One Horse Power Is Equal To How Many Watts
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
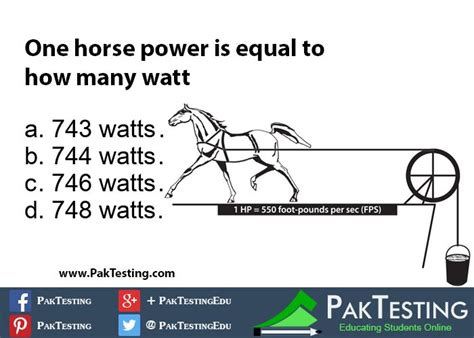
Table of Contents
One Horsepower is Equal to How Many Watts? A Deep Dive into Power Measurement
Understanding power is crucial in numerous fields, from engineering and mechanics to everyday electricity usage. One common unit of power, particularly in the context of mechanical systems, is horsepower (hp). But how does this relate to the more commonly used watt (W), the standard unit of power in the International System of Units (SI)? This article will explore the equivalence between horsepower and watts, delve into the history of the unit, and examine its applications in various contexts.
The Origin of Horsepower: A Historical Perspective
The term "horsepower" may seem quaint in our modern technological world, yet its roots lie in the dawn of the Industrial Revolution. Before the widespread adoption of electric motors and internal combustion engines, the primary source of mechanical power was the horse. Inventor James Watt, renowned for his improvements to the steam engine, needed a way to quantify the power output of his machines in a manner easily understood by potential buyers accustomed to animal labor.
Watt's ingenious method involved measuring the rate at which a strong draft horse could lift water from a mine shaft using a rope and pulley system. Through meticulous observation and experimentation, he determined that a typical horse could lift a weight of 33,000 pounds one foot in one minute. This became the foundation for the definition of one horsepower.
Defining One Horsepower: The Conversion Factor
So, one horsepower (hp) is defined as 33,000 foot-pounds per minute. This seemingly archaic unit has persisted throughout history, finding its place in rating various mechanical devices, from engines to motors. However, in the modern world, the watt (W) has emerged as the preferred and more universally understood unit of power.
To convert horsepower to watts, we need to consider the fundamental definitions of both units. A watt represents one joule of energy per second (1 W = 1 J/s), while a joule is a unit of work or energy equal to a force of one newton acting through a distance of one meter (1 J = 1 N⋅m).
Therefore, we need to convert the foot-pounds per minute of horsepower into joules per second. This involves several conversion factors:
- Feet to meters: 1 foot ≈ 0.3048 meters
- Pounds to newtons: 1 pound ≈ 4.448 newtons
- Minutes to seconds: 1 minute = 60 seconds
Performing these conversions on the 33,000 ft⋅lb/min definition of horsepower, we get:
33,000 ft⋅lb/min * (0.3048 m/ft) * (4.448 N/lb) * (1 min/60 s) ≈ 745.7 watts
Therefore, one horsepower is approximately equal to 745.7 watts (746 watts is often used as a convenient approximation).
Different Types of Horsepower: Mechanical vs. Metric
It is important to note that there are slight variations in the definition of horsepower depending on the context. The definition we've explored is often referred to as mechanical horsepower (hp). Another common variation is metric horsepower (PS or cv), which is based on the kilogram-meter-second system of units and is slightly different from mechanical horsepower. Metric horsepower is approximately 735.5 watts.
These differences are relatively small and often inconsequential in many applications. However, for precision engineering and scientific calculations, it's crucial to specify the exact type of horsepower being used.
Practical Applications of Horsepower and Watts
The understanding of horsepower and watts and their interconversion is vital in various applications:
1. Automotive Engineering:
Horsepower is a common metric used to describe the power output of car engines. Knowing the horsepower of an engine provides a measure of its ability to accelerate and perform various tasks. This figure, however, is often coupled with other metrics like torque to provide a complete picture of engine performance.
2. Industrial Machinery:
The power requirements of industrial machinery, such as pumps, compressors, and motors, are frequently specified in horsepower. Understanding this allows engineers to select appropriate motors and power sources to meet the required performance specifications.
3. Electrical Systems:
While watts are the standard unit in electrical systems, the horsepower equivalent can be helpful when dealing with electric motors converting electrical power to mechanical power. The conversion allows for a direct comparison of electrical motor capacity to the output of a mechanical system.
4. Agriculture and Construction:
Equipment such as tractors and excavators often have their power output rated in horsepower. This aids in comparing the capabilities of different models and determining suitability for specific tasks.
5. Aviation:
Aircraft engines, both piston and jet, frequently have their power specified in terms of horsepower or its equivalent thrust. Understanding the power-to-weight ratio is paramount in aviation design.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Power and Efficiency
While the conversion between horsepower and watts is straightforward, it's crucial to understand the broader context of power measurement and efficiency. The horsepower rating of a machine doesn’t always fully reflect its real-world performance. Several factors can affect actual power delivery:
-
Efficiency: Engines and motors don't convert all input energy into useful work. Losses occur due to friction, heat, and other inefficiencies. The efficiency of a system is crucial in determining the actual usable power output.
-
Load: The power output of a machine can vary depending on the load placed upon it. A motor rated at 10 horsepower may only deliver a fraction of that power when operating under heavy load.
-
Operating Conditions: Temperature, altitude, and other environmental factors can impact power output.
-
Maintenance: Proper maintenance is critical for optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced power output and increased inefficiency.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Power Measurement
The horsepower unit, despite its historical origins, remains relevant in many applications. Its conversion to watts, however, is essential for seamless integration into the broader world of SI units. Understanding the intricacies of horsepower and watts, along with the impact of efficiency and operating conditions, is crucial for engineers, mechanics, and anyone working with mechanical or electrical power systems. By grasping these concepts, we can better understand, design, and optimize various systems to achieve maximum performance and efficiency. The conversion from horsepower to watts isn't merely a mathematical exercise; it's a bridge connecting the past's practical units to the modern world's standardized system of measurement, enabling more effective communication and collaboration across disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Covalent Compounds Dissolve In Water
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Specific Heat Capacity Of Aluminium
Mar 27, 2025
-
Do Noble Gases Have Ionization Energy
Mar 27, 2025
-
How To Write An Invitation Letter To A Friend
Mar 27, 2025
-
The System In The Figure Below Is In Equilibrium
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One Horse Power Is Equal To How Many Watts . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
