 90 Degree Celsius In Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
