The Patellar Reflex Is A Type Of __________.
News Leon
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
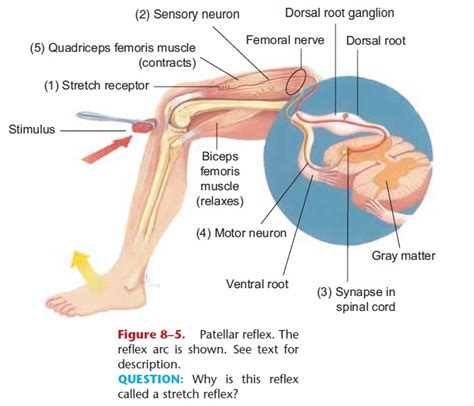
Table of Contents
The Patellar Reflex is a Type of Stretch Reflex
The patellar reflex, also known as the knee-jerk reflex, is a classic example of a stretch reflex. This seemingly simple reflex arc, elicited by a tap just below the kneecap, provides valuable insights into the intricacies of the nervous system and its ability to maintain posture and coordinate movement. Understanding the patellar reflex requires exploring the components of the reflex arc, its neurological pathways, and its clinical significance. This article will delve into these aspects, clarifying the patellar reflex's classification and its importance in neurological assessment.
Understanding the Reflex Arc
Before diving into the specifics of the patellar reflex, let's establish a foundational understanding of the reflex arc. A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex action. It's a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus, bypassing the brain's conscious processing for speed and efficiency. A typical reflex arc consists of five key components:
1. Receptor:
The receptor is the specialized sensory nerve ending that detects the stimulus. In the patellar reflex, the receptor is a muscle spindle located within the quadriceps femoris muscle. Muscle spindles are sensory organs that detect changes in muscle length and rate of change. They are exquisitely sensitive to stretching.
2. Sensory Neuron:
The sensory neuron (also known as an afferent neuron) transmits the sensory information from the receptor to the central nervous system (CNS). The sensory neuron's axon carries the signal from the muscle spindle to the spinal cord.
3. Integration Center:
The integration center is the location within the CNS where the sensory information is processed. In the patellar reflex, the integration center is the spinal cord. Specifically, the signal synapses with motor neurons in the grey matter of the spinal cord. Importantly, there's minimal synaptic delay in this monosynaptic reflex, contributing to its speed.
4. Motor Neuron:
The motor neuron (also known as an efferent neuron) transmits the signal from the CNS to the effector. In the patellar reflex, the motor neuron innervates the quadriceps femoris muscle.
5. Effector:
The effector is the muscle or gland that responds to the signal. In the patellar reflex, the effector is the quadriceps femoris muscle, which contracts in response to the stimulus. This contraction causes the leg to extend.
The Patellar Reflex: A Detailed Look
The patellar reflex beautifully illustrates the principles of the reflex arc. The process unfolds as follows:
-
Stimulus: A sharp tap on the patellar tendon just below the kneecap stretches the quadriceps muscle.
-
Receptor Activation: The stretching of the quadriceps muscle stimulates the muscle spindles within the muscle. These spindles detect the change in muscle length and the rate of that change.
-
Sensory Neuron Activation: The activated muscle spindles generate nerve impulses that travel along the sensory neuron's axon to the spinal cord.
-
Synapse in the Spinal Cord: The sensory neuron synapses directly with a motor neuron in the spinal cord. This is a monosynaptic reflex, meaning there's only one synapse involved. This direct connection contributes to the reflex's speed.
-
Motor Neuron Activation: The motor neuron receives the signal and transmits it to the quadriceps muscle.
-
Effector Response: The quadriceps muscle contracts, causing the lower leg to extend – the characteristic "knee-jerk" response.
Simultaneously, a second, polysynaptic reflex occurs. This involves an inhibitory interneuron that inhibits the hamstring muscles (antagonistic muscles to the quadriceps). This reciprocal inhibition ensures that the hamstrings relax, allowing for unimpeded extension of the leg. The coordinated contraction of the quadriceps and relaxation of the hamstrings are essential for the smooth and efficient execution of the patellar reflex.
