Points That Lie On The Same Line Are Called
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
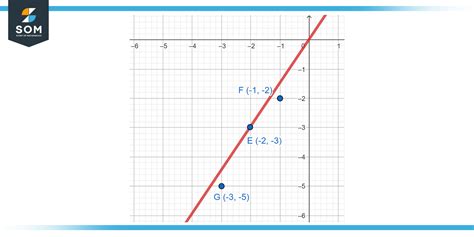
Table of Contents
Points That Lie on the Same Line Are Called Collinear Points: A Comprehensive Guide
Points that lie on the same line are called collinear points. This seemingly simple concept forms the bedrock of many geometric principles and is crucial for understanding more advanced topics in mathematics. This article will delve deep into the meaning of collinearity, explore its applications, and discuss related concepts. We'll also examine how to determine collinearity, looking at both algebraic and geometric approaches, and explore some real-world examples of this fundamental concept.
Understanding Collinearity
Collinearity, at its core, is the property of points lying on the same straight line. Imagine drawing a line on a piece of paper. Any point you mark directly on that line is collinear with all other points on the same line. Conversely, points that do not lie on the same line are called non-collinear points. These points, when connected, would form a triangle or some other polygon, rather than a straight line.
Visualizing Collinearity
Visualizing collinearity is straightforward. Consider three points, A, B, and C. If you can draw a single straight line that passes through all three points without altering the line's direction, then points A, B, and C are collinear. If you need multiple lines to connect all three points, they are non-collinear.
The Importance of Collinearity in Geometry
Collinearity is a fundamental concept in geometry, underpinning many theorems and proofs. It's essential for understanding:
- Lines and Line Segments: The very definition of a line implies collinearity – infinitely many points lying along a single, straight path.
- Angles: Collinearity plays a role in defining angles, particularly supplementary and vertically opposite angles, formed by intersecting lines.
- Triangles and Polygons: Determining whether the vertices of a triangle are collinear determines whether a triangle exists. Non-collinearity is a prerequisite for the existence of a triangle.
- Coordinate Geometry: Collinearity is easily determined using algebraic methods in coordinate geometry, a powerful tool for solving geometric problems.
- Vectors: Collinear vectors are vectors that lie along the same line, either in the same or opposite direction. This is a fundamental concept in linear algebra and physics.
Determining Collinearity: Methods and Techniques
There are several ways to determine if a set of points are collinear. We'll explore both geometric and algebraic approaches.
1. Geometric Methods: Using a Straight Edge
The simplest method, especially for a small number of points, is using a straight edge (like a ruler) and visually checking if a single straight line passes through all points. While intuitive and easy for simple cases, this method is unreliable for a large number of points or points with coordinates defined to a high degree of precision. It's prone to inaccuracies caused by human error in visual judgment.
2. Algebraic Methods: Using Slopes
This is a more precise and powerful method, particularly suitable for points defined by their coordinates in a Cartesian plane. The basic idea is to calculate the slope between pairs of points. If the slope between all pairs of points is the same, the points are collinear.
Steps:
- Consider three points: Let's say we have points A(x₁, y₁), B(x₂, y₂), and C(x₃, y₃).
- Calculate the slopes: Find the slopes between pairs of points using the formula: m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁)
- m₁₂ = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁) (slope of AB)
- m₂₃ = (y₃ - y₂) / (x₃ - x₂) (slope of BC)
- m₁₃ = (y₃ - y₁) / (x₃ - x₁) (slope of AC)
- Check for equality: If m₁₂ = m₂₃ = m₁₃, then points A, B, and C are collinear. If the slopes are not equal, the points are non-collinear.
Important Note: This method is undefined if any denominator (x₂ - x₁, x₃ - x₂, or x₃ - x₁) is zero. This occurs when two or more points have the same x-coordinate. In such cases, the points lie on a vertical line, and collinearity can be established by checking if all points share the same x-coordinate.
3. Algebraic Methods: Using the Area of a Triangle
Another algebraic method utilizes the concept that the area of a triangle formed by three collinear points is zero. The area of a triangle with coordinates (x₁, y₁), (x₂, y₂), and (x₃, y₃) can be calculated using the determinant formula:
Area = (1/2) |x₁(y₂ - y₃) + x₂(y₃ - y₁) + x₃(y₁ - y₂)|
If the area calculated using this formula is zero, the points are collinear. This method elegantly handles cases with vertical lines, unlike the slope method.
4. Vector Method
Vectors provide another elegant approach to determine collinearity. If vectors AB and AC are collinear (meaning one is a scalar multiple of the other), points A, B, and C are also collinear. In other words, there exists a scalar 'k' such that AB = kAC. This approach is particularly useful in higher-dimensional spaces.
Applications of Collinearity
Collinearity isn't just a theoretical concept; it has numerous applications in various fields.
1. Surveying and Mapping
In surveying, determining if points are collinear is crucial for accurate land measurement and mapping. Collinearity checks help ensure that survey measurements are consistent and accurate.
2. Computer Graphics
Computer graphics rely heavily on collinearity to render lines and shapes accurately. Algorithms for line drawing and polygon filling utilize collinearity checks to optimize performance and ensure smooth visuals.
3. Physics
Collinearity is essential in physics, particularly in mechanics and dynamics. For example, analyzing the motion of objects often involves determining if the forces acting on an object are collinear, which simplifies calculations.
4. Engineering
Civil and mechanical engineers use collinearity concepts in structural analysis and design. Verifying collinearity of structural elements is vital for ensuring stability and structural integrity.
5. Image Processing
In image processing and computer vision, collinearity is used in tasks such as object detection and recognition. Identifying collinear points can help define edges and boundaries in images.
Extending the Concept: More than Three Points
While we've primarily discussed collinearity with three points, the concept extends to more points. A set of four or more points is collinear if all possible pairs of points are collinear, or, equivalently, if all the points lie on the same line. The algebraic methods described above can be extended to handle larger sets of points.
Distinguishing Collinearity from Concurrency
It's important to differentiate collinearity from concurrency. While collinearity refers to points lying on the same line, concurrency refers to lines intersecting at the same point. These are distinct but related concepts in geometry.
Conclusion
Collinearity, the property of points lying on the same line, is a fundamental concept in geometry with wide-ranging applications. Understanding how to determine collinearity, using both geometric and algebraic methods, is essential for anyone working with geometric problems or applying geometry to other fields. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of collinearity, its importance, its applications, and related concepts, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently tackle problems involving this key geometric principle. Remember that mastering these concepts will not only enhance your understanding of geometry but also open doors to understanding more advanced mathematical and scientific disciplines. The seemingly simple idea of points lying on the same line unveils a world of intricate mathematical relationships and practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Give The Iupac Name For The Following Compound
Mar 15, 2025
-
Do Gases Have A Fixed Volume
Mar 15, 2025
-
Ode To The West Wind Interpretation
Mar 15, 2025
-
Phase Of The Cell Cycle During Which Dna Replication Occurs
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Pairing Of Homologous Chromosomes Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Points That Lie On The Same Line Are Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
