What Is The Radian Of 45 Degrees
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
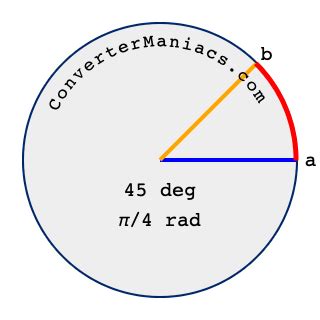
Table of Contents
What is the Radian of 45 Degrees? A Deep Dive into Angle Measurement
Understanding angles is fundamental to numerous fields, from mathematics and physics to engineering and computer graphics. While degrees are a common unit for measuring angles, radians offer a more natural and mathematically elegant approach, especially in calculus and higher-level mathematics. This article delves into the concept of radians, explaining what they are, how they relate to degrees, and specifically, how to determine the radian equivalent of 45 degrees.
Understanding Degrees and Radians
Before we tackle the conversion, let's solidify our understanding of the two primary angle measurement systems: degrees and radians.
Degrees: A Familiar Friend
Degrees are a familiar system for measuring angles. A full circle is divided into 360 degrees (360°). This system, while widely used, is somewhat arbitrary; its origin likely stems from ancient Babylonian mathematics and their base-60 number system. While convenient for many everyday applications, degrees lack the mathematical elegance and simplicity that radians possess.
Radians: The Mathematical Standard
Radians, on the other hand, are defined based on the radius of a circle. One radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc that is equal in length to the radius of the circle. This definition is far less arbitrary than that of degrees and provides a direct link between the angle and the arc length, simplifying many mathematical formulas and calculations.
Imagine this: Draw a circle. Now, measure out a distance along the circumference equal to the radius of the circle. The angle formed at the center by connecting the two endpoints of this arc to the center is one radian.
A complete circle (360°) encompasses 2π radians, which is approximately 6.28 radians (since π ≈ 3.14159). This relationship between degrees and radians is the cornerstone of their conversion.
Converting Degrees to Radians: The Formula
The conversion between degrees and radians hinges on the following fundamental relationship:
2π radians = 360°
This implies that:
- 1 radian = (180/π)°
- 1° = (π/180) radians
Using these formulas, we can seamlessly convert any angle measurement from degrees to radians and vice versa.
Calculating the Radian Equivalent of 45 Degrees
Now, let's apply the conversion formula to determine the radian measure of a 45-degree angle. Using the second formula above:
45° = 45 * (π/180) radians
Simplifying this expression:
45° = (45π/180) radians = (π/4) radians
Therefore, 45 degrees is equal to π/4 radians. This is a commonly used and important radian measure, frequently encountered in trigonometry and other mathematical contexts.
The Significance of π/4 Radians
The radian measure π/4 (approximately 0.7854 radians) holds significant importance in mathematics and its applications:
-
Trigonometric Functions: The trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, and tangent) take on particularly simple and elegant values at π/4 radians. For example:
- sin(π/4) = √2/2
- cos(π/4) = √2/2
- tan(π/4) = 1
-
Geometry: A right-angled isosceles triangle (a triangle with two equal sides and a 90° angle) has two angles of 45° each, or π/4 radians. This triangle is fundamental in geometry and trigonometry.
-
Calculus: Radians simplify calculus significantly, particularly in differentiation and integration involving trigonometric functions. Using radians avoids the need for cumbersome conversion factors that would arise if degrees were used.
Visualizing Radians: A Geometric Interpretation
To further understand radians, consider a unit circle (a circle with a radius of 1). One radian on this circle corresponds to an arc length of 1. Since the circumference of a unit circle is 2π, the entire circumference represents 2π radians. This visual representation makes it clear why radians are intrinsically linked to the circle's geometry.
Applications of Radians in Real-World Scenarios
Radians are not merely an abstract mathematical concept; they find widespread application in various real-world scenarios:
-
Engineering and Physics: In fields like engineering and physics, radians are essential for calculations involving circular motion, rotation, oscillations, and wave phenomena. Examples include calculating angular velocity, torque, and the motion of pendulums.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Radians are crucial in computer graphics and game development for representing rotations, transformations, and movements of objects in two and three dimensions. Many graphics libraries and game engines use radians as their default angle unit.
-
Navigation and GPS: Understanding radians is essential for calculations involved in navigation and GPS systems, particularly those that involve determining locations and distances based on spherical coordinates.
Beyond 45 Degrees: Mastering Radian Conversions
Understanding the conversion of 45 degrees to radians is a crucial stepping stone. To further solidify your understanding, practice converting other angles:
- Convert 30 degrees to radians: 30° = 30 * (π/180) = π/6 radians.
- Convert 60 degrees to radians: 60° = 60 * (π/180) = π/3 radians.
- Convert 90 degrees to radians: 90° = 90 * (π/180) = π/2 radians.
- Convert 180 degrees to radians: 180° = 180 * (π/180) = π radians.
- Convert 270 degrees to radians: 270° = 270 * (π/180) = (3π/2) radians.
- Convert 360 degrees to radians: 360° = 360 * (π/180) = 2π radians.
Mastering these conversions will significantly enhance your understanding of angles and their applications in various mathematical and scientific contexts.
Conclusion: Embracing the Elegance of Radians
While degrees may be more familiar in everyday life, radians offer a more mathematically elegant and fundamentally sound system for measuring angles. Understanding the conversion between degrees and radians, particularly the radian equivalent of 45 degrees (π/4 radians), is crucial for success in many scientific and technical fields. The inherent simplicity and elegance of radians make them the preferred unit in advanced mathematics and its numerous applications. By mastering this fundamental concept, you will unlock a deeper understanding of geometry, trigonometry, and calculus, ultimately enhancing your capabilities in various scientific and technical disciplines. Remember that π/4 radians is not just a number; it's a key to unlocking a more profound comprehension of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is The Smallest Unit Of Measurement
Mar 26, 2025
-
When Lithium Hydroxide Pellets Are Added
Mar 26, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 36 And 54
Mar 26, 2025
-
Inventory Is Classified On The Balance Sheet As A
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Opposite Of Hyperbole
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Radian Of 45 Degrees . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