Why is it a Stretch Reflex?
The patellar reflex is classified as a stretch reflex because it's initiated by the stretching of a muscle. The muscle spindle, the key receptor in this reflex, is highly sensitive to changes in muscle length. When the muscle is stretched, the muscle spindle is activated, initiating the reflex arc and ultimately leading to muscle contraction. This reflex helps maintain muscle tone and posture by responding to unexpected changes in muscle length. It's a crucial mechanism for stabilizing our body against external forces. Think of maintaining balance – the stretch reflex is constantly making tiny adjustments to keep you upright.
Clinical Significance of the Patellar Reflex
The patellar reflex is a cornerstone of neurological examinations. Assessing the presence, strength, and symmetry of the reflex provides valuable information about the integrity of the nervous system. Abnormal findings may indicate damage to the nervous system at various levels:
-
Hyperreflexia: Exaggerated or overly brisk reflex response suggests upper motor neuron lesions. This could be caused by conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries.
-
Hyporeflexia: Diminished or absent reflex response indicates lower motor neuron lesions. Possible causes include peripheral nerve damage, muscle diseases, or certain types of neuromuscular junction disorders.
-
Asymmetry: Differences in reflex response between the two legs may point towards a lesion affecting one side of the nervous system.
-
Clonus: A series of involuntary muscle contractions following a single tap on the tendon. This is a sign of hyperreflexia and often indicative of serious neurological conditions.
The patellar reflex, therefore, is not just a simple knee-jerk; it's a window into the health and function of the nervous system. The careful evaluation of this reflex plays a vital role in diagnosing a wide range of neurological disorders.
Beyond the Knee: Other Stretch Reflexes
While the patellar reflex is a well-known example, the stretch reflex mechanism isn't limited to the knee. Similar reflexes occur in other parts of the body:
-
Biceps reflex: This reflex is elicited by tapping the biceps tendon, causing contraction of the biceps brachii muscle.
-
Triceps reflex: Tapping the triceps tendon elicits contraction of the triceps brachii muscle.
-
Achilles reflex (ankle jerk): This reflex is elicited by tapping the Achilles tendon, causing plantar flexion of the foot.
All these reflexes are examples of stretch reflexes, sharing the fundamental mechanism of muscle spindle activation in response to muscle stretching. The principles underlying the patellar reflex apply to these other stretch reflexes as well.
Factors Affecting the Patellar Reflex
Several factors can influence the strength and speed of the patellar reflex response:
-
Muscle fatigue: Fatigue can reduce the responsiveness of the reflex.
-
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect nerve conduction velocity, impacting the reflex.
-
Mental state: A patient's level of anxiety or relaxation can influence the reflex response. Stress can sometimes exaggerate the reflex.
-
Medication: Certain medications, such as sedatives or muscle relaxants, can depress the reflex.
Clinicians are aware of these factors and take them into account when assessing the patellar reflex. A proper neurological examination requires considering various aspects and potential confounding factors to arrive at an accurate interpretation.
The Patellar Reflex: A Complex Simplicity
In conclusion, the patellar reflex is a fascinating example of a stretch reflex. Its seemingly simple mechanism belies a complex interplay of sensory and motor neurons within the nervous system. Its importance extends far beyond a simple "knee-jerk" response; it's a critical tool for neurological assessment, offering valuable insights into the health and function of the nervous system. Understanding the patellar reflex provides a fundamental understanding of basic neurological principles and their clinical applications. The monosynaptic pathway, the reciprocal inhibition, and the clinical significance associated with deviations from the norm all contribute to its significance in both physiology and clinical practice. By studying this seemingly simple reflex, we gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and complexity of the human body.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Diagonals In An Octagon
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Ratio Of Purple Flowers To White Flowers
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Inches In Cubic Foot
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Person Who Study History Is Called
Mar 31, 2025
-
Is Calcium Oxide Ionic Or Covalent
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Patellar Reflex Is A Type Of __________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
