Which Compound Contains A Triple Bond
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
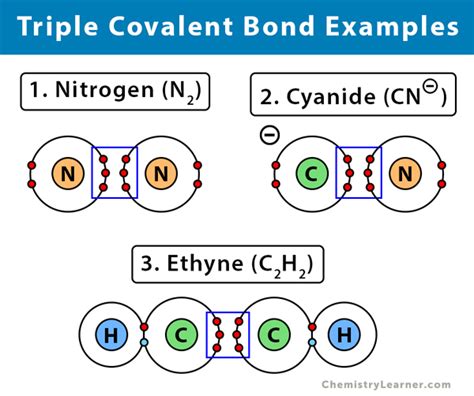
Table of Contents
- Which Compound Contains A Triple Bond
- Table of Contents
- Which Compound Contains a Triple Bond? A Deep Dive into Triple Bond Chemistry
- Understanding Triple Bonds: A Covalent Connection
- Key Characteristics of Triple Bonds:
- Compounds Containing Triple Bonds: A Diverse Family
- 1. Alkynes: The Carbon-Carbon Triple Bond
- 2. Nitriles: The Carbon-Nitrogen Triple Bond
- 3. Cyanides: Inorganic Compounds with a C≡N Bond
- 4. Other Compounds with Triple Bonds:
- The Implications of Triple Bonds on Chemical Properties
- Applications of Compounds with Triple Bonds
- Safety Considerations: Handling Compounds with Triple Bonds
- Conclusion: A Bond of Significance
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Compound Contains a Triple Bond? A Deep Dive into Triple Bond Chemistry
Triple bonds, a fascinating aspect of chemistry, represent a strong and unique type of covalent bond. Understanding which compounds contain these bonds is crucial for comprehending their distinct properties and reactivity. This comprehensive guide explores the nature of triple bonds, the types of compounds that feature them, and the implications of this bonding arrangement on chemical behavior. We’ll delve into examples, applications, and the broader context of triple bond chemistry.
Understanding Triple Bonds: A Covalent Connection
A triple bond is a type of covalent bond where three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. This is in contrast to single bonds (one shared electron pair) and double bonds (two shared electron pairs). The sharing of three electron pairs results in a significantly stronger and shorter bond compared to single or double bonds. The most common type of triple bond involves carbon atoms, although other elements can also participate.
Key Characteristics of Triple Bonds:
- Strength: Triple bonds are significantly stronger than single or double bonds due to the increased electron density between the atoms. This leads to higher bond dissociation energies.
- Bond Length: The bond length in a triple bond is considerably shorter than that of single or double bonds due to the stronger attraction between the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
- Linear Geometry: The atoms involved in a triple bond are typically arranged linearly, creating a straight-line structure.
- Reactivity: While strong, triple bonds are still reactive, undergoing various reactions such as addition reactions, where atoms or groups are added across the triple bond.
Compounds Containing Triple Bonds: A Diverse Family
Many organic and inorganic compounds incorporate triple bonds into their structures. Let’s explore some prominent examples:
1. Alkynes: The Carbon-Carbon Triple Bond
Alkynes are a class of hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. These compounds are unsaturated, meaning they possess fewer hydrogen atoms than the corresponding alkane (single bonds only). The simplest alkyne is ethyne (acetylene), C₂H₂, which plays a vital role in industrial chemistry.
Examples of alkynes:
- Ethyne (Acetylene): The simplest alkyne, used in welding and as a precursor to other chemicals.
- Propyne: A three-carbon alkyne with a terminal triple bond.
- Butyne: Exists as two isomers: 1-butyne (terminal triple bond) and 2-butyne (internal triple bond).
- Higher Alkynes: Alkynes can have longer carbon chains with multiple triple bonds or combinations of single, double, and triple bonds.
2. Nitriles: The Carbon-Nitrogen Triple Bond
Nitriles are organic compounds featuring a carbon-nitrogen triple bond (C≡N). This functional group is polar due to the difference in electronegativity between carbon and nitrogen. Nitriles are prevalent in various organic synthesis routes and possess significant applications.
