What Energy Transformation Occurs In A Mototr
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
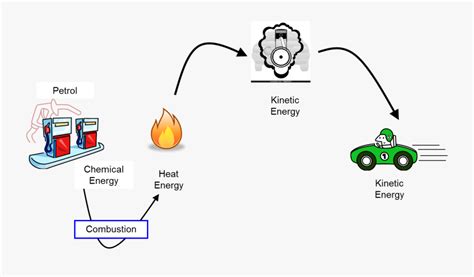
Table of Contents
What Energy Transformations Occur in a Motor? A Deep Dive into Efficiency and Mechanics
Electric motors are ubiquitous in modern life, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machinery. Understanding the energy transformations within these devices is crucial for appreciating their efficiency and optimizing their performance. This article delves into the intricate processes involved, explaining the various energy conversions and losses that occur within a typical motor.
From Electrical to Mechanical: The Core Transformation
At its heart, an electric motor performs a fundamental energy transformation: it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This process relies on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents. The specific mechanisms vary depending on the motor type (DC, AC induction, AC synchronous, etc.), but the underlying principle remains consistent.
The Role of Magnetic Fields
Electric motors employ electromagnets, which are created by passing an electric current through coils of wire. These coils, when energized, generate magnetic fields. The interaction of these magnetic fields with permanent magnets or other electromagnets within the motor creates a force that causes rotation.
Types of Motors and their Transformations
Let's examine the energy transformation in different types of motors:
1. DC Motors: In DC motors, a direct current flowing through the armature coil interacts with the magnetic field produced by permanent magnets or field coils. This interaction generates a torque, causing the rotor to rotate. The energy transformation here is straightforward: electrical energy (DC current) → magnetic field energy → mechanical rotational energy. However, losses due to friction, resistance, and eddy currents reduce the overall efficiency.
2. AC Induction Motors: These motors, the most common type, use a rotating magnetic field generated by the stator (stationary part) to induce currents in the rotor (rotating part). These induced currents create their own magnetic field in the rotor, which interacts with the stator's field, resulting in rotation. The energy transformation is more complex: electrical energy (AC current) → rotating magnetic field energy in stator → induced currents and magnetic field in rotor → mechanical rotational energy. Slip, which represents the difference between the stator field's speed and the rotor's speed, causes energy losses.
3. AC Synchronous Motors: These motors are characterized by the rotor's speed being synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply. The rotor contains permanent magnets or electromagnets that are excited by a separate DC source. The interaction between the stator's rotating magnetic field and the rotor's magnetic field produces rotation. The energy transformation: electrical energy (AC current in stator + DC current in rotor) → magnetic field energy (stator & rotor) → mechanical rotational energy. These motors generally have higher efficiency than induction motors at certain loads.
Energy Losses: Where Does the Energy Go?
While the core function of a motor is to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, several factors contribute to energy losses. Understanding these losses is crucial for improving motor efficiency.
1. Copper Losses (I²R Losses):**
These losses arise from the resistance of the motor windings (both stator and rotor). The heat generated due to the flow of current through these resistive elements is directly proportional to the square of the current (I²) and the resistance (R). Minimizing resistance through the use of high-conductivity materials helps reduce these losses.
2. Iron Losses (Core Losses):**
Iron losses, also known as core losses, occur in the motor's iron core. They are composed of two main components:
- Hysteresis Losses: These losses are due to the continuous magnetization and demagnetization of the iron core as the magnetic field changes. The energy required for this cyclical process is converted into heat.
- Eddy Current Losses: Eddy currents are circulating currents induced in the iron core by the changing magnetic field. These currents generate heat, thus representing a loss of energy. Using laminated cores helps mitigate eddy current losses by breaking up the current paths.
3. Mechanical Losses:**
Mechanical losses are associated with the moving parts of the motor. These include:
- Friction Losses: Friction between the rotating parts of the motor (bearings, brushes, etc.) generates heat and reduces efficiency. Using high-quality lubricants and minimizing contact surfaces helps reduce friction.
- Windage Losses: These losses occur due to air resistance against the rotating parts of the motor. Proper motor design and ventilation can help minimize windage losses.
4. Stray Load Losses:**
These are miscellaneous losses that are difficult to quantify precisely. They include losses due to harmonic currents, leakage flux, and other stray magnetic fields.
Efficiency and Power Factor: Key Metrics
Motor efficiency is a crucial parameter that reflects the effectiveness of the energy conversion process. It's defined as the ratio of the mechanical output power to the electrical input power:
Efficiency = (Mechanical Output Power) / (Electrical Input Power)
A higher efficiency indicates less energy loss and better performance.
Power factor is another important metric, particularly for AC motors. It represents the ratio of real power (used for actual work) to apparent power (total power drawn from the supply). A low power factor indicates a significant portion of the current is not contributing to useful work, leading to higher energy consumption and potential penalties from utility companies.
Optimizing Motor Performance and Efficiency
Several strategies can be employed to improve motor efficiency and reduce energy losses:
- Material Selection: Using high-conductivity materials for windings and low-loss materials for the core reduces copper and iron losses.
- Design Optimization: Advanced motor designs minimize air gaps, optimize magnetic circuits, and reduce friction.
- Cooling Systems: Effective cooling systems remove heat generated by losses, allowing the motor to operate at higher efficiency.
- Control Strategies: Sophisticated control systems optimize motor operation based on load conditions, reducing energy consumption.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including lubrication and cleaning, helps minimize mechanical losses and prolong motor life.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
The energy transformations within a motor are complex and depend on a variety of factors, including load, operating temperature, and motor design. Advanced analysis techniques such as finite element analysis (FEA) are used to model and optimize motor performance.
Furthermore, the development of new materials and control techniques is continually pushing the boundaries of motor efficiency. High-efficiency motors are crucial for reducing energy consumption and mitigating environmental impact across various sectors.
Conclusion
The energy transformation within an electric motor is a fascinating interplay of electrical and magnetic forces, ultimately converting electrical energy into the mechanical energy that powers countless applications. Understanding the core principles, energy losses, and efficiency metrics associated with these transformations is essential for engineers, designers, and anyone seeking to improve the performance and sustainability of electric motor systems. By focusing on material selection, design optimization, and efficient control strategies, we can continue to refine and improve the efficiency of these indispensable machines, contributing to a more energy-efficient future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Iodine Is Essential For The Synthesis Of
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is Osmosis High To Low Or Low To High
Mar 15, 2025
-
Concave Mirror And Convex Mirror Difference
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Cranial Bone Of The Skull
Mar 15, 2025
-
Mountain Range That Separates Europe And Asia
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Energy Transformation Occurs In A Mototr . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
