Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Is Found Lining
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
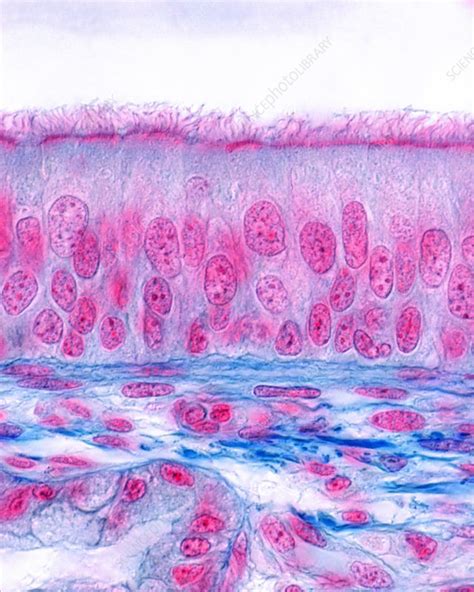
Table of Contents
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium: Where It's Found and Why It Matters
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (PSCCE) is a fascinating type of epithelial tissue. Its name itself hints at its unique structure – seemingly stratified (layered) but actually a single layer of cells. This article delves deep into the location and function of this specialized epithelium, exploring its crucial role in various bodily systems.
Understanding the Structure of Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Before exploring its location, let's understand the defining characteristics of PSCCE. The term "pseudostratified" signifies that while all cells connect to the basement membrane, they appear layered due to variations in cell height and the nuclei's positions. This creates the illusion of multiple layers, even though it's a single layer of cells.
Key features of PSCCE:
- Single layer of cells: Despite its layered appearance, only one layer of cells rests on the basement membrane.
- Variable cell heights: Cells vary in height, with some reaching the apical surface and others shorter, resulting in nuclei at different levels.
- Cilia: The apical surface is adorned with cilia, hair-like projections that beat rhythmically, propelling mucus and other substances.
- Goblet cells: These specialized cells are interspersed among the columnar cells and secrete mucus, a sticky substance that traps foreign particles.
- Basement membrane: A thin, supportive layer underlying the epithelium, anchoring it to the underlying connective tissue.
The coordinated movement of the cilia and the sticky mucus secreted by goblet cells are vital to the function of PSCCE, as we will see in the sections below.
Locations of Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium in the Body
PSCCE is strategically located in areas where its unique structure and functionality are essential. Its presence is not random; it's directly linked to its critical roles in protection and transportation.
1. Respiratory System: The Primary Location
The most prominent location of PSCCE is undoubtedly the lining of the respiratory tract. It's found in:
-
Nasal Cavity: The PSCCE lines the nasal cavity, trapping inhaled particles and initiating the process of removing them from the body. The cilia’s rhythmic beating helps propel mucus containing trapped debris towards the pharynx for swallowing or expectoration.
-
Nasopharynx: This area connecting the nasal cavity and the oral cavity also features PSCCE. Its mucus-trapping and cilia-clearing action continue to filter the incoming air.
-
Trachea (Windpipe): The trachea's inner lining is predominantly PSCCE. The cilia here efficiently move mucus containing trapped dust, pollutants, and pathogens upwards towards the larynx and pharynx, preventing them from reaching the lungs.
-
Bronchi: The primary and secondary bronchi, the larger branches of the airway system leading from the trachea to the lungs, are lined with PSCCE. This ensures that the same protective mechanism of mucus entrapment and cilia-driven clearance continues at this level.
-
Bronchioles (Smaller Airways): While the PSCCE is prominent in larger bronchi, it gradually transitions to simpler columnar or cuboidal epithelium in the smaller bronchioles as the need for mucus clearance changes.
The respiratory system’s reliance on PSCCE underlines its critical role in maintaining the cleanliness and health of the lungs. Without the effective filtration provided by PSCCE, the lungs would be constantly vulnerable to infection and damage.
