Is Methane A Compound Or An Element
News Leon
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
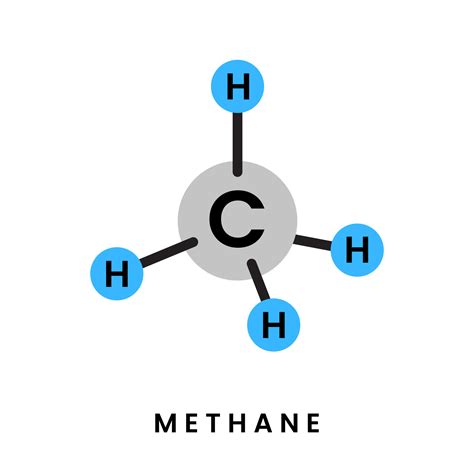
Table of Contents
Is Methane a Compound or an Element? A Deep Dive into Chemical Classification
The question, "Is methane a compound or an element?" might seem simple at first glance, but it opens the door to a fascinating exploration of fundamental chemistry concepts. Understanding the difference between elements and compounds is crucial for grasping the building blocks of matter and how they interact. This article will delve deep into the nature of methane, clarifying its classification and exploring related chemical principles.
Understanding Elements and Compounds
Before we tackle methane specifically, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms "element" and "compound."
What is an Element?
An element is a pure substance consisting only of atoms that all have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei. This number of protons, also known as the atomic number, defines the element. Elements are the fundamental building blocks of all matter, and they cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. The periodic table organizes and displays all known elements. Examples include hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), carbon (C), and iron (Fe).
What is a Compound?
A compound, on the other hand, is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. These bonds can be ionic (involving the transfer of electrons) or covalent (involving the sharing of electrons). Compounds have distinct properties that differ from the properties of their constituent elements. For instance, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from hydrogen and oxygen; its properties are vastly different from those of hydrogen gas or oxygen gas. Table salt (NaCl), another example, is a compound composed of sodium and chlorine.
Methane: A Detailed Analysis
Now, let's focus on methane (CH₄). Methane is a simple hydrocarbon, the simplest alkane, and the primary component of natural gas. Its chemical formula, CH₄, reveals its composition: one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
The Covalent Bonds in Methane
The bonds in methane are covalent bonds. The carbon atom shares one electron with each of the four hydrogen atoms, forming four strong single bonds. This arrangement satisfies the octet rule for carbon (achieving a stable electron configuration) and the duet rule for hydrogen (achieving a stable electron configuration with two electrons).
Why Methane is a Compound
Given the definition of a compound, it's clear that methane fits the description perfectly. It consists of two different elements, carbon and hydrogen, chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio (one carbon atom to four hydrogen atoms). It's not a mixture; the carbon and hydrogen atoms are inextricably linked through strong covalent bonds. Therefore, methane is unequivocally a compound, not an element.
Distinguishing Methane from its Constituent Elements
The properties of methane are dramatically different from those of its constituent elements:
- Carbon: In its elemental form, carbon exists as graphite or diamond, both solid materials with vastly different physical and chemical properties compared to methane, which is a gas at room temperature.
- Hydrogen: Elemental hydrogen is a highly flammable, diatomic gas (H₂). While methane is also flammable, its combustion properties and energy content differ significantly from those of pure hydrogen.
The Importance of Chemical Formulas
Chemical formulas, such as CH₄ for methane, are essential for representing the composition of compounds. The subscripts indicate the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of the compound. This precise notation ensures unambiguous communication in chemistry. Understanding chemical formulas is crucial for predicting the properties of compounds and their reactions.
Methane's Role in Nature and Industry
Methane plays significant roles in various natural processes and industrial applications.
Methane in the Environment
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to climate change. It's released into the atmosphere through various natural sources, including wetlands, livestock, and natural gas leaks. Understanding its environmental impact is crucial for mitigating climate change.
Methane as a Fuel Source
Methane is a valuable fuel source, widely used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. It's a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal and oil, producing less carbon dioxide per unit of energy. However, its extraction and transportation can still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Methane in Chemical Industry
Methane serves as a raw material in the chemical industry, used to produce various chemicals such as methanol, formaldehyde, and hydrogen. It's a crucial building block for numerous industrial processes.
Differentiating Mixtures from Compounds
It's important to contrast compounds with mixtures. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture can be separated by physical methods, such as filtration or distillation. Air, for instance, is a mixture of gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. Unlike compounds, mixtures do not have a fixed composition. Methane, as a compound, is distinctly different from mixtures.
Further Exploration of Chemical Bonding
Understanding the nature of covalent bonding is key to comprehending the properties of methane. The shared electron pairs in the C-H bonds create a stable molecule with specific geometric structure (tetrahedral). This structure influences the physical and chemical properties of methane, such as its boiling point, reactivity, and solubility.
The Significance of the Periodic Table
The periodic table provides a framework for understanding the relationships between elements and their chemical behavior. The position of an element on the periodic table reflects its electron configuration, which dictates its bonding properties. The properties of carbon and hydrogen, as indicated by their positions in the periodic table, explain why they form the stable covalent bonds found in methane.
Conclusion: Methane - A Definitive Compound
In conclusion, methane (CH₄) is definitively a compound, not an element. It's a pure substance composed of two different elements, carbon and hydrogen, chemically bonded in a fixed ratio through strong covalent bonds. Its properties are distinct from those of its constituent elements, showcasing the fundamental difference between elements and compounds. Understanding the nature of methane contributes significantly to grasping fundamental chemical concepts and their real-world applications in environmental science, energy production, and the chemical industry. The distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures underscores the richness and complexity of the material world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Ultimate Source Of All New Alleles Is
Apr 01, 2025
-
Distance Between A Line And A Plane
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Long Run Perfectly Competitive Equilibrium
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Are Hydrogen Bonds Different From Covalent
Apr 01, 2025
-
Find The Modulus Of The Following 1 Es002 1 Jpg
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Methane A Compound Or An Element . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
