What Is The Product Of A Number And Its Reciprocal
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
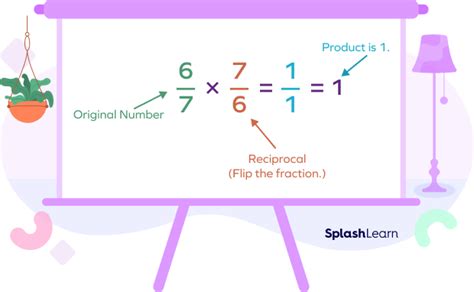
Table of Contents
What is the Product of a Number and Its Reciprocal? A Deep Dive into Multiplicative Inverses
The seemingly simple question, "What is the product of a number and its reciprocal?" unlocks a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching implications across various fields. This exploration delves into the definition of reciprocals, their properties, applications in different number systems (including real numbers, complex numbers, and matrices), and their significance in solving equations and simplifying expressions.
Understanding Reciprocals: The Multiplicative Inverse
A reciprocal, also known as a multiplicative inverse, is a number that, when multiplied by a given number, yields the multiplicative identity, which is 1. In simpler terms, if we have a number 'a', its reciprocal is denoted as 1/a or a⁻¹. The crucial relationship is:
a * (1/a) = 1
This definition holds true for most number systems, although there are exceptions, as we'll see later.
Examples of Reciprocals:
- The reciprocal of 5 is 1/5. (5 * (1/5) = 1)
- The reciprocal of -2 is -1/2. (-2 * (-1/2) = 1)
- The reciprocal of 1 is 1 itself. (1 * 1 = 1)
- The reciprocal of 3/4 is 4/3. (3/4 * 4/3 = 1)
- The reciprocal of 0 is undefined. This is a critical point. Division by zero is undefined in mathematics because there's no number that, when multiplied by zero, equals one.
Exploring Reciprocals in Different Number Systems
The concept of reciprocals extends beyond simple integers and fractions. Let's examine its application in various number systems:
1. Real Numbers:
The set of real numbers encompasses rational numbers (fractions) and irrational numbers (numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction, like π or √2). For every non-zero real number, a reciprocal exists. The product of a real number and its reciprocal is always 1.
2. Complex Numbers:
Complex numbers have the form a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers, and 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1). The reciprocal of a complex number z = a + bi is given by:
1/z = 1/(a + bi) = (a - bi) / (a² + b²)
This involves the concept of the complex conjugate (a - bi), which is used to eliminate the imaginary part from the denominator. The product of a complex number and its reciprocal is always 1.
3. Matrices:
Matrices are rectangular arrays of numbers. The reciprocal of a matrix is its inverse. However, not all matrices have inverses. A square matrix (same number of rows and columns) has an inverse only if its determinant is non-zero. The product of a matrix and its inverse is the identity matrix (a square matrix with 1s on the main diagonal and 0s elsewhere). Finding the inverse of a matrix often involves techniques like Gaussian elimination or adjugate matrices.
Applications of Reciprocals
The concept of reciprocals has numerous applications across various fields:
1. Solving Equations:
Reciprocals are crucial in solving algebraic equations. For instance, to solve the equation 3x = 12, we multiply both sides by the reciprocal of 3 (which is 1/3):
(1/3) * 3x = (1/3) * 12
x = 4
2. Simplifying Fractions:
Reciprocals are fundamental to simplifying complex fractions. When dividing fractions, we multiply by the reciprocal of the divisor. For example:
(2/3) / (4/5) = (2/3) * (5/4) = 10/12 = 5/6
3. Unit Conversion:
Reciprocals are extensively used in unit conversions. For instance, to convert kilometers to miles, you would use the conversion factor and its reciprocal depending on the direction of conversion.
4. Physics and Engineering:
Reciprocals play a crucial role in various physics and engineering formulas, like Ohm's law (resistance is the reciprocal of conductance) or the lens formula in optics.
5. Computer Science:
Reciprocals are employed in various computer algorithms, especially those involving matrix operations and signal processing.
Exceptional Cases and Considerations
While the product of a number and its reciprocal is generally 1, there are important exceptions:
-
Zero: As previously mentioned, the reciprocal of zero is undefined. This is because there's no number that, when multiplied by zero, results in 1.
-
Infinite Numbers: In the extended real number system (which includes positive and negative infinity), the reciprocal of infinity approaches zero, and the reciprocal of zero approaches infinity. However, the notion of multiplication with infinity requires careful consideration within the context of limits.
The Significance of the Multiplicative Identity
The fact that the product of a number and its reciprocal always equals 1 (except for zero) underscores the importance of the multiplicative identity, which is 1. The multiplicative identity plays a fundamental role in algebra, allowing us to maintain the equivalence of equations when manipulating them. Multiplying an equation by the reciprocal of a coefficient isolates the variable and helps in solving for its value.
Conclusion: A Cornerstone of Mathematics
The concept of the reciprocal, or multiplicative inverse, is a seemingly simple yet deeply impactful idea in mathematics. It underpins numerous algebraic operations, facilitates problem-solving across various disciplines, and provides a foundation for advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding reciprocals and their properties is essential for mastering algebra, calculus, linear algebra, and many other areas of mathematical study and application. Its profound role extends beyond theoretical mathematics and deeply influences our understanding and utilization of quantitative relationships in the real world. From solving simple equations to handling complex matrix manipulations, reciprocals consistently prove to be an invaluable tool. The consistent product of 1, resulting from the multiplication of a number and its reciprocal (excluding zero), solidifies its importance as a fundamental principle in the mathematical landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Value Of K In Coulombs Law
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Part Of The Cell Cycle Is The Longest
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Sodium Chloride A Homogeneous Mixture
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Grain Farming Subsistence Or Commercial
Mar 23, 2025
-
Express 8 Hours As A Percentage Of 2 Days
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Product Of A Number And Its Reciprocal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
