Is Steel An Element Compound Or Mixture
News Leon
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
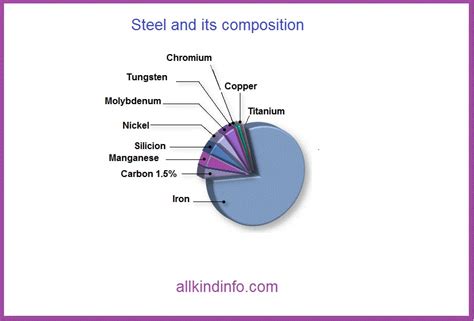
Table of Contents
Is Steel an Element, Compound, or Mixture? A Deep Dive into Material Science
The question, "Is steel an element, compound, or mixture?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the true nature of steel requires a deeper exploration of chemistry and material science. The answer isn't as straightforward as you might think, and delving into the intricacies will provide a richer understanding of this crucial material. This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamental differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures, and definitively answer the question regarding steel's classification. We'll also explore the properties of steel that stem from its composition and the implications of this for its diverse applications.
Understanding the Basics: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Before we classify steel, let's establish a clear understanding of the three categories of matter: elements, compounds, and mixtures.
Elements: The Building Blocks of Matter
Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. The periodic table organizes all known elements, each identified by its unique atomic number (the number of protons in its nucleus). Examples include iron (Fe), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). These elements possess distinct physical and chemical properties that define their behavior.
Compounds: Elements Combining
Compounds are pure substances formed when two or more elements chemically combine in fixed proportions. This chemical bonding results in a new substance with properties distinctly different from its constituent elements. The elements in a compound are bonded together through chemical forces, and separating them requires a chemical reaction. Examples include water (H₂O), where two hydrogen atoms bond with one oxygen atom, and table salt (NaCl), a combination of sodium and chlorine. The properties of a compound are distinct from those of its constituent elements; water, for example, is a liquid at room temperature, whereas hydrogen and oxygen are gases.
Mixtures: A Blend of Substances
Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The substances in a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical methods, such as filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition, like sand and water). The ratio of components in a mixture can vary.
The Composition of Steel: Unveiling the Truth
Steel, a cornerstone of modern construction and manufacturing, is an alloy primarily composed of iron (Fe). However, what truly distinguishes steel from pure iron is the presence of other elements, most notably carbon (C). The carbon content is crucial in determining the properties of steel, influencing its strength, hardness, and ductility. Different grades of steel are characterized by varying proportions of carbon and other alloying elements.
Besides iron and carbon, steel often includes other elements like:
- Manganese (Mn): Improves strength and hardness.
- Silicon (Si): A deoxidizer during steelmaking, and contributes to strength and magnetic properties.
- Phosphorus (P): Generally considered an impurity, but small amounts can enhance certain properties.
- Sulfur (S): Similar to phosphorus, usually an impurity; can affect machinability.
- Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr), Molybdenum (Mo), Vanadium (V), Tungsten (W): These alloying elements are added to enhance specific properties like corrosion resistance (stainless steel), high-temperature strength, or toughness. The specific combination and proportions of these elements dictate the grade and resulting properties of the steel.
Why Steel is a Mixture
Given this composition, it is evident that steel is not an element. It's a combination of multiple elements. It also isn't a compound because the elements within steel are not chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. The proportions of these elements can vary significantly depending on the desired properties of the resulting steel. This variable composition is a hallmark of a mixture. The iron and other elements are physically combined, not chemically bound in a specific molecular structure like a compound would be.
Steel's properties are a direct consequence of the interactions between the constituent elements. The carbon atoms within the iron lattice structure affect the arrangement of iron atoms, significantly influencing the mechanical properties. The addition of other alloying elements further modifies the microstructure, leading to the wide range of steel grades available with tailored properties. These interactions are characteristic of mixtures, not compounds.
The Importance of Alloying Elements in Steel
The deliberate addition of alloying elements is a defining characteristic of steel production. This process significantly alters the properties of the base iron, creating a material with far greater versatility and application potential.
Carbon's Critical Role
Carbon plays a crucial role in determining the strength and hardness of steel. Low-carbon steels, containing less than 0.25% carbon, are relatively soft and ductile, making them suitable for applications requiring formability. Medium-carbon steels (0.25% - 0.55% carbon) strike a balance between strength and ductility. High-carbon steels (greater than 0.55% carbon) are very strong and hard but can be more brittle.
Enhancing Properties with Other Alloys
The inclusion of other alloying elements provides further control over steel's properties. For example:
- Stainless steel incorporates chromium to create a passive oxide layer, providing exceptional corrosion resistance.
- High-strength low-alloy steels use small amounts of various elements to improve yield strength and toughness.
- Tool steels incorporate elements like tungsten and molybdenum to achieve high hardness and wear resistance, ideal for cutting tools.
Differentiating Steel from Iron: A Crucial Distinction
It’s important to distinguish steel from its primary component, iron. While steel is primarily iron, it's the addition of other elements, particularly carbon, that fundamentally transforms its properties. Pure iron is relatively soft and easily corrodes. Steel, due to its alloying, exhibits significantly enhanced strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance, making it a vastly superior material for countless applications. This transformation is the result of the mixture's properties, not those of a single element or a defined compound.
Steel's Diverse Applications: A Testament to its Versatility
The diverse applications of steel are a testament to its versatility. Its properties can be fine-tuned through alloying to meet the demands of various industries. This makes steel indispensable in:
- Construction: Steel's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for buildings, bridges, and other large structures.
- Automotive: Steel forms the chassis and body panels of most vehicles, offering a combination of strength and formability.
- Manufacturing: Steel is crucial in machinery, tools, and industrial equipment, where strength, durability, and wear resistance are essential.
- Energy: Steel is used in pipelines, wind turbines, and other energy infrastructure projects.
- Medical devices: Certain grades of stainless steel are biocompatible and used in medical implants and instruments.
Conclusion: Steel – A Complex Mixture
In conclusion, steel is definitively a mixture. It is a heterogeneous mixture of iron, carbon, and other alloying elements, each contributing to its overall properties. The elements within steel are not chemically bonded in fixed ratios, and their relative proportions can be altered to tailor the material's characteristics. The understanding that steel is a mixture is crucial to appreciate its versatility, its wide range of applications, and the sophisticated processes used in its manufacture. This careful control over composition allows for the creation of specialized steel grades, each optimized for specific purposes, a testament to the power of material science and the complex nature of this ubiquitous material.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Balanced Equation For Copper And Nitric Acid
Mar 31, 2025
-
Passwords Passphrases And Pins Are Examples Of Which Security Term
Mar 31, 2025
-
Both Glucose And Fructose Are
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Perfectly Elastic Demand Curve Implies That The Firm
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Complementary Bases In Dna
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Steel An Element Compound Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
