What Is The Molecular Mass Of Calcium Phosphate
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
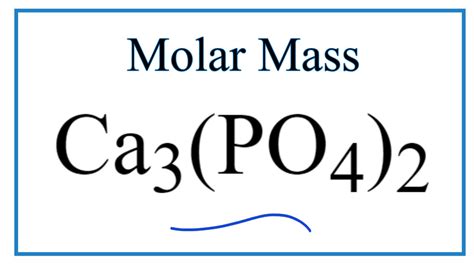
Table of Contents
What is the Molecular Mass of Calcium Phosphate? A Deep Dive into Chemical Calculations
Calcium phosphate, a ubiquitous compound in biological systems and industrial applications, holds significant importance in various fields. Understanding its molecular mass is fundamental to numerous calculations in chemistry, biology, and materials science. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "What is the molecular mass of calcium phosphate?" but will also delve into the intricacies of calculating molar mass, explore the different forms of calcium phosphate, and discuss its relevance in different contexts.
Understanding Molecular Mass and Molar Mass
Before diving into the specifics of calcium phosphate, let's clarify the terms "molecular mass" and "molar mass." While often used interchangeably, there's a subtle difference:
-
Molecular mass refers to the mass of a single molecule, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu). This is relevant for covalent compounds where discrete molecules exist.
-
Molar mass refers to the mass of one mole (6.022 x 10²³ particles) of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). This is a more practical term used in chemical calculations, particularly for ionic compounds like calcium phosphate, where discrete molecules aren't always clearly defined. For our purposes, we'll primarily use the term molar mass.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Calcium Phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂)
Calcium phosphate exists in several forms, each with its own properties. However, the most common form is tricalcium phosphate, with the chemical formula Ca₃(PO₄)₂. To calculate its molar mass, we need the atomic masses of its constituent elements:
- Calcium (Ca): Approximately 40.08 g/mol
- Phosphorus (P): Approximately 30.97 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): Approximately 16.00 g/mol
Here's the step-by-step calculation:
-
Calcium (Ca): There are 3 calcium atoms, so we multiply its atomic mass by 3: 3 * 40.08 g/mol = 120.24 g/mol
-
Phosphorus (P): There are 2 phosphorus atoms, so we multiply its atomic mass by 2: 2 * 30.97 g/mol = 61.94 g/mol
-
Oxygen (O): There are 8 oxygen atoms (2 phosphate groups x 4 oxygen atoms/phosphate group), so we multiply its atomic mass by 8: 8 * 16.00 g/mol = 128.00 g/mol
-
Total Molar Mass: Add the molar masses of all the constituent elements: 120.24 g/mol + 61.94 g/mol + 128.00 g/mol = 310.18 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of tricalcium phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂) is approximately 310.18 g/mol. This value might slightly vary depending on the source of atomic mass data used, as these are average values considering isotopic abundances.
Different Forms of Calcium Phosphate and Their Significance
While tricalcium phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂) is the most common form, several other calcium phosphates exist, including:
-
Hydroxyapatite (Ca₅(PO₄)₃OH): A major component of tooth enamel and bone. Its molar mass calculation follows a similar process to that of tricalcium phosphate, taking into account the addition of the hydroxyl (OH) group.
-
Octacalcium phosphate (Ca₈H₂(PO₄)₆·5H₂O): A precursor in the formation of hydroxyapatite. Its molar mass calculation requires considering the water molecules of hydration.
-
Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (CaHPO₄·2H₂O): Commonly used as a food additive and in fertilizers. Again, the water molecules need to be included in the molar mass calculation.
-
Monocalcium phosphate monohydrate (Ca(H₂PO₄)₂·H₂O): Used in baking powders and as a fertilizer. The calculation requires accounting for the additional hydrogen and water molecule.
The molar mass of each of these forms differs due to the varying numbers and types of atoms present in their respective chemical formulas. Each calculation follows the same fundamental principle: sum the atomic masses of all atoms present in the compound.
Applications of Calcium Phosphate and the Importance of Molar Mass
Understanding the molar mass of calcium phosphate is crucial in various applications:
1. Biological Systems:
-
Bone and Tooth Formation: Calcium phosphate compounds, particularly hydroxyapatite, are fundamental building blocks of bones and teeth. Knowing the molar mass allows researchers to study bone growth, mineral density, and related health issues.
-
Metabolic Processes: Accurate molar mass is essential for understanding calcium and phosphate metabolism in the body, helping diagnose and treat related disorders.
-
Biomaterial Development: Researchers use molar mass data to design biocompatible materials for bone grafts, dental implants, and drug delivery systems.
2. Industrial Applications:
-
Fertilizers: Calcium phosphates are essential components of fertilizers, providing phosphorus, a crucial nutrient for plant growth. Molar mass calculations are vital for determining fertilizer composition and nutrient content.
-
Food Additives: Certain calcium phosphates are used as food additives (e.g., leavening agents). Molar mass information ensures accurate formulation and consistent product quality.
-
Water Treatment: Calcium phosphate can be used in water treatment to remove impurities. Precise molar mass calculations are necessary for optimizing treatment processes.
-
Cement Manufacturing: Some forms of calcium phosphate are used as a component in cement and related materials, and knowledge of molar mass is important for controlling the material’s properties.
3. Materials Science:
-
Ceramic Production: Calcium phosphate-based ceramics are used in various applications, from biomedical implants to high-temperature components. Knowing molar mass is important for predicting material properties and designing optimized materials.
-
Catalysis: Certain forms of calcium phosphate can act as catalysts in chemical reactions. Understanding molar mass helps in studying reaction kinetics and catalytic activity.
Beyond the Basics: Isotopes and Isotopic Abundance
The molar masses we've calculated are based on the average atomic masses of elements, taking into account the natural isotopic abundances. However, different isotopes of an element have slightly different masses. For high-precision work, it might be necessary to account for the specific isotopic composition of the calcium phosphate sample, leading to slight variations in the calculated molar mass.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Calculations
Determining the molar mass of calcium phosphate is a fundamental step in various scientific and industrial endeavors. While the approximate value of 310.18 g/mol for tricalcium phosphate is widely used, it's crucial to remember that the exact value may vary depending on the specific form of calcium phosphate and the level of precision required. Understanding the underlying principles of molar mass calculation and the different forms of calcium phosphate is essential for researchers, students, and professionals working in related fields. The accurate calculation of molar mass is a cornerstone for numerous applications, from understanding biological processes to developing innovative materials. This detailed analysis provides a strong foundation for anyone needing a deeper understanding of this important chemical compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Polynomial
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is Boiling Water A Physical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is A Webcam An Input Or Output Device
Mar 17, 2025
-
Word For A Person Who Uses Big Words
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 375 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molecular Mass Of Calcium Phosphate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
