Molar Mass Of Helium In Kg
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
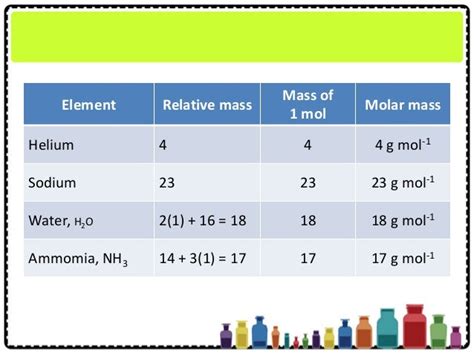
Table of Contents
Molar Mass of Helium in kg: A Deep Dive into Atomic Weight and its Applications
The molar mass of helium, a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, plays a crucial role in various scientific and engineering applications. Understanding its value and implications is vital for accurate calculations and informed decision-making across numerous fields. This comprehensive article delves into the molar mass of helium in kilograms, exploring its calculation, significance, and real-world applications. We'll also discuss related concepts like atomic mass, atomic weight, and the differences between them.
Understanding Atomic Mass and Atomic Weight
Before delving into the molar mass of helium, it's essential to clarify the terms atomic mass and atomic weight. These terms are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion, but they represent slightly different concepts:
-
Atomic Mass: This refers to the mass of a single atom of an element, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or daltons (Da). It's the sum of the masses of the protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus. Electrons contribute negligible mass.
-
Atomic Weight (Standard Atomic Weight): This is the weighted average of the atomic masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The weighting accounts for the relative abundance of each isotope. Because the isotopic composition of an element can vary slightly depending on its source, the standard atomic weight is a globally agreed-upon average value. It's also expressed in amu.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Helium
Helium (He) is a chemical element with an atomic number of 2. This means it has two protons in its nucleus. Naturally occurring helium consists primarily of two stable isotopes: helium-3 (³He) and helium-4 (⁴He). Helium-4 is the most abundant isotope, accounting for approximately 99.99986% of all naturally occurring helium.
The standard atomic weight of helium is approximately 4.002602 amu. This value reflects the weighted average of the atomic masses of ³He and ⁴He, considering their relative abundances.
To convert the atomic weight from amu to kilograms, we use the following conversion factor:
1 amu ≈ 1.660539 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
Therefore, the molar mass of helium in kilograms can be calculated as:
4.002602 amu * (1.660539 × 10⁻²⁷ kg/amu) ≈ 6.646476 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
This represents the mass of a single helium atom in kilograms. However, in practice, we usually work with moles of substances.
Molar Mass and the Mole Concept
A mole (mol) is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 × 10²³) of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, or ions. The molar mass of an element or compound is the mass of one mole of that substance. It's numerically equal to the atomic or molecular weight but expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) or kilograms per mole (kg/mol).
Molar Mass of Helium in kg/mol
Since the atomic weight of helium is approximately 4.002602 amu, its molar mass is approximately 4.002602 g/mol. To convert this to kilograms per mole, we divide by 1000:
4.002602 g/mol / 1000 g/kg = 0.004002602 kg/mol
This means that one mole of helium has a mass of approximately 0.004002602 kilograms.
Significance and Applications of Helium's Molar Mass
The molar mass of helium has numerous applications across diverse fields:
1. Aerospace Engineering:
-
Buoyancy Calculations: Helium's low molar mass translates to low density, making it an ideal lifting gas for airships and balloons. Accurate calculations of lift capacity require precise knowledge of helium's molar mass.
-
Leak Detection: The rate of helium leakage from spacecraft or other sealed systems can be determined using its molar mass and diffusion properties.
2. Cryogenics:
-
Liquid Helium Production and Handling: Helium's low boiling point (-268.93 °C) makes it crucial for cryogenic applications. Understanding its molar mass is important for efficient production, storage, and handling of liquid helium.
-
Superconductivity Research: Many superconductors require extremely low temperatures, often achieved using liquid helium. Accurate molar mass data ensures precise temperature control.
3. Medical Applications:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Superconducting magnets in MRI machines rely on liquid helium for cooling. Precise molar mass measurements are essential for maintaining the required operating temperature.
-
Respiratory Therapy: Helium-oxygen mixtures are used in respiratory therapy to reduce airway resistance. Knowledge of helium's molar mass is crucial for preparing these mixtures with the correct proportions.
4. Scientific Research:
-
Mass Spectrometry: Helium is often used as a carrier gas in mass spectrometry, a technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. Its known molar mass facilitates accurate mass measurements.
-
Gas Chromatography: Helium serves as the carrier gas in gas chromatography, a method for separating and analyzing mixtures of volatile compounds. Its low molar mass contributes to efficient separation.
5. Industrial Applications:
-
Welding: Helium is used as a shielding gas in welding processes to prevent oxidation and contamination. Its molar mass influences its diffusion properties and shielding effectiveness.
-
Leak Detection in Industrial Processes: Helium's low molar mass and small atomic size allow it to penetrate even tiny leaks, making it a valuable tool for detecting leaks in pipelines, pressure vessels, and other industrial equipment.
Conclusion
The molar mass of helium, whether expressed in grams per mole or kilograms per mole, is a fundamental physical quantity with significant implications across various scientific and engineering disciplines. Its low value contributes to several key properties, including low density, high diffusivity, and its suitability as a cryogenic coolant and lifting gas. Accurate knowledge of helium's molar mass is paramount for precise calculations and the efficient operation of numerous technologies and research methods. From aerospace engineering to medical applications and scientific research, understanding this seemingly simple value is crucial for advancement in many fields. This detailed exploration of the molar mass of helium in kg highlights its importance and broad applicability in the modern world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Figure Has 6 Faces 12 Edges And 8 Vertices
Mar 25, 2025
-
Resolution Of A Printer Is Measured In
Mar 25, 2025
-
Most Stable Measure Of Central Tendency
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Sexually Transmitted Infection
Mar 25, 2025
-
168 Cm In Inches And Feet
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molar Mass Of Helium In Kg . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
