Value Of K In Coulomb's Law
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
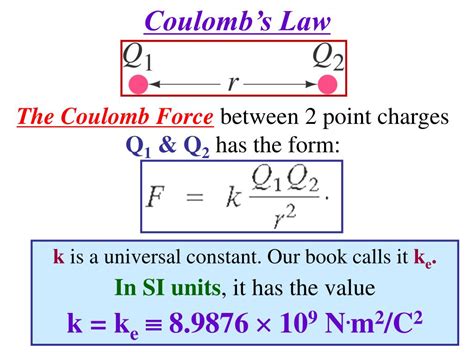
Table of Contents
- Value Of K In Coulomb's Law
- Table of Contents
- The Value of k in Coulomb's Law: A Deep Dive into Electrostatic Constants
- Understanding Coulomb's Constant (k)
- The Role of Permittivity
- The Value of k in Different Systems of Units
- The Significance of the Permittivity of Free Space (ε₀)
- Accuracy and Measurement of k
- Applications and Implications of Coulomb's Law and k
- 1. Electrostatic Interactions in Atoms and Molecules:
- 2. Capacitors and Dielectrics:
- 3. Electric Fields and Potentials:
- 4. Particle Accelerators:
- 5. Materials Science and Nanotechnology:
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Value of k in Coulomb's Law: A Deep Dive into Electrostatic Constants
Coulomb's Law is a cornerstone of electrostatics, elegantly describing the force between two charged particles. The equation, often represented as F = k|q₁q₂|/r², introduces a crucial constant, 'k', known as Coulomb's constant. Understanding the value of k, its origins, and its implications is essential for grasping the intricacies of electrostatic interactions and their applications in various fields. This article will delve deep into the significance of k, exploring its different representations, units, and the factors influencing its precise value.
Understanding Coulomb's Constant (k)
Coulomb's constant, denoted by 'k', quantifies the strength of the electrostatic force between two point charges. It's a proportionality constant that links the force (F) to the magnitudes of the charges (q₁ and q₂) and the distance (r) separating them. A higher value of k indicates a stronger force for a given set of charges and distance.
The commonly used value of k is approximately 8.98755 × 10⁹ N⋅m²/C². However, this is an approximation, and the precise value depends on the system of units used and the permittivity of the medium.
The Role of Permittivity
The value of k is intrinsically linked to the permittivity of the medium surrounding the charges. Permittivity (ε) represents a material's ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. A higher permittivity implies a greater ability to store energy, resulting in a weaker electrostatic force.
Coulomb's law can be expressed more generally as:
F = |q₁q₂| / (4πεr²)
Here, ε is the permittivity of the medium. For a vacuum, ε is denoted as ε₀ (epsilon naught), which has a defined value. The relationship between k and ε₀ is:
k = 1 / (4πε₀)
This equation highlights the inverse relationship between k and ε₀. A higher permittivity (ε₀) leads to a smaller value of k, reflecting the weakening of the electrostatic force in a medium with higher permittivity.
The Value of k in Different Systems of Units
The numerical value of k depends heavily on the system of units employed. The value 8.98755 × 10⁹ N⋅m²/C² is specific to the SI (International System of Units). In other systems, the value will differ. The choice of units influences not only the numerical value but also the dimensional analysis of the equation.
For instance, in the Gaussian system of units, Coulomb's law is expressed without a constant:
F = |q₁q₂|/r²
This seemingly simpler equation hides the fact that the charges and the force are expressed in units that implicitly incorporate the constant. This illustrates how the choice of units significantly impacts the apparent presence and value of k.
The Significance of the Permittivity of Free Space (ε₀)
The permittivity of free space (ε₀) is a fundamental physical constant that plays a crucial role in electromagnetism. Its value is approximately 8.854 × 10⁻¹² C²/N⋅m². It represents the ability of a vacuum to permit the passage of electric fields. This constant is a key element in Maxwell's equations, the cornerstone of classical electromagnetism.
The significance of ε₀ stems from its connection to other fundamental constants, including the speed of light (c) and the permeability of free space (μ₀). These constants are interconnected through the following relation:
c² = 1 / (ε₀μ₀)
This equation demonstrates the deep relationship between electricity, magnetism, and the speed of light, highlighting the fundamental nature of ε₀ and its pervasive influence on electromagnetic phenomena.
Accuracy and Measurement of k
The accuracy of Coulomb's constant is crucial for numerous applications, particularly in precision measurements and calculations in fields like particle physics and materials science. Measuring k directly is challenging due to the extremely small magnitude of the electrostatic force at macroscopic distances.
Historically, k's value was determined indirectly through precise measurements of other related constants, such as the permittivity of free space (ε₀). Modern techniques utilize sophisticated experimental setups and advanced data analysis to refine the value of k, improving its precision over time. The current accepted value reflects decades of research and refinement.
Applications and Implications of Coulomb's Law and k
Coulomb's Law, with its embedded constant k, has far-reaching implications across diverse scientific and technological domains. Here are some key applications:
1. Electrostatic Interactions in Atoms and Molecules:
Coulomb's Law governs the interactions between charged particles within atoms and molecules. It explains the stability of atoms and the formation of chemical bonds. The strength of electrostatic forces dictates the arrangement of electrons and nuclei, profoundly influencing the properties of matter.
2. Capacitors and Dielectrics:
The value of k (or ε) is central to understanding the behavior of capacitors, devices that store electrical energy. Dielectric materials, inserted between the capacitor plates, alter the permittivity, affecting the capacitor's capacitance and energy storage capacity.
3. Electric Fields and Potentials:
Coulomb's Law forms the foundation for calculating electric fields and potentials generated by various charge distributions. It enables the analysis of complex electrostatic systems and the design of electronic components.
4. Particle Accelerators:
In particle accelerators, the precise manipulation of electrostatic forces is critical for guiding and accelerating charged particles. The value of k is essential in designing and controlling the trajectories of these particles.
5. Materials Science and Nanotechnology:
Understanding electrostatic interactions is crucial in materials science, particularly at the nanoscale. The design of novel materials and nanostructures often relies on precisely controlling electrostatic forces.
Conclusion
Coulomb's constant, k, is far more than a simple proportionality constant; it is a fundamental parameter reflecting the strength of electrostatic interactions and its intrinsic link to other fundamental constants. Its value, inextricably tied to the permittivity of the medium, dictates the behavior of charged particles and influences numerous phenomena across various scientific disciplines and technological applications. While the accepted value of k is a well-established approximation, ongoing research continues to refine its precision, further enhancing our understanding of the fundamental forces governing our universe. The continuing exploration of its nuances underscores its enduring importance in physics and engineering.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Triangle With 3 Lines Of Symmetry
Mar 26, 2025
-
An Infinite Nonconducting Sheet Has A Surface
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Image Produced By A Concave Mirror Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
An Element Cannot Be Broken Down By Chemical Means
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Standard Unit For Mass Is The
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Value Of K In Coulomb's Law . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
