Mountain Range That Separates Europe And Asia
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
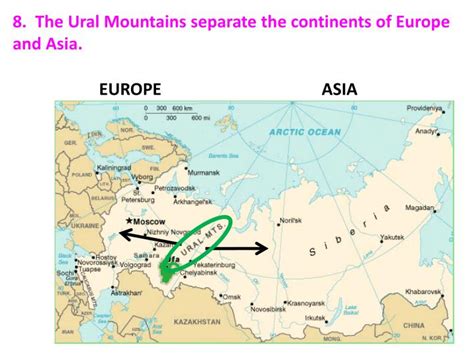
Table of Contents
- Mountain Range That Separates Europe And Asia
- Table of Contents
- The Ural Mountains: Dividing Europe and Asia, a Natural Boundary and More
- Geological Formation: A Collision of Tectonic Plates
- Ancient Origins and Gradual Uplift
- Diverse Rock Formations and Mineral Wealth
- Ecological Diversity: From Arctic Tundra to Steppe
- Unique Flora and Fauna
- Conservation Efforts and Challenges
- Historical Significance: A Crossroads of Cultures and Empires
- Early Human Habitation and Nomadic Cultures
- The Rise and Fall of Empires
- The Industrial Revolution and Beyond
- Cultural Impact: A Meeting Place of East and West
- Indigenous Cultures and Traditions
- Russian Influence and National Identity
- Modern Cultural Expressions
- The Ural Mountains Today: Challenges and Opportunities
- Sustainable Development Initiatives
- Tourism and Cultural Preservation
- The Enduring Legacy
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Ural Mountains: Dividing Europe and Asia, a Natural Boundary and More
The Ural Mountains, a seemingly unassuming range stretching over 1,500 miles (2,500 kilometers) from the Arctic Ocean to the vast Kazakh steppes, hold a unique position in geography and history. They are widely considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia, a distinction that's more nuanced than a simple line on a map. This article delves into the geological formation, ecological diversity, historical significance, and cultural impact of this remarkable mountain range, examining its role as both a physical and symbolic divider of two continents.
Geological Formation: A Collision of Tectonic Plates
The Ural Mountains aren't your typical towering, jagged peaks. Their formation, spanning over 300 million years, resulted from the collision of the East European Craton and the Siberian Craton, two ancient continental plates. This process, known as orogeny, involved immense pressure and folding of the Earth's crust, creating the long, relatively low-elevation range we see today.
Ancient Origins and Gradual Uplift
The mountains' origins trace back to the late Paleozoic Era. The collision, which started slowly, gradually intensified, leading to the uplift of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. This wasn't a single, dramatic event; instead, it was a complex series of movements and deformations spread over millions of years. The resulting Ural Mountains aren't uniformly high; they feature a series of parallel ridges and valleys, with peaks reaching up to nearly 6,200 feet (1,894 meters) above sea level, at Mount Narodnaya, the highest point.
Diverse Rock Formations and Mineral Wealth
The protracted formation process led to a diverse range of rock types within the Ural Mountains. You'll find igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, reflecting the various stages of tectonic activity. This geological diversity translates into a rich endowment of mineral resources. The Urals have historically been a significant source of platinum, gold, iron ore, copper, nickel, and various precious stones, playing a vital role in the industrial development of Russia and neighboring regions.
Ecological Diversity: From Arctic Tundra to Steppe
The Ural Mountains' extensive length and varied altitudes translate to a remarkable diversity of ecosystems. The northernmost reaches are characterized by Arctic tundra, a treeless landscape of mosses, lichens, and dwarf shrubs. Further south, the taiga, or boreal forest, dominates, characterized by dense coniferous forests of spruce, fir, and larch. As one moves further south, the taiga transitions into mixed forests and eventually steppe, a grassland ecosystem.
Unique Flora and Fauna
The Urals support a wide variety of flora and fauna, reflecting the gradient of ecosystems. Several endemic species, found nowhere else, inhabit the range. This includes various plants adapted to the harsh conditions of the tundra and specialized animal species adapted to the varied habitats. The Ural Mountains act as a corridor for migratory birds, providing crucial nesting and resting grounds. The range also plays a critical role in maintaining the genetic diversity of many species.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
The ecological significance of the Ural Mountains has led to the establishment of several national parks and reserves, aimed at protecting its unique biodiversity. However, the region faces several environmental challenges, including pollution from industrial activities, deforestation, and the impact of climate change. Balancing economic development with environmental conservation remains a key challenge for the region.
