What Is The Ratio Of Purple Flowers To White Flowers
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
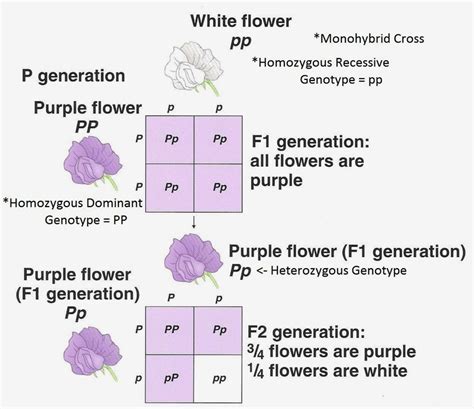
Table of Contents
What's the Ratio of Purple Flowers to White Flowers? A Deep Dive into Flower Genetics and Population Dynamics
The seemingly simple question, "What's the ratio of purple flowers to white flowers?" opens a fascinating window into the complex world of genetics, population dynamics, and environmental influences. There isn't a single, universally applicable answer. The ratio is highly dependent on several factors, including the specific plant species, its genetic makeup, environmental conditions, and the selective pressures at play. This article will delve into the intricacies of flower color inheritance, exploring the various mechanisms influencing the purple-to-white flower ratio in a population.
Understanding Flower Color Genetics: The Role of Pigments
Flower color is primarily determined by the presence and concentration of pigments, with anthocyanins being the most crucial for purple hues. These pigments are produced through a series of complex biochemical reactions governed by multiple genes. The absence or deficiency of anthocyanins typically results in white flowers. This isn't simply a case of a single gene controlling color; it’s often a multifaceted interplay of many genes, each influencing different steps in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway.
The Inheritance of Flower Color: Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Patterns
While Mendelian inheritance, characterized by simple dominant and recessive alleles, provides a fundamental framework, flower color inheritance often exhibits complexities beyond this simple model.
-
Simple Mendelian Inheritance: In some cases, a single gene with two alleles (one for purple, one for white) might dictate flower color. If purple (P) is dominant over white (p), a homozygous purple (PP) plant will have purple flowers, a heterozygous plant (Pp) will also have purple flowers (due to dominance), and only a homozygous recessive plant (pp) will display white flowers. In this scenario, a cross between two heterozygous plants (Pp x Pp) would yield a 3:1 ratio of purple to white flowers (PP, Pp, Pp, pp).
-
Incomplete Dominance: Here, neither allele is completely dominant. A heterozygote displays an intermediate phenotype. For instance, a cross between a homozygous purple and a homozygous white might result in pink flowers in the heterozygote. The ratio would depend on the specific cross.
-
Codominance: Both alleles are expressed equally in the heterozygote. Imagine a situation where a red allele and a blue allele, when combined, result in purple flowers. Specific ratios again depend on the cross.
-
Polygenic Inheritance: Many genes can contribute to flower color. Each gene might have a small additive effect on the final pigment concentration, leading to a range of color variations from deep purple to light purple to white. This significantly complicates the prediction of ratios, often leading to continuous variation rather than distinct classes.
-
Environmental Influences: Environmental factors, such as temperature, sunlight exposure, soil pH, and nutrient availability, can significantly alter anthocyanin production and consequently influence the expression of flower color genes. This environmental plasticity makes predicting exact ratios even more challenging.
Factors Influencing the Purple-to-White Ratio in Natural Populations
Beyond the genetics of individual plants, various ecological factors heavily impact the observed purple-to-white flower ratio in natural populations:
Pollinator Preferences
Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, often display preferences for specific flower colors. If purple flowers attract more pollinators, they might have a higher reproductive success, leading to a skewed ratio in favor of purple flowers over time. This is a prime example of natural selection.
Competition and Resource Availability
Plants compete for resources like sunlight, water, and nutrients. The availability of these resources can influence the intensity of pigment production, potentially affecting the observed flower color and the overall purple-to-white ratio.
Genetic Drift and Founder Effects
In smaller populations, random fluctuations in allele frequencies can lead to significant changes in the purple-to-white ratio. Genetic drift, the random sampling of alleles from one generation to the next, can cause certain alleles to become more or less common, even in the absence of selective pressure. Similarly, a founder effect, where a new population is established by a small group of individuals, can result in a skewed allele frequency distribution compared to the original population.
Mutation and Gene Flow
Mutations can introduce new alleles into a population, potentially altering the balance between purple and white flower colors. Gene flow, the movement of alleles between populations, can also influence the overall ratio by introducing new genetic variation.
Natural Selection and Adaptive Significance
In some cases, flower color might be directly related to survival and reproduction. For example, if white flowers provide better camouflage against predators or attract different pollinators in specific environments, they might be favored by natural selection, leading to a higher proportion of white flowers. Conversely, if purple flowers are more effective at attracting pollinators in certain habitats, the ratio might shift in favor of purple.
Investigating the Ratio: Observational Studies and Experimental Approaches
Determining the actual purple-to-white flower ratio in a specific population requires careful observation and potentially experimental approaches:
Field Surveys and Data Collection
Researchers can conduct field surveys to count the number of purple and white flowers in a defined area. This method provides a snapshot of the ratio in a specific location at a particular time. It's crucial to consider sampling bias and the potential for variations across different locations and times.
Controlled Experiments: Cultivating and Crossing Plants
Controlled experiments can help to disentangle the effects of different genes and environmental factors. Researchers can cultivate plants with known genotypes, subject them to various environmental conditions, and then analyze the resulting flower color ratios. These experiments can provide valuable insights into the genetic basis of flower color and the environmental influences on its expression.
Statistical Analysis and Data Interpretation
The collected data requires statistical analysis to determine if the observed ratio differs significantly from the expected ratio based on genetic models. Statistical tests can help to assess the impact of different factors on the flower color distribution.
Conclusion: The Dynamic Nature of Flower Color Ratios
The ratio of purple flowers to white flowers in a population is not a static figure. It’s a dynamic quantity constantly shaped by a complex interplay of genetics, environmental factors, and evolutionary pressures. Understanding these interactions requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining knowledge from genetics, ecology, and statistics. By studying these factors, we can gain a deeper understanding of the processes that drive the diversity of life on Earth. Further research, including genomic sequencing and advanced statistical modeling, is essential to fully unravel the intricate mechanisms determining flower color and the ever-changing ratios we observe in the natural world. This complex topic continues to fascinate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike, providing endless avenues for investigation and discovery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Value Of Log Subscript 27 Baseline 9
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes In Liver Cells
Apr 01, 2025
-
All Of The Following Refer To Mitosis Except
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Temperatures Is The Coldest
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Short Term Unsecured Promissory Note Issued By A Company Is
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Ratio Of Purple Flowers To White Flowers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
