Ratio Of Mass Of Proton And Electron
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
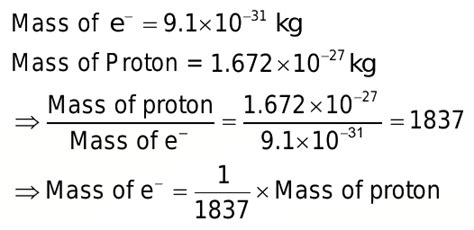
Table of Contents
The Astonishing Ratio: Exploring the Mass Difference Between Protons and Electrons
The universe is built upon fundamental particles, the most familiar being protons and electrons. While seemingly simple building blocks of matter, the relationship between these subatomic particles, specifically their mass ratio, reveals profound insights into the nature of the cosmos and the forces that govern it. This article delves deep into the mass ratio of a proton to an electron, exploring its significance in various fields of physics and chemistry.
Understanding the Basics: Protons and Electrons
Before diving into the intricacies of their mass ratio, let's establish a clear understanding of protons and electrons themselves.
Protons: The Heart of the Atom's Nucleus
Protons are positively charged particles residing within the atom's nucleus. They are significantly heavier than electrons and contribute significantly to an atom's mass. Crucially, the number of protons in an atom's nucleus defines its atomic number and determines its chemical properties. Protons are baryons, meaning they are composite particles made of three quarks held together by the strong nuclear force. This strong force is what overcomes the electrostatic repulsion between the positively charged protons, allowing the nucleus to remain stable.
Electrons: Orbiting the Nucleus
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. Their mass is considerably smaller than that of protons. The number of electrons in a neutral atom equals the number of protons, ensuring a net neutral charge. Electrons are fundamental particles, meaning they are not made up of smaller constituents, as far as our current understanding allows. Their behavior is governed by the electromagnetic force and plays a vital role in chemical bonding and reactions.
The Mass Ratio: A Striking Disparity
The most striking difference between protons and electrons lies in their masses. A proton is approximately 1836 times more massive than an electron. This substantial mass difference has profound consequences for various physical phenomena, from atomic structure to nuclear reactions.
Precise Measurement and Significance
The precise mass of a proton is approximately 1.6726 x 10^-27 kg, while the mass of an electron is approximately 9.1094 x 10^-31 kg. The ratio, therefore, is roughly 1836.15. This seemingly simple number holds immense significance, reflecting the fundamental forces at play within the atom. The disparity in mass is not arbitrary; it's a direct consequence of the different compositions and the interactions governed by the fundamental forces.
Implications for Atomic Structure and Stability
The large mass difference between protons and electrons directly influences the atom's structure. The relatively massive nucleus, dominated by protons and neutrons (which have a similar mass to protons), occupies a tiny fraction of the atom's volume. The lighter electrons orbit this nucleus at a much greater distance, creating the atom's overall size. This arrangement is crucial for chemical interactions and the stability of matter. If the mass ratio were significantly different, atomic structure and, by extension, the chemical properties of elements, would be drastically altered, potentially leading to a completely different universe.
Delving Deeper: The Origin of the Mass Difference
The substantial mass difference between protons and electrons isn't simply a matter of arbitrary numerical values. It's intricately linked to the fundamental forces and the constituents of these particles.
The Role of Quarks and the Strong Force
The proton, unlike the electron, is a composite particle made of three quarks: two up quarks and one down quark. These quarks possess intrinsic mass, but a significant portion of the proton's mass arises from the strong nuclear force binding them together. This energy, according to Einstein's famous equation E=mc², contributes to the overall mass of the proton.
The Higgs Mechanism and Electron Mass
The electron, being a fundamental particle, obtains its mass through a different mechanism: the Higgs mechanism. This mechanism involves the interaction of electrons with the Higgs field, a pervasive field permeating the universe. The interaction with the Higgs field gives electrons their mass, which is considerably smaller than that of the composite proton.
Beyond the Standard Model: Unanswered Questions
While the Standard Model of particle physics provides a framework for understanding the mass of these particles, some questions remain unanswered. The precise origin and values of the quark masses and the strength of the strong force are still areas of active research. Moreover, the vast difference in mass between the proton and the electron, despite both particles experiencing the electromagnetic force, points towards the profound influence of the strong force and the Higgs mechanism in shaping the universe.
The Mass Ratio's Impact on Various Scientific Disciplines
The proton-to-electron mass ratio has far-reaching implications across various scientific disciplines:
Chemistry and Molecular Interactions
The mass disparity significantly influences chemical bonding and reactivity. The relatively light electrons are the primary participants in chemical bonds, while the much heavier protons form the stable core of the atoms. The mass difference dictates the strength and nature of these bonds and influences reaction rates and molecular properties.
Nuclear Physics and Stellar Nucleosynthesis
In nuclear physics, the mass difference plays a critical role in understanding nuclear reactions and stability. The strong nuclear force overcomes the electromagnetic repulsion between protons within the nucleus. This balance is crucial for the stability of atomic nuclei and is heavily influenced by the mass of protons and neutrons. Stellar nucleosynthesis, the process by which stars create heavier elements, also relies on the precise mass ratios of protons and neutrons.
Astrophysics and Cosmology
The proton-to-electron mass ratio is crucial in understanding the evolution of stars and the formation of galaxies. The abundance of protons and electrons in the early universe, and their mass ratio, dictates the processes leading to the formation of stars, galaxies, and other cosmic structures. Any significant variation in this ratio would drastically alter the course of cosmic evolution.
Atomic Physics and Spectroscopy
In atomic physics, the mass ratio influences the energy levels of electrons within an atom. This affects atomic spectra, the unique patterns of light emitted or absorbed by atoms. High-precision measurements of atomic spectra are used to determine fundamental constants, including the proton-to-electron mass ratio, with extraordinary accuracy.
Further Exploration and Ongoing Research
The seemingly simple mass ratio of a proton to an electron continues to fascinate and challenge scientists. Ongoing research explores various aspects related to this ratio:
Precision Measurements and Fundamental Constants
Scientists continue to refine the measurement of the proton-to-electron mass ratio with ever-increasing precision. These highly accurate measurements provide valuable insights into the fundamental constants of nature and potentially reveal new physics beyond the Standard Model.
Variations in the Mass Ratio Across the Universe
Some theories suggest that the fundamental constants, including the proton-to-electron mass ratio, might have varied over cosmological timescales. This possibility is being explored through observations of distant quasars and other astronomical objects.
The Search for New Physics
Discrepancies between theoretical predictions and experimental measurements of the proton-to-electron mass ratio could indicate the presence of new physics beyond the Standard Model. These discrepancies drive further research and the development of new theoretical frameworks.
Conclusion: A Fundamental Ratio with Profound Implications
The ratio of the mass of a proton to the mass of an electron, approximately 1836, is far more than a simple numerical value. It is a fundamental constant reflecting the profound interplay of fundamental forces, the structure of matter, and the evolution of the universe. From the intricacies of chemical bonding to the vast expanse of the cosmos, this ratio plays a vital role in shaping the world around us and continues to inspire scientific inquiry and discovery. Understanding this ratio is crucial for grasping the fundamental nature of reality and the laws governing our universe. Its ongoing study promises further revelations about the deep mysteries of physics and cosmology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Time Is 180 Minutes
Mar 21, 2025
-
Al Oh 3 H2so4 Balanced Equation
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Transition Element
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 24 And 30
Mar 21, 2025
-
Why Is Europe Called Peninsula Of Peninsulas
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ratio Of Mass Of Proton And Electron . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
