The Study Of The Cells Is Called
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
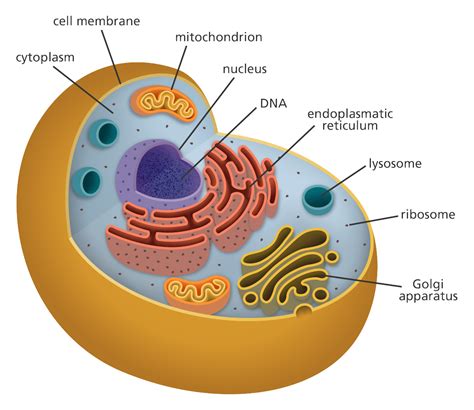
Table of Contents
- The Study Of The Cells Is Called
- Table of Contents
- The Study of Cells is Called Cytology: A Deep Dive into the Microscopic World
- A Brief History of Cytology: From Discovery to Modern Techniques
- Key Techniques in Cytology: Unraveling Cellular Secrets
- 1. Microscopy: Visualizing the Invisible
- 2. Cell Culture: Studying Cells in a Controlled Environment
- 3. Cell Fractionation: Separating Cellular Components
- 4. Molecular Biology Techniques: Unraveling Cellular Processes at the Molecular Level
- 5. Immunocytochemistry and Immunofluorescence: Visualizing Specific Cellular Components
- Significant Discoveries in Cytology: Shaping Our Understanding of Life
- Applications of Cytology: A Multidisciplinary Field
- The Future of Cytology: Emerging Technologies and Research Directions
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Study of Cells is Called Cytology: A Deep Dive into the Microscopic World
The study of cells is called cytology, a fascinating branch of biology that delves into the intricate structures, functions, and life cycles of these fundamental building blocks of life. From the smallest bacteria to the complex neurons in the human brain, cells are the microscopic powerhouses driving all biological processes. This comprehensive guide will explore the multifaceted world of cytology, covering its history, key techniques, significant discoveries, and its crucial role in various fields of science and medicine.
A Brief History of Cytology: From Discovery to Modern Techniques
The journey of cytology begins with the invention of the microscope. While rudimentary magnifying lenses existed earlier, the crucial development came in the 17th century with the advancements made by scientists like Robert Hooke. In his groundbreaking work, Micrographia (1665), Hooke coined the term "cell" after observing the honeycomb-like structure of cork under his microscope. This marked the dawn of cellular observation.
However, Hooke's observations were limited by the technology of his time. The true understanding of cells as the fundamental units of life emerged later, thanks to the contributions of Anton van Leeuwenhoek, who meticulously documented his observations of single-celled organisms, bacteria, and even human blood cells using his superior microscopes.
The 19th century witnessed a surge in cytological advancements. The development of the cell theory, a cornerstone of modern biology, is attributed to the collective efforts of Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. This theory postulates that:
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
- Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
This solidified the central role of cells in biology and laid the foundation for future cytological investigations. Further refinements to microscopic techniques, such as the invention of the electron microscope in the 20th century, allowed for unprecedented visualization of cellular structures at the subcellular level, revealing intricate details previously unimaginable.
Key Techniques in Cytology: Unraveling Cellular Secrets
Modern cytology employs a diverse range of sophisticated techniques to study cells. These methods allow researchers to visualize, manipulate, and analyze cells in detail, revealing crucial information about their structure, function, and behavior. Some of the most prominent techniques include:
1. Microscopy: Visualizing the Invisible
Microscopy remains the cornerstone of cytology. Different types of microscopes offer unique advantages:
-
Light Microscopy: Provides high-resolution images of stained cells, allowing for the observation of cellular components like the nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles. Techniques like brightfield, darkfield, phase-contrast, and fluorescence microscopy offer various ways to enhance contrast and visualize specific structures.
-
Electron Microscopy: Utilizes beams of electrons to achieve significantly higher resolution than light microscopy, revealing ultrastructural details of cellular organelles and macromolecules. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) allows visualization of internal cellular structures, while scanning electron microscopy (SEM) provides detailed images of the cell surface.
-
Confocal Microscopy: Uses lasers to scan specimens, providing high-resolution, three-dimensional images by eliminating out-of-focus light. This is particularly useful for visualizing complex cellular structures and processes.
2. Cell Culture: Studying Cells in a Controlled Environment
Cell culture techniques allow scientists to grow and maintain cells in vitro (outside a living organism). This provides a controlled environment for studying cell behavior, growth, and response to various stimuli. Cell cultures are crucial for research in areas like drug discovery, cancer biology, and regenerative medicine.
