What Is The Conjugate Base Of H2so4
News Leon
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
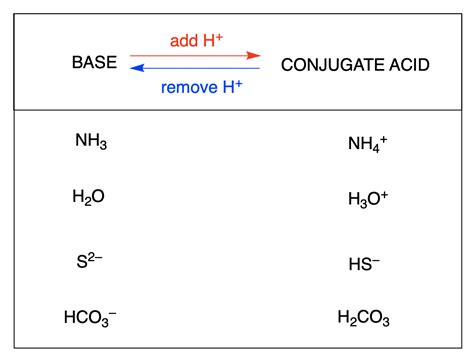
Table of Contents
What is the Conjugate Base of H₂SO₄? Understanding Acid-Base Chemistry
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), a strong diprotic acid, plays a crucial role in numerous industrial processes and chemical reactions. Understanding its behavior in acid-base reactions, particularly identifying its conjugate bases, is fundamental to comprehending its chemical properties and applications. This article delves into the concept of conjugate bases, focusing specifically on the conjugate bases of H₂SO₄, exploring their properties and significance.
Understanding Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Before diving into the specifics of sulfuric acid, let's establish a firm understanding of the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory. This theory defines an acid as a substance that donates a proton (H⁺), and a base as a substance that accepts a proton. Crucially, acid-base reactions involve the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base.
The key concept here is the conjugate acid-base pair. When an acid donates a proton, it forms its conjugate base. Conversely, when a base accepts a proton, it forms its conjugate acid. These pairs are related by the difference of a single proton.
For example, consider the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and water (H₂O):
HCl + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + Cl⁻
In this reaction:
- HCl is the acid (proton donor)
- H₂O is the base (proton acceptor)
- H₃O⁺ (hydronium ion) is the conjugate acid of H₂O
- Cl⁻ (chloride ion) is the conjugate base of HCl
The Conjugate Bases of H₂SO₄: A Step-by-Step Analysis
Sulfuric acid is a diprotic acid, meaning it can donate two protons. Therefore, it has two conjugate bases. Let's examine each step:
The First Dissociation and its Conjugate Base: Bisulfate Ion (HSO₄⁻)
The first dissociation of sulfuric acid in water is essentially complete:
H₂SO₄ + H₂O → H₃O⁺ + HSO₄⁻
In this step:
- H₂SO₄ acts as the acid, donating one proton.
- H₂O acts as the base, accepting the proton.
- HSO₄⁻ (bisulfate ion) is the conjugate base of H₂SO₄. It retains the ability to donate another proton, making it amphiprotic (can act as both an acid and a base).
Properties of the Bisulfate Ion (HSO₄⁻):
- Amphiprotic nature: As mentioned, HSO₄⁻ can act as both an acid and a base. It can donate a proton to a stronger base, or accept a proton from a stronger acid.
- Weak acidity: While a weaker acid than H₂SO₄, HSO₄⁻ still exhibits acidic properties in aqueous solutions. It undergoes a second dissociation (discussed below).
- Solubility: Bisulfate salts are generally soluble in water.
- Industrial applications: Bisulfate salts find applications in various industrial processes, including water treatment and metal processing.
The Second Dissociation and its Conjugate Base: Sulfate Ion (SO₄²⁻)
The second dissociation of HSO₄⁻ is significantly less complete than the first:
HSO₄⁻ + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + SO₄²⁻
In this step:
- HSO₄⁻ acts as the acid, donating its remaining proton.
- H₂O acts as the base, accepting the proton.
- SO₄²⁻ (sulfate ion) is the conjugate base of HSO₄⁻, and the second conjugate base of H₂SO₄. It is a much weaker base than HSO₄⁻.
Properties of the Sulfate Ion (SO₄²⁻):
- Weak basicity: SO₄²⁻ is a relatively weak base and does not readily accept protons in aqueous solutions.
- Solubility: Many sulfate salts are soluble in water, although some exceptions exist (e.g., barium sulfate).
- Abundance in nature: Sulfate ions are widely found in nature, occurring in minerals, groundwater, and seawater.
- Industrial applications: Sulfate salts are used extensively in various industries, including fertilizers, detergents, and pharmaceuticals.
Comparing the Two Conjugate Bases of H₂SO₄
It's crucial to understand the differences between the two conjugate bases of H₂SO₄:
| Feature | Bisulfate Ion (HSO₄⁻) | Sulfate Ion (SO₄²⁻) |
|---|---|---|
| Acidity/Basicity | Weak acid, Weak base (Amphiprotic) | Weak base |
| Charge | -1 | -2 |
| Reactivity | More reactive than SO₄²⁻ | Less reactive than HSO₄⁻ |
| Stability | Less stable than SO₄²⁻ | More stable than HSO₄⁻ |
Significance and Applications of H₂SO₄ Conjugate Bases
The conjugate bases of sulfuric acid, HSO₄⁻ and SO₄²⁻, are far from mere byproducts of acid-base reactions. They play crucial roles in numerous chemical and biological processes, and have important industrial applications.
1. Industrial Applications:
- Fertilizers: Sulfate salts are essential components of many fertilizers, providing sulfur, a vital nutrient for plant growth.
- Detergents: Sulfate-containing compounds are used as surfactants in detergents, aiding in cleaning and emulsifying.
- Water Treatment: Bisulfate ions can be used to adjust the pH of water, making it suitable for various purposes.
- Metal Processing: Bisulfate salts are used in the processing of various metals, acting as both cleaning agents and catalysts.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sulfate salts appear in some pharmaceutical formulations, playing different roles depending on the specific compound.
2. Biological Significance:
- Sulfur Metabolism: Sulfate ions are involved in various biological processes related to sulfur metabolism in plants and animals. They're incorporated into amino acids like cysteine and methionine.
- Enzyme Function: Sulfate groups can be found in several enzymes, affecting their catalytic activity.
Key Differences between Strong and Weak Conjugate Bases
The strength of a conjugate base is inversely related to the strength of its parent acid. Since H₂SO₄ is a strong acid (at least in its first dissociation), its conjugate base, HSO₄⁻, is a relatively weak base. The second dissociation, forming SO₄²⁻, is even weaker. This difference in strength significantly affects their reactivity and behavior in solutions. Strong conjugate bases readily accept protons, while weak conjugate bases do so only minimally.
Conclusion: Understanding the Chemistry of Sulfuric Acid and its Conjugate Bases
The conjugate bases of sulfuric acid, HSO₄⁻ and SO₄²⁻, are crucial in understanding the full chemical behavior of this ubiquitous acid. Their properties, differing reactivities, and numerous applications highlight their significance in chemistry, industry, and biology. By understanding the concept of conjugate acid-base pairs and the specific properties of these ions, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of acid-base chemistry and the role sulfuric acid plays in various processes. This knowledge is essential for anyone working in fields ranging from industrial chemistry and environmental science to biochemistry and materials science. The interplay between acid strength, conjugate base strength, and their respective properties provides a framework for deeper investigation into chemical reactions and their applications. Further research into the specific reactions and applications of HSO₄⁻ and SO₄²⁻ reveals a fascinating world of chemical diversity and functionality.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Organisms Can Fix Nitrogen
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Correct About Viruses
Apr 01, 2025
-
How To Find Density Of Air
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Disaccharides
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Carbon Are True
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Conjugate Base Of H2so4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