2. Male Reproductive System: A Specialized Role
Beyond the respiratory system, PSCCE also plays a role in the male reproductive system. It lines portions of:
-
Epididymis: This coiled duct adjacent to the testes is partly lined with PSCCE, though it's often accompanied by stereocilia (non-motile, microvilli-like structures). Here, the epithelium’s role is less about mucus clearance and more about facilitating the maturation and transport of sperm.
-
Efferent Ducts: These small tubes connect the rete testis (network of tubules within the testis) to the epididymis. They are also lined with PSCCE, aiding in the movement of sperm towards the epididymis.
In the male reproductive system, the function of PSCCE might be less about trapping and expelling foreign particles and more about facilitating sperm transport and maturation, albeit through slightly different mechanisms than in the respiratory tract.
3. Auditory Tube (Eustachian Tube): Maintaining Pressure Equilibrium
The auditory tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, playing a crucial role in equalizing pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. The lining of the auditory tube also contains PSCCE, which helps to:
-
Clear Debris: The epithelium facilitates the removal of debris and mucus that might accumulate in the auditory tube, preventing blockages and infections.
-
Maintain Patency: The regular beating of cilia keeps the auditory tube open, allowing for proper pressure equalization.
4. Other Minor Locations: Occasional Presence
While the respiratory and male reproductive tracts are the main locations, PSCCE can also be found in trace amounts in other regions, though this is less common and often regionally restricted.
The Functional Significance of Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
The unique structure of PSCCE is directly linked to its vital functions:
-
Protection: The mucus layer secreted by goblet cells traps foreign particles, pathogens, and irritants, preventing them from reaching the underlying tissues. This is crucial for preventing infections in the respiratory system.
-
Mucociliary Clearance: The rhythmic beating of cilia propels the mucus layer containing trapped debris towards the pharynx. This continuous movement effectively clears the airway passages of potentially harmful substances.
-
Fluid Transport: In the male reproductive system, the cilia, while perhaps less prominently motile, aid in the movement of fluids, including sperm, through the ducts.
-
Maintaining Patency: In the auditory tube, the cilia ensure that the tube remains open, facilitating pressure regulation and preventing obstruction.
Consequences of PSCCE Dysfunction
Damage or dysfunction of PSCCE can have significant consequences, particularly within the respiratory system:
-
Chronic Bronchitis: Damage to the cilia and/or goblet cells can impair mucociliary clearance, leading to chronic accumulation of mucus and recurrent infections.
-
Cystic Fibrosis: Genetic defects affecting mucus production and hydration can lead to thick, sticky mucus that the cilia cannot effectively clear, resulting in airway obstruction and recurrent lung infections.
-
Smoking-Related Damage: Smoking damages the cilia and goblet cells, impairing their function and leading to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and chronic lung diseases.
-
Environmental Pollutants: Exposure to pollutants can also damage the PSCCE, impacting its protective and clearance functions.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of a Unique Epithelium
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is a remarkable example of specialized epithelial tissue. Its strategically located presence in the respiratory, male reproductive, and auditory systems reflects its pivotal role in protection, transport, and maintenance of vital bodily functions. Understanding its structure and function is crucial in appreciating the complex mechanisms that maintain our health and the consequences when this delicate system is disrupted. Further research into PSCCE will undoubtedly continue to shed light on its intricate roles and potential therapeutic targets in various diseases. The intricate interplay between its cellular components, its protective mucus layer, and the rhythmic action of the cilia is a testament to the elegance of biological design. The continued study of PSCCE is essential for our understanding of respiratory health and disease, as well as other areas where it contributes to overall bodily function.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Three Properties Of A Magnet
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Polysaccharide
Mar 25, 2025
-
Lysosomes Are Membrane Bound Vesicles That Arise From The
Mar 25, 2025
-
Calculate The Radius Of Gyration Of A Cylindrical Rod
Mar 25, 2025
-
Definition Of Order Of A Reaction
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Is Found Lining . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
