The Number Of Protons In An Atom Is Called
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
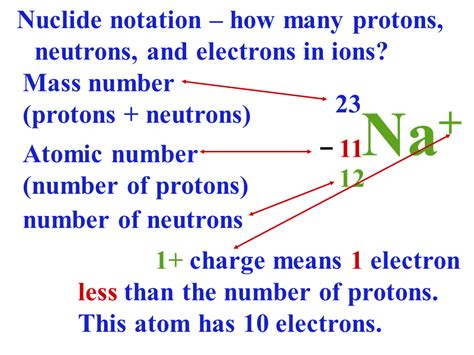
Table of Contents
The Number of Protons in an Atom is Called the Atomic Number: A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is a fundamental characteristic that defines the element itself. This number is known as the atomic number. Understanding the atomic number is crucial to grasping the basics of chemistry and physics, as it dictates an element's properties, its position on the periodic table, and its interactions with other atoms. This comprehensive article will explore the significance of the atomic number, its relationship to other atomic properties, and its role in various scientific fields.
What is the Atomic Number?
The atomic number, represented by the symbol Z, is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. It's a whole number, meaning it can't be a fraction. Each element has a unique atomic number, which distinguishes it from all other elements. For instance, hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1, meaning it possesses one proton. Helium (He) has an atomic number of 2, indicating two protons. The heaviest naturally occurring element, uranium (U), has an atomic number of 92, signifying 92 protons in its nucleus.
The Uniqueness of Atomic Number
The atomic number is so crucial because it uniquely identifies an element. No two elements share the same atomic number. This is the fundamental principle underpinning the organization of the periodic table of elements. Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, reflecting their increasing proton count. This arrangement allows us to predict and understand the periodic trends in elemental properties.
Relationship Between Atomic Number and Other Atomic Properties
The atomic number is intricately linked to other atomic properties:
1. Number of Electrons:
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus is equal to the number of protons. This balance of positive and negative charges ensures the atom is electrically neutral. However, atoms can gain or lose electrons to form ions, becoming positively charged (cations) if they lose electrons or negatively charged (anions) if they gain electrons. The number of protons, however, remains constant and defines the element.
2. Chemical Properties:
The atomic number dictates an element's chemical properties. The arrangement of electrons in the electron shells, determined by the number of protons, dictates how an atom will interact with other atoms. This interaction is the foundation of chemical bonding and determines an element's reactivity, whether it readily forms compounds, and the types of compounds it forms. Elements with similar electron configurations in their outermost shells (valence electrons) exhibit similar chemical behavior, a phenomenon reflected in the periodic table's grouping of elements into families or groups.
3. Isotopes and Atomic Mass:
While the atomic number defines the element, the number of neutrons in the nucleus can vary, resulting in isotopes of the same element. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. This variation in neutron number affects the atomic mass of the atom (the sum of protons and neutrons), but not the atomic number, which remains constant for all isotopes of a given element. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are both isotopes of carbon, both having an atomic number of 6 (6 protons), but differing in their neutron count (6 neutrons in carbon-12 and 8 neutrons in carbon-14).
4. Position in the Periodic Table:
The periodic table is organized based on atomic number. Elements are arranged in ascending order of their atomic number, reflecting their increasing proton count and resulting periodic trends in their properties. This organization allows scientists to predict and understand the relationships between different elements and their properties. The periodic table is an invaluable tool in chemistry, providing a visual representation of the organization of elements based on their atomic numbers and properties.
Applications of Atomic Number in Science and Technology
The understanding and application of the atomic number are fundamental to many scientific disciplines:
1. Nuclear Chemistry and Physics:
In nuclear chemistry and physics, the atomic number is crucial for understanding nuclear reactions, radioactive decay, and the properties of isotopes. It plays a vital role in determining the stability of a nucleus and predicting the type of radioactive decay an unstable isotope will undergo. For instance, knowing the atomic number of a radioactive element is essential to determine the type and energy of radiation it emits.
2. Analytical Chemistry:
Analytical techniques used to identify and quantify elements often rely on the atomic number. Techniques like X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy exploit the unique X-ray emission spectra produced by elements to determine their composition. The energy of the emitted X-rays is directly related to the atomic number of the element.
3. Materials Science:
The atomic number is essential for understanding the properties of materials and designing new materials with specific properties. The interaction between atoms, governed by their atomic numbers and electron configurations, determines the macroscopic properties of the material, such as strength, conductivity, and reactivity. This understanding is essential in designing materials for specific applications, ranging from aerospace engineering to medical implants.
4. Astrophysics and Cosmology:
In astrophysics and cosmology, the atomic number is used to understand the formation and evolution of stars and galaxies. The abundance of different elements in stars and interstellar matter is determined through spectroscopic analysis which relies heavily on understanding the atomic numbers and spectral lines of elements. This provides insights into the processes that have shaped the universe since the Big Bang.
Conclusion: The Fundamental Role of Atomic Number
The atomic number, representing the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, is a cornerstone of our understanding of the structure of matter. It uniquely identifies an element, dictates its chemical and physical properties, and plays a fundamental role in various scientific disciplines. From the organization of the periodic table to the study of nuclear reactions and the analysis of stellar composition, the atomic number serves as a key parameter for understanding the behavior and interactions of matter at the atomic level. Its fundamental role in chemistry, physics, and numerous technological advancements underscores its enduring significance in the scientific world.
Further Exploration: Beyond the Basics
While this article provides a comprehensive overview of the atomic number, several areas warrant further exploration:
- Isobaric Analog States: Isobars, atoms with the same mass number but different atomic numbers, can exhibit similar energy levels, known as isobaric analog states. Understanding these states provides insight into nuclear structure and interactions.
- Nuclear Shell Model: The nuclear shell model uses the concept of atomic number and nuclear energy levels to explain the stability of certain isotopes and the existence of magic numbers (specific proton and neutron numbers that result in exceptionally stable nuclei).
- Advanced Spectroscopic Techniques: Modern spectroscopic techniques provide extremely precise measurements of atomic properties, including atomic number, offering detailed insights into atomic structure and behavior.
- Applications in Medicine: Nuclear medicine and medical imaging techniques utilize radioactive isotopes, often identified by their atomic numbers, for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Exploring these topics will provide a deeper understanding of the far-reaching implications and practical applications of the atomic number in scientific research and technological advancements. The atomic number is not just a simple number; it's a fundamental characteristic that unlocks the secrets of the universe and drives innovation in various fields. The continued research and exploration in these areas promise further advancements and discoveries in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Basic Unit Of Heredity
Mar 15, 2025
-
9 Is What Percent Of 72
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In H
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Regular Quadrilateral Has What Type Of Symmetry
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Oh
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Number Of Protons In An Atom Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