3. Cell Fractionation: Separating Cellular Components
Cell fractionation techniques involve separating different cellular components based on their size, density, and other properties. This allows researchers to isolate specific organelles or macromolecules for further analysis, providing valuable insights into their individual functions. Techniques like centrifugation are commonly used for cell fractionation.
4. Molecular Biology Techniques: Unraveling Cellular Processes at the Molecular Level
A wide array of molecular biology techniques is employed to study cellular processes at the molecular level. These include:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): Amplifies specific DNA sequences, allowing for the analysis of gene expression and genetic mutations.
-
DNA Sequencing: Determines the precise order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule, providing crucial information about genetic information and mutations.
-
Flow Cytometry: Allows for the identification and sorting of cells based on their physical and chemical properties, enabling the analysis of cell populations and their heterogeneity.
5. Immunocytochemistry and Immunofluorescence: Visualizing Specific Cellular Components
These techniques use antibodies to specifically label and visualize particular proteins or other molecules within cells. This provides valuable insights into the location and distribution of specific molecules, allowing researchers to study cellular processes and interactions.
Significant Discoveries in Cytology: Shaping Our Understanding of Life
Cytology has been instrumental in numerous groundbreaking discoveries that have revolutionized our understanding of life. Some of the most significant achievements include:
-
The discovery of DNA's structure: The elucidation of the double helix structure of DNA by James Watson and Francis Crick (with crucial contributions from Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins) is a landmark achievement in biology, directly impacting our understanding of how genetic information is stored and transmitted within cells.
-
Understanding cell signaling pathways: The unraveling of complex cell signaling pathways has revealed how cells communicate with each other and respond to their environment. This knowledge is crucial for understanding various biological processes, including development, immunity, and disease.
-
Advances in cancer research: Cytology has played a pivotal role in cancer research, providing tools for early diagnosis, understanding cancer cell behavior, and developing targeted therapies. Techniques like Pap smears and biopsies are crucial diagnostic tools in cancer detection.
-
Stem cell research: Cytology is at the forefront of stem cell research, investigating the properties and potential therapeutic applications of stem cells. Understanding stem cell differentiation and manipulation is crucial for regenerative medicine.
Applications of Cytology: A Multidisciplinary Field
Cytology is not confined to a single discipline; its applications span a wide range of scientific and medical fields:
-
Medicine: Cytology plays a crucial role in disease diagnosis, particularly in cancer detection (Pap smears, biopsies) and infectious disease identification.
-
Pharmacology and Drug Discovery: Cell cultures are extensively used to screen potential drug candidates and study their effects on cells.
-
Genetics and Genomics: Cytological techniques are essential for studying genetic material, gene expression, and genetic mutations.
-
Developmental Biology: Cytology provides crucial insights into embryonic development, cell differentiation, and tissue formation.
-
Immunology: Cytological techniques are used to study the immune system's cells, their interactions, and their responses to pathogens.
-
Environmental Science: Cytology can be applied to study the effects of environmental pollutants on cells and organisms.
The Future of Cytology: Emerging Technologies and Research Directions
Cytology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, driven by technological advancements and new research questions. Emerging technologies are pushing the boundaries of what we can learn about cells:
-
Advanced Microscopy Techniques: Super-resolution microscopy, light-sheet microscopy, and other advanced techniques are providing ever-increasing resolution and detail in cellular imaging.
-
Single-Cell Genomics: This field allows researchers to analyze the genomes of individual cells, revealing cellular heterogeneity and providing valuable insights into cell populations.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cytology: AI algorithms are being applied to analyze large datasets generated by cytological techniques, automating data analysis and accelerating scientific discovery.
The study of cells, cytology, is an ever-evolving field with profound implications for our understanding of life and its processes. From its historical roots in simple observations to its current state at the cutting edge of scientific technology, cytology remains a cornerstone of modern biological research, impacting various fields and driving innovations that shape the future of medicine, biotechnology, and our understanding of the natural world. Its continued development holds immense potential for addressing some of humanity's most pressing challenges, from disease to environmental protection.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Where Is The Olecranon Process Found
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Joints Between Cranial Bones Of The Skull Are Called
Mar 19, 2025
-
2000 Mg Is Equal To How Many Grams
Mar 19, 2025
-
Water Boiling Is A Physical Change
Mar 19, 2025
-
Birds And Mammals Share Which Characteristic
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Study Of The Cells Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
