The Number Of Protons Is Also Called The
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 7 min read
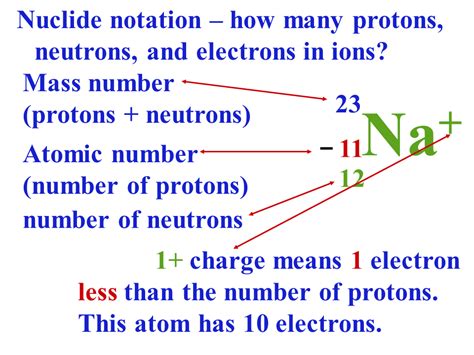
Table of Contents
- The Number Of Protons Is Also Called The
- Table of Contents
- The Number of Protons is Also Called the Atomic Number: A Deep Dive into the Heart of Matter
- Understanding the Atom: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- The Atomic Number: The Defining Characteristic of an Element
- The Periodic Table and Atomic Number
- Isotopes and Atomic Number
- The Significance of the Atomic Number in Chemistry and Physics
- 1. Chemical Reactions and Bonding:
- 2. Predicting Chemical Properties:
- 3. Nuclear Reactions:
- 4. Spectroscopic Analysis:
- 5. Radioactive Decay:
- Beyond the Basics: Deeper Implications of Atomic Number
- 1. Nuclear Chemistry and Physics:
- 2. Astrophysics and Cosmology:
- 3. Materials Science:
- 4. Medical Applications:
- Conclusion: The Foundation of Chemistry and Physics
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Number of Protons is Also Called the Atomic Number: A Deep Dive into the Heart of Matter
The fundamental building blocks of matter, atoms, are incredibly complex entities. Understanding their structure is crucial to comprehending the properties of everything around us, from the air we breathe to the stars in the sky. A key characteristic defining an atom, and indeed its very identity, is the number of protons within its nucleus. This number is also called the atomic number. This seemingly simple concept underpins much of chemistry and physics, providing a framework for understanding the periodic table, chemical reactions, and the behavior of matter under various conditions.
Understanding the Atom: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before delving into the significance of the atomic number, let's briefly recap the structure of an atom. Atoms consist of three fundamental particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles residing within the atom's nucleus.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also found in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels.
The nucleus, the atom's dense central core, contains both protons and neutrons. The electrons, much lighter than protons and neutrons, occupy the space surrounding the nucleus. The attractive force between the positively charged protons and the negatively charged electrons holds the atom together.
The Atomic Number: The Defining Characteristic of an Element
The atomic number, also known as the proton number, is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. This number is unique to each element and is the defining characteristic that distinguishes one element from another. For example:
- Hydrogen (H): Atomic number 1 (1 proton)
- Helium (He): Atomic number 2 (2 protons)
- Carbon (C): Atomic number 6 (6 protons)
- Oxygen (O): Atomic number 8 (8 protons)
- Gold (Au): Atomic number 79 (79 protons)
The atomic number is represented by the symbol 'Z'. Thus, we can write Z = 1 for hydrogen, Z = 6 for carbon, and so on. It's a fundamental concept in chemistry and is used extensively in the periodic table of elements.
The Periodic Table and Atomic Number
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic numbers and recurring chemical properties. Elements are arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups) according to their electronic configurations, which are directly related to the number of protons in their nuclei. Elements within the same group share similar chemical properties due to the similarities in their outer electron shell configurations.
The periodic table's arrangement reflects the underlying principles of atomic structure. As you move across a period from left to right, the atomic number increases by one with each element, indicating the addition of one proton to the nucleus. This increase in protons leads to a change in the number of electrons, influencing the element's chemical behavior.
Isotopes and Atomic Number
While the atomic number defines an element, it's important to understand the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same atomic number) that have different numbers of neutrons. This means they have the same number of protons but varying numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon-12 (¹²C), carbon-13 (¹³C), and carbon-14 (¹⁴C) are all isotopes of carbon. They all have 6 protons (atomic number 6), but they have 6, 7, and 8 neutrons, respectively.
Despite having different numbers of neutrons, isotopes of the same element exhibit similar chemical behavior because they possess the same number of electrons and thus the same electronic configuration in their outermost shell. However, they may differ in their physical properties, such as mass and radioactive decay characteristics.