Historical Significance: A Crossroads of Cultures and Empires
The Ural Mountains have served as a crucial geographical feature throughout history, shaping human settlement, migration patterns, and political boundaries. For millennia, they acted as a natural barrier, influencing the movements of nomadic tribes and the expansion of empires.
Early Human Habitation and Nomadic Cultures
Evidence suggests human habitation in the Ural region dating back to the Paleolithic era. Nomadic groups, like the Scythians and the Samoyeds, inhabited the region for centuries, utilizing its resources and adapting to its challenging environment. The mountains provided protection, but also posed challenges to communication and trade.
The Rise and Fall of Empires
The Ural Mountains played a vital role in the expansion of the Russian Empire. Control over the mineral wealth of the region became strategically important, fueling industrialization and economic growth. The mountains themselves served as a natural defense against external threats, while the numerous rivers flowing through the region facilitated transportation and communication.
The Industrial Revolution and Beyond
The discovery and exploitation of mineral resources in the Urals spurred industrial growth. Cities and towns developed around mines and factories, leading to a significant demographic shift. The industrial revolution further intensified this development, transforming the region's economy and social structure. Today, the legacy of this industrialization remains visible in the region's landscape and its economy.
Cultural Impact: A Meeting Place of East and West
The Ural Mountains haven't just shaped the physical landscape; they have also profoundly influenced the cultural tapestry of the region. The range acts as a fascinating intersection of East and West, where diverse cultural influences intermingle.
Indigenous Cultures and Traditions
Several indigenous groups have historically called the Ural region home, each with unique traditions, languages, and lifestyles. Their culture reflects a close relationship with the natural environment, with traditional practices linked to hunting, fishing, and herding. The preservation and promotion of these indigenous cultures are essential for maintaining cultural diversity.
Russian Influence and National Identity
The Ural Mountains have played a crucial role in shaping Russian national identity. They are frequently depicted in Russian literature, art, and music, representing a symbol of strength, resilience, and the vastness of the Russian land. The region's mineral wealth and strategic importance further solidified its place in the national consciousness.
Modern Cultural Expressions
The unique blend of cultures and the dramatic landscape of the Ural Mountains continue to inspire contemporary artists, writers, and musicians. The region's rich history and diverse cultural heritage provide fertile ground for artistic expression. The mountains themselves remain a powerful symbol, evoking feelings of awe, wonder, and the vastness of nature.
The Ural Mountains Today: Challenges and Opportunities
The Ural Mountains face several contemporary challenges, including environmental degradation, economic disparities, and the need to balance development with conservation. However, the region also presents significant opportunities for sustainable development, tourism, and cultural preservation.
Sustainable Development Initiatives
Efforts are underway to promote sustainable development in the Ural region, aiming to reconcile economic growth with environmental protection. These include initiatives focusing on responsible resource management, eco-tourism, and the promotion of renewable energy sources.
Tourism and Cultural Preservation
The Ural Mountains are increasingly recognized as a destination for eco-tourism. The region's diverse ecosystems, unique flora and fauna, and rich cultural heritage attract visitors from around the world. The development of sustainable tourism practices is vital to protect the region's natural and cultural assets.
The Enduring Legacy
The Ural Mountains stand as a testament to the power of geological processes, the resilience of nature, and the enduring influence of geographical features on human societies. Their role as a symbolic boundary between Europe and Asia adds to their historical and cultural significance. Preserving this unique landscape and its rich cultural heritage for future generations remains a critical challenge and a vital goal. The ongoing efforts to protect its biodiversity, promote sustainable development, and celebrate its rich cultural legacy ensure that the Ural Mountains will continue to hold their place as a remarkable and significant feature of the Earth's landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Aqua Regia Is A Mixture Of
Mar 18, 2025
-
Literary Devices In The Road Not Taken
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Seconds Are In 2 5 Hours
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Chamber Of The Heart Has The Thickest Walls
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Most Abundant Molecule In A Cell Is
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mountain Range That Separates Europe And Asia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
