What Is The Formula For Magnesium Carbonate
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
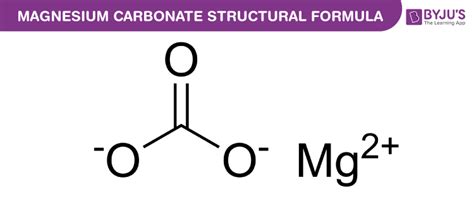
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Magnesium Carbonate? Exploring its Chemistry, Properties, and Applications
Magnesium carbonate is a naturally occurring mineral compound with a wide range of applications in various industries. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and uses is crucial for anyone working with this versatile substance. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of magnesium carbonate, covering everything from its basic chemical structure to its practical applications in diverse fields.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: MgCO₃
The chemical formula for magnesium carbonate is MgCO₃. This simple formula tells us that one molecule of magnesium carbonate is composed of one magnesium ion (Mg²⁺) and one carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻). The ionic bond between these two ions forms the stable magnesium carbonate compound. It's important to note that this is the formula for the anhydrous form, meaning it doesn't contain any water molecules. However, different hydrated forms exist, and we will explore those further below.
The Role of Ions in the Formula
The magnesium ion (Mg²⁺) carries a positive charge of two, while the carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻) carries a negative charge of two. The equal and opposite charges of these ions attract each other electrostatically, leading to the formation of a neutral compound. This ionic bonding is responsible for many of magnesium carbonate's physical and chemical properties.
Different Forms of Magnesium Carbonate: Hydrates and Variations
While MgCO₃ represents the basic formula, magnesium carbonate exists in several forms, primarily differing in their hydration levels:
1. Anhydrous Magnesium Carbonate (MgCO₃)
This is the pure, water-free form of magnesium carbonate. It's a white powder that is relatively insoluble in water. This anhydrous form is often the starting point for the production of other magnesium carbonate forms.
2. Hydrated Magnesium Carbonates:
Magnesium carbonate also forms hydrates, meaning it incorporates water molecules into its crystal structure. The most common hydrated form is magnesium carbonate trihydrate (MgCO₃·3H₂O), also known as nesquehonite. Other hydrates also exist, but are less common. These hydrated forms often exhibit slightly different properties compared to the anhydrous form.
3. Basic Magnesium Carbonates:
These are more complex forms where additional hydroxide ions (OH⁻) are incorporated into the crystal structure. A common example is hydromagnesite, a naturally occurring mineral with the formula Mg₅(CO₃)₄(OH)₂·4H₂O. These basic carbonates can have different stoichiometries and therefore slightly altered properties.
Key Properties of Magnesium Carbonate
Magnesium carbonate's properties make it suitable for numerous applications. These properties include:
- Appearance: Typically a white, odorless powder. Different forms might exhibit slight variations in texture and appearance.
- Solubility: Relatively insoluble in water but soluble in dilute acids. This property is crucial in many of its applications, allowing it to react and provide desired effects.
- Thermal Stability: Decomposes at high temperatures, releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂). This thermal decomposition is utilized in some industrial processes.
- Reactivity: Reacts with acids to produce magnesium salts, carbon dioxide, and water. This reaction is exothermic (releases heat).
- Alkalinity: It exhibits mild alkaline properties, impacting its pH in aqueous solutions.
- Hardness: While not exceptionally hard, it possesses sufficient hardness for many of its intended uses.
Diverse Applications of Magnesium Carbonate
The unique combination of properties exhibited by magnesium carbonate makes it valuable across a vast array of industries and applications:
1. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Antacid: Magnesium carbonate is a common ingredient in antacids, neutralizing stomach acid and relieving heartburn. Its mild alkaline nature makes it well-suited for this purpose.
- Laxative: Certain formulations utilize it as a mild laxative, promoting bowel movements.
- Tablet Binder: Its ability to bind ingredients together makes it useful in formulating tablets and capsules.
- Filler: It can also act as a filler or diluent in pharmaceutical preparations.
2. Industrial Applications:
- Fire Retardant: Magnesium carbonate's ability to release carbon dioxide upon heating makes it an effective fire retardant, particularly in plastics and other materials. The released CO₂ helps to displace oxygen, suppressing combustion.
- Insulator: Its thermal insulating properties are exploited in certain insulation materials.
- Catalyst: It can act as a catalyst or catalyst support in various chemical reactions.
- Rubber and Plastic Industry: Used as a filler and reinforcing agent in rubber and plastic production. This contributes to improved strength, processing properties, and cost reduction.
3. Food Industry:
- Food Additive: It serves as a food additive, often functioning as an anticaking agent or a stabilizer in certain processed foods. Its use is carefully regulated to ensure food safety.
- Nutritional Supplement: Magnesium carbonate is a source of magnesium, an essential mineral for human health. However, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before using it as a supplement.
4. Agriculture:
- Soil Conditioner: Magnesium carbonate can be applied to soil to improve its pH and magnesium content, thus enhancing plant growth.
- Animal Feed: It is sometimes incorporated into animal feed as a source of magnesium and to improve mineral balance.
5. Cosmetics and Personal Care:
- Toothpaste: Its mild abrasiveness and alkalinity can be found in some toothpaste formulations to help clean teeth and improve oral hygiene.
- Cosmetics: It acts as a filler and stabilizer in various cosmetic products.
Production and Sourcing of Magnesium Carbonate
Magnesium carbonate can be obtained through both natural mining and industrial synthesis:
- Natural Sources: Magnesium carbonate is mined as a naturally occurring mineral, such as magnesite. Magnesite is then purified and processed to obtain magnesium carbonate.
- Industrial Production: It can be synthesized through various chemical processes, often involving the reaction of magnesium oxide or hydroxide with carbon dioxide.
The selection of production method depends on factors like the desired purity, scale of production, and cost-effectiveness.
Safety Precautions and Handling
While generally considered safe in its intended applications, certain precautions should be observed:
- Inhalation: Avoid inhaling dust, as it can irritate the respiratory system. Proper ventilation is essential when handling magnesium carbonate powder.
- Eye Contact: Avoid contact with eyes, as it can cause irritation. Immediate flushing with water is recommended in case of contact.
- Ingestion: Accidental ingestion should be reported to a medical professional.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from moisture and incompatible materials.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of magnesium carbonate is generally low, but responsible sourcing and disposal practices are crucial:
- Sourcing: Minimizing the environmental impact of mining and processing is vital. Sustainable practices should be prioritized.
- Disposal: Disposal should follow local regulations and best practices to minimize environmental contamination.
Conclusion: A Versatile Mineral Compound
Magnesium carbonate, with its simple formula MgCO₃, belies its complex chemistry and diverse applications. From its role as a common antacid to its use as a fire retardant and even a food additive, this versatile compound plays a crucial role in numerous industries. Understanding its properties, production methods, and handling precautions is vital for its safe and effective utilization. Further research into its specific forms and interactions continues to unveil its potential for innovative applications in the future. This understanding is crucial for researchers, engineers, and anyone involved in the manufacture, application, and regulation of this important mineral compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Is Dictatorship Different From Democracy
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Describes An Image That A Plane Mirror Can Make
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Corners Does A Rectangular Pyramid Have
Apr 05, 2025
-
True Or False Every Real Number Is A Rational Number
Apr 05, 2025
-
Reaction Of Zinc With Sulphuric Acid
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Magnesium Carbonate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
