Provincial Governor Of The Mogul Empire
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
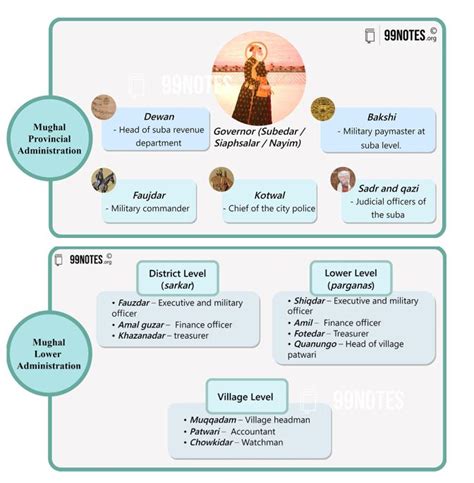
Table of Contents
The Provincial Governors of the Mughal Empire: Power, Patronage, and Rebellion
The Mughal Empire, a vast and powerful realm that dominated much of the Indian subcontinent for centuries, relied heavily on a complex system of provincial administration. At the heart of this system were the Subahdars, or provincial governors, individuals wielding immense power and influence, yet constantly navigating the precarious balance between imperial authority and local autonomy. Understanding their role is crucial to comprehending the empire's successes and its eventual decline.
The Structure of Provincial Governance
The Mughal empire was divided into several Subahs, or provinces, each governed by a Subahdar. These provinces were further subdivided into smaller administrative units, each with its own hierarchy of officials. The Subahdar was the supreme authority within his province, responsible for maintaining law and order, collecting taxes, and administering justice. However, their power was not absolute. The emperor, residing in the capital, held ultimate authority and maintained a complex system of checks and balances to prevent excessive provincial autonomy.
Selection and Appointment of Subahdars
The selection of Subahdars was a critical decision, reflecting the emperor's political strategy and personal preferences. While merit played a role, loyalty to the emperor was paramount. Often, Subahdars were chosen from amongst the emperor's own family members, nobles, or trusted military commanders. This system, while designed to ensure loyalty, sometimes led to nepotism and the appointment of individuals lacking the necessary administrative skills.
The appointment process involved formal investiture, signifying the transfer of power and responsibility. This ceremony, typically conducted in the imperial court, served as a public demonstration of the emperor's authority and the Subahdar's acceptance of his duties. The farmans, or imperial decrees, outlining the Subahdar's responsibilities and powers, served as the legal foundation of their authority.
The Powers and Responsibilities of a Subahdar
The Subahdar possessed extensive powers within their province. Their responsibilities encompassed a wide range of tasks, including:
-
Revenue Collection: This was arguably the most crucial function. The Subahdar oversaw the collection of land revenue, the backbone of the Mughal economy. He appointed and supervised revenue officials, ensuring efficient tax collection and remittance to the imperial treasury. Efficient revenue collection was essential for maintaining the empire's military and administrative apparatus.
-
Military Command: Many Subahdars were also experienced military commanders, responsible for raising and maintaining troops within their province. They led military campaigns against rebels or external threats, ensuring the security and stability of their assigned territory. The strength of their armies often reflected the power they wielded within the empire's hierarchy.
-
Justice and Law Enforcement: The Subahdar acted as the chief justice within their province, overseeing the judicial system. They appointed judges and ensured the enforcement of imperial laws, playing a crucial role in maintaining order and resolving disputes. Their decisions, while ideally aligned with imperial law, were often influenced by local customs and practices.
-
Infrastructure Development: Subahdars were responsible for maintaining infrastructure within their provinces. This involved overseeing the construction and upkeep of roads, canals, and other public works essential for trade and communication. Successful Subahdars often invested in infrastructure development to enhance the prosperity of their province, thereby increasing their own revenue and influence.
-
Patronage and Local Politics: Subahdars often wielded considerable influence over local politics and society. They appointed officials, granted patronage to influential figures, and intervened in local disputes. This patronage system helped maintain stability, but also created opportunities for corruption and the development of powerful regional factions.
Challenges and Constraints Faced by Subahdars
Despite their significant power, Subahdars faced numerous challenges:
-
Maintaining Control over Vast Territories: Governing large provinces presented logistical difficulties. Communication and transportation were slow, making it challenging to maintain effective control across vast distances. Revolts and uprisings were frequent occurrences, often spurred by local grievances or ambitious regional leaders.
-
Balancing Imperial Demands and Local Needs: Subahdars had to reconcile the demands of the imperial court with the needs and aspirations of the local populace. This delicate balancing act required skillful diplomacy and political acumen. Failure to strike a balance could lead to unrest and rebellion.
-
Dealing with Powerful Regional Elites: Subahdars frequently had to contend with powerful regional elites, who often resisted imperial control and sought to maintain their own autonomy. Managing these powerful individuals required a deft hand, involving a combination of negotiation, compromise, and, when necessary, the use of force.
-
Financial Accountability: Subahdars were expected to remit a significant portion of the collected revenue to the imperial treasury. This created pressure to maximize revenue collection, sometimes leading to oppressive taxation and resentment amongst the peasantry. Failure to meet financial obligations could lead to imperial displeasure and even dismissal.
Notable Subahdars and Their Impact
Throughout the Mughal Empire's history, numerous Subahdars left their mark on the empire's trajectory. Some, like Man Singh I, were loyal and efficient administrators who contributed significantly to the empire's consolidation and expansion. Others, driven by ambition, challenged imperial authority, leading to rebellions and internal conflicts. The reigns of powerful Subahdars often reflected the overall stability or instability of the empire itself.
The actions and decisions of individual Subahdars played a crucial role in shaping regional politics, fostering economic development, or conversely, sowing the seeds of rebellion. Their success or failure often hinged on their ability to navigate the complexities of imperial politics, manage local populations, and balance the demands of the emperor with the needs of their province.
The Decline of Subahdar Power and the Fall of the Mughal Empire
As the Mughal Empire weakened in later centuries, the power of the Subahdars fluctuated. Some became increasingly autonomous, effectively ruling their provinces as independent entities. This decentralization of power contributed to the empire's decline, as internal conflicts and rebellions became more frequent and harder to suppress. The loss of central control over the provinces was a key factor in the eventual disintegration of the Mughal Empire.
The Legacy of the Provincial Governors
The Subahdars played a critical role in shaping the Mughal Empire's history. Their actions, both positive and negative, left an indelible mark on the political, social, and economic landscape of the Indian subcontinent. Their system of governance, though flawed, provided a framework for administering a vast and diverse empire. Studying their roles offers valuable insights into the complexities of imperial administration, the challenges of maintaining control over a sprawling empire, and the dynamics of power and influence in a pre-modern society.
The system of provincial governance under the Mughal Empire, with its Subahdars at its core, remains a complex and fascinating topic for historical analysis. The interplay of imperial authority and local autonomy, the challenges of maintaining stability amidst diverse populations, and the significant impact of individual Subahdars all contribute to a rich and detailed understanding of one of history's most significant empires. Further research into the lives and actions of specific Subahdars and detailed regional studies can illuminate even more of the nuances of this vital administrative structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Conjugate Base Of Hso4
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of Areolar Tissue
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 6 25 As A Fraction
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Compounds Is Ionic
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Characteristic Is Common To All Chordates
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Provincial Governor Of The Mogul Empire . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
