Is Helium A Metal Or A Nonmetal
News Leon
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
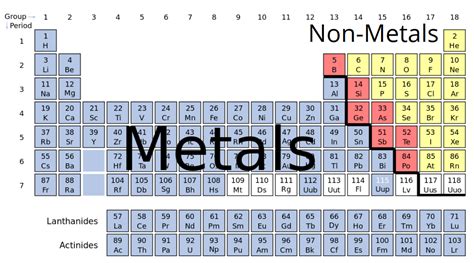
Table of Contents
Is Helium a Metal or a Nonmetal? A Deep Dive into its Properties
Helium, the second element on the periodic table, is a fascinating and unique substance. Its lightness, inertness, and unusual properties have led to widespread applications, from inflating balloons to cooling powerful magnets. But a fundamental question often arises: is helium a metal or a nonmetal? The answer, as we'll explore in detail, is unequivocally nonmetal. However, understanding why requires a deeper look into its atomic structure and chemical behavior.
Understanding the Metal/Nonmetal Dichotomy
Before classifying helium, let's establish the key differences between metals and nonmetals. This distinction is primarily based on their electronic configurations and resulting physical and chemical properties.
Metals: A Shared Identity
Metals are generally characterized by:
- High electrical conductivity: They readily conduct electricity due to the presence of freely moving electrons in their outer shells.
- High thermal conductivity: They efficiently transfer heat.
- Malleability and ductility: They can be hammered into sheets (malleability) and drawn into wires (ductility) without breaking. This is due to the ability of metal atoms to slide past one another without disrupting the metallic bond.
- Metallic luster: They exhibit a shiny appearance.
- Low ionization energy: They relatively easily lose electrons to form positive ions (cations).
Nonmetals: A Diverse Group
Nonmetals, in contrast, typically display:
- Low electrical conductivity: They are poor conductors of electricity.
- Low thermal conductivity: They are poor conductors of heat.
- Brittleness: They tend to be brittle and shatter when subjected to stress.
- Lack of metallic luster: They generally lack the shiny appearance of metals.
- High electronegativity: They have a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- High ionization energy: They require a significant amount of energy to remove electrons.
Helium: A Nonmetal's Profile
Helium definitively fits the profile of a nonmetal. Let's examine its key properties in relation to the metal/nonmetal criteria:
1. Atomic Structure: The Key to Understanding
Helium's atomic number is 2, meaning it has two protons and, in its neutral state, two electrons. These electrons occupy the 1s orbital, the lowest energy level. This completely filled electron shell is the crucial factor that dictates helium's nonmetallic behavior. A full valence shell leads to exceptional stability, making helium extremely unreactive and inert.
Unlike metals which readily lose electrons to achieve a stable configuration, helium has no tendency to lose or share its electrons. This lack of inclination to participate in electron transfer is a defining characteristic of nonmetals.
2. Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Poor Conductors
Helium is an extremely poor conductor of both electricity and heat. This is directly linked to its filled electron shell. The electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and not free to move throughout the material, a key requirement for electrical and thermal conductivity. In contrast, metals have delocalized electrons allowing for efficient charge and energy transfer.
3. Physical State and Appearance: Gaseous and Transparent
Helium exists as a gas under standard conditions. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless—properties inconsistent with the metallic luster and often solid states of metals.
4. Chemical Reactivity: Inertness
Helium's inertness is perhaps its most defining nonmetallic characteristic. Its completely filled electron shell provides exceptional stability. This means it has little tendency to form chemical bonds with other elements. It is one of the noble gases, a group known for their extreme unreactivity. This contrasts sharply with the reactivity displayed by many metals which readily form compounds.
5. Ionization Energy: High Value
Helium possesses a very high ionization energy. This means that a considerable amount of energy is required to remove an electron from a helium atom. This high ionization energy further underscores its stability and lack of willingness to lose electrons, another characteristic that separates it from metals.
Helium's Unique Position on the Periodic Table
Helium's placement in Group 18, the noble gases, further reinforces its classification as a nonmetal. The noble gases are all nonmetals, sharing the common trait of a completely filled outermost electron shell, leading to exceptional stability and inertness.
Applications Highlighting its Nonmetallic Nature
The applications of helium directly reflect its nonmetallic properties:
- Balloons and Airships: Helium's low density makes it ideal for lifting objects lighter than air. This is a purely physical property, unrelated to any chemical reactivity.
- Cryogenics: Helium's extremely low boiling point (-268.93 °C) makes it invaluable as a coolant for superconducting magnets used in MRI machines and other scientific instruments. Again, this is a physical property based on its weak interatomic forces.
- Leak Detection: Its inertness and ability to diffuse through small openings make it useful for detecting leaks in various systems.
- Welding: Helium's inert nature makes it a shielding gas, protecting the weld from oxidation during welding processes.
Addressing Potential Confusion
While helium's classification as a nonmetal is clear-cut, some might be confused by its unusual properties, such as its extremely low boiling point. Low boiling points are not exclusively characteristic of metals or nonmetals. Helium's low boiling point arises from its weak interatomic forces, a consequence of its complete electron shell, not an indicator of metallic behavior.
Conclusion: Helium is Undeniably a Nonmetal
In conclusion, based on its atomic structure, chemical behavior, and physical properties, helium is definitively a nonmetal. Its inertness, low conductivity, and lack of metallic luster clearly distinguish it from metals. Its unique properties, stemming from its completely filled electron shell, have made it indispensable in various technological applications. The understanding of helium's nonmetallic nature is fundamental to its use and its significance in the wider world of chemistry and physics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Nonrenewable Energy Source
Apr 04, 2025
-
Electron Dot Structure For Magnesium Oxide
Apr 04, 2025
-
Boiling Point Of Sugar And Water
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Planet Is Known As The Morning Star
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is A Volt Equal To
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Helium A Metal Or A Nonmetal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