Examples of Nitriles:
- Acetonitrile (CH₃CN): A common solvent used in organic chemistry.
- Benzonitrile (C₆H₅CN): An aromatic nitrile with a benzene ring.
- Acrylonitrile (CH₂=CHCN): A crucial monomer used in the production of acrylic fibers and plastics.
3. Cyanides: Inorganic Compounds with a C≡N Bond
Cyanides are inorganic compounds containing the cyanide ion (CN⁻), which also features a carbon-nitrogen triple bond. These compounds are highly toxic, and their use necessitates careful handling and safety precautions.
Examples of Cyanides:
- Hydrogen cyanide (HCN): A highly poisonous gas.
- Sodium cyanide (NaCN): A highly toxic salt used in various industrial applications (though its use is increasingly restricted due to its toxicity).
- Potassium cyanide (KCN): Similar in toxicity and applications to sodium cyanide.
4. Other Compounds with Triple Bonds:
While carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen triple bonds are most common, triple bonds can also form between other elements, though these are less prevalent:
- Dinitrogen (N₂): The most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, containing a nitrogen-nitrogen triple bond (N≡N). This incredibly strong bond contributes to its inert nature.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A highly toxic gas possessing a carbon-oxygen triple bond (C≡O). The polar nature of this bond contributes to its reactivity.
The Implications of Triple Bonds on Chemical Properties
The presence of a triple bond significantly influences the chemical properties of a compound. Several key features stem from this unique bonding arrangement:
- Acidity: Terminal alkynes (alkynes with the triple bond at the end of the carbon chain) exhibit weak acidity due to the sp hybridization of the carbon atom involved in the triple bond.
- Reactivity: Triple bonds undergo various addition reactions, where atoms or groups add across the triple bond, breaking it and forming new single or double bonds. This is particularly important in organic synthesis.
- Polarity: The polarity of a triple bond depends on the electronegativity difference between the participating atoms. For example, C≡N bonds are polar, leading to higher dipole moments.
- Isomerism: Alkynes can exhibit geometrical isomerism in certain cases. However, due to the linear geometry, rotational isomerism around the triple bond is not observed.
Applications of Compounds with Triple Bonds
Compounds containing triple bonds find extensive applications across diverse fields:
- Industrial Chemistry: Acetylene (ethyne) is a crucial building block in the production of various chemicals, including acetic acid, vinyl chloride (for PVC), and other valuable compounds.
- Materials Science: Triple bonds are incorporated into polymers to enhance their strength and durability. For instance, polyacrylonitrile, containing C≡N bonds, is a key component of acrylic fibers.
- Medicine: Some nitriles and cyanides find applications in pharmaceuticals, although their toxicity demands careful consideration.
- Energy: Research is ongoing to utilize alkynes as potential fuels and energy sources.
Safety Considerations: Handling Compounds with Triple Bonds
Many compounds containing triple bonds, especially cyanides, exhibit significant toxicity. Always follow safety protocols when handling these materials, including proper ventilation, protective equipment, and adherence to established safety guidelines. Never underestimate the potential hazards associated with their use.
Conclusion: A Bond of Significance
Triple bonds represent a unique and significant type of covalent bond, strongly influencing the chemical and physical properties of the compounds they inhabit. From the simple alkyne ethyne to the complex polymeric structures, triple bonds play critical roles in diverse industrial processes and scientific applications. Understanding their nature and implications is vital for advancements in chemistry, materials science, and related fields. While their properties and applications are numerous, the inherent risks associated with many triple bond-containing compounds emphasize the need for careful handling and safety awareness. Further research into the unique characteristics and potential applications of triple bonds will undoubtedly continue to shape progress across various scientific disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Boyles Charles And Gay Lussacs Gas Problems
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is Ethanol An Acid Or A Base
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Length Of Ab
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Type Of Device Is Computer Keyboard
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is Considered The Functional Unit Of The Kidney
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Compound Contains A Triple Bond . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