The Significance of the Atomic Number in Chemistry and Physics
The atomic number plays a pivotal role in various aspects of chemistry and physics:
1. Chemical Reactions and Bonding:
The atomic number determines the number of electrons an atom possesses. The arrangement of electrons in energy levels, particularly the valence electrons (outermost electrons), dictates how an atom will interact with other atoms. Valence electrons are directly involved in chemical bonding, determining the type of bond (ionic, covalent, metallic) formed between atoms and, therefore, the properties of the resulting molecules or compounds.
2. Predicting Chemical Properties:
By knowing an element's atomic number, we can predict its chemical properties with a high degree of accuracy. The periodic table is a testament to this; elements in the same group (vertical column) exhibit similar chemical behaviors because they have the same number of valence electrons.
3. Nuclear Reactions:
The atomic number is crucial in understanding nuclear reactions. Nuclear reactions involve changes in the nucleus of an atom, typically involving changes in the number of protons and neutrons. Nuclear fission, for example, involves the splitting of a heavy atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei, resulting in a change in atomic number. Nuclear fusion, conversely, involves the combination of light atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, also leading to a change in atomic number.
4. Spectroscopic Analysis:
Each element emits a unique spectrum of light when excited. This unique spectral fingerprint is directly related to the element's atomic number and electronic configuration. Spectroscopic analysis uses this characteristic to identify the elements present in a sample, a technique crucial in various fields, including astronomy, environmental science, and forensic science.
5. Radioactive Decay:
Certain isotopes are radioactive, meaning their nuclei are unstable and undergo spontaneous decay. This decay process often involves changes in the atomic number, as a radioactive nucleus might emit alpha particles (two protons and two neutrons), beta particles (electrons or positrons), or gamma rays. The rate of decay is characterized by the element's half-life, which depends on the specific isotope and its nuclear structure.
Beyond the Basics: Deeper Implications of Atomic Number
The significance of the atomic number extends beyond basic chemistry and physics. It plays a vital role in various advanced scientific fields:
1. Nuclear Chemistry and Physics:
Nuclear chemistry and physics heavily rely on the atomic number to understand and predict the behavior of radioactive isotopes, nuclear reactions, and the stability of atomic nuclei. The atomic number, along with the neutron number, determines the nuclide’s stability and its decay pathway.
2. Astrophysics and Cosmology:
In astrophysics and cosmology, the atomic number is used to study the composition of stars and other celestial bodies. Spectral analysis of starlight allows astronomers to determine the elemental composition of stars, providing valuable insights into stellar evolution and the formation of galaxies. The abundance of certain elements in the universe is directly related to their nuclear properties, influenced by the number of protons in their nuclei.
3. Materials Science:
In materials science, the atomic number helps to predict the physical and chemical properties of materials, influencing their suitability for various applications. The properties of a material depend heavily on the bonding and interactions between its constituent atoms, which are determined by their electronic configurations and therefore their atomic numbers.
4. Medical Applications:
The concept of atomic number is crucial in several medical applications. Radioactive isotopes, identified by their atomic number and mass number, are used in medical imaging techniques like PET (positron emission tomography) and SPECT (single-photon emission computed tomography) scans. These isotopes allow doctors to visualize internal organs and detect diseases. Furthermore, radiation therapy, used to treat cancer, utilizes radioactive isotopes with specific atomic numbers and decay properties.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Chemistry and Physics
The number of protons, also known as the atomic number, is a fundamental property of an atom, acting as its unique identifier. This seemingly simple number underlies much of our understanding of chemistry and physics, influencing chemical reactions, nuclear processes, and the properties of matter at all levels. From the intricate workings of the periodic table to the vast expanse of the universe, the atomic number remains a cornerstone of our understanding of the physical world. Its importance permeates numerous scientific disciplines, emphasizing its central role in the study of matter and its behavior. Further research and exploration into atomic structure and nuclear physics continue to unravel deeper insights into the nature of matter and its fundamental components, continually refining our understanding of this crucial concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Bonds Is The Most Polar
Apr 04, 2025
-
Is A Cheek Cell Eukaryotic Or Prokaryotic
Apr 04, 2025
-
Attraction Among Molecules Of The Same Type Is Called
Apr 04, 2025
-
In The Structure Of 4 Isopropyl 2 4 5 Trimethylheptane
Apr 04, 2025
-
Is Water Or Ethanol More Polar
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Number Of Protons Is Also Called The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
