In The Figure Below Find X
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
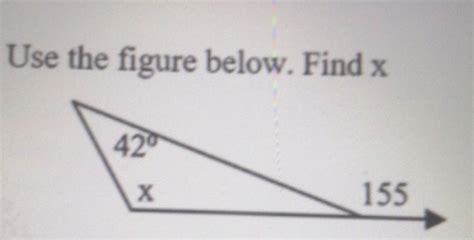
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Finding 'x' in Geometric Figures
Finding the value of 'x' in geometric figures is a fundamental skill in mathematics, applicable across various fields from architecture and engineering to computer graphics and game development. This article will explore diverse methods for solving for 'x' in different geometric scenarios, providing a comprehensive guide for beginners and a valuable refresher for experienced learners. We’ll delve into the core concepts, offer practical examples, and highlight common pitfalls to avoid.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Geometric Theorems and Properties
Before tackling specific problems, let's review some essential geometric theorems and properties. These principles form the bedrock of solving for 'x' in most geometric figures.
1. Angles in a Triangle:
- The Sum of Angles: The sum of interior angles in any triangle always equals 180 degrees. This is a cornerstone theorem used extensively in solving for unknown angles. If you know two angles in a triangle, you can easily find the third.
- Isosceles Triangles: In an isosceles triangle, two sides are equal in length, and the angles opposite these sides are also equal.
- Equilateral Triangles: An equilateral triangle has all three sides equal in length, and all three angles are equal to 60 degrees.
2. Angles in Other Polygons:
- Quadrilaterals: The sum of interior angles in a quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
- Polygons with 'n' sides: The sum of interior angles in a polygon with 'n' sides is given by the formula (n-2) * 180 degrees.
- Exterior Angles: The sum of exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees.
3. Similar Triangles:
Similar triangles have the same shape but different sizes. Corresponding angles are equal, and corresponding sides are proportional. This proportionality is crucial for solving for unknown sides or angles.
4. Pythagorean Theorem (Right-Angled Triangles):
In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (legs). This theorem, a=² + b² = c², is invaluable for solving problems involving right-angled triangles.
5. Circle Theorems:
Various theorems govern angles and segments within circles, including:
- Angles subtended by the same arc: Angles subtended by the same arc at the circumference are equal.
- Angle at the center is twice the angle at the circumference: The angle subtended by an arc at the center of a circle is twice the angle subtended by the same arc at the circumference.
Solving for 'x': Practical Examples and Step-by-Step Solutions
Let's now delve into specific examples, illustrating how to find 'x' in various geometric figures. Remember, the key is to identify the relevant theorems and properties and apply them systematically.
Example 1: Finding 'x' in a Triangle
Imagine a triangle with angles 70°, 50°, and x°. Using the sum of angles theorem:
70° + 50° + x° = 180°
120° + x° = 180°
x° = 180° - 120°
x = 60°
Example 2: Finding 'x' in an Isosceles Triangle
Consider an isosceles triangle with two equal angles of 75° each and a third angle of x°. Since the sum of angles in a triangle is 180°:
75° + 75° + x° = 180°
150° + x° = 180°
x° = 180° - 150°
x = 30°
Example 3: Finding 'x' using Similar Triangles
Suppose we have two similar triangles. The sides of the first triangle are 3, 4, and 5. The corresponding sides of the second triangle are x, 8, and 10. Since the triangles are similar, the ratio of corresponding sides is constant:
3/x = 4/8 = 5/10
We can use any of these ratios to solve for x:
3/x = 5/10
30 = 5x
x = 6
Example 4: Finding 'x' using the Pythagorean Theorem
Let's say we have a right-angled triangle with legs of length 6 and 8, and a hypotenuse of length x. Applying the Pythagorean theorem:
6² + 8² = x²
36 + 64 = x²
100 = x²
x = 10
Example 5: Finding 'x' in a Circle
Consider a circle with an angle at the center of 120° subtending a certain arc. The angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc is x°. Using the circle theorem:
Angle at center = 2 * Angle at circumference
120° = 2 * x°
x = 60°
Example 6: Finding 'x' in a Complex Geometric Figure
Sometimes, finding 'x' requires a combination of techniques and a strategic approach. For instance, a complex figure might involve multiple triangles, some similar, some isosceles. You may need to systematically identify individual triangles, find relationships between angles, and progressively work towards the value of 'x'.
Advanced Techniques and Problem-Solving Strategies
Solving for 'x' in more intricate geometric problems often involves more advanced techniques:
- Trigonometry: Trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) are essential when dealing with angles and sides of triangles, especially non-right-angled triangles.
- Coordinate Geometry: Representing geometric figures on a coordinate plane allows the use of algebraic methods to find unknown values.
- Vectors: Vectors provide a powerful tool for solving geometric problems, particularly those involving direction and magnitude.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can lead to incorrect solutions when solving for 'x':
- Incorrectly applying theorems: Ensure you understand the conditions under which a theorem is applicable.
- Misinterpreting diagrams: Carefully examine diagrams and identify all relevant information.
- Calculation errors: Double-check your calculations to avoid arithmetic mistakes.
- Ignoring units: Always include appropriate units in your final answer.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Finding 'x'
Finding 'x' in geometric figures is a fundamental mathematical skill that builds confidence and proficiency in geometry. By understanding the core geometric principles, systematically applying appropriate theorems, and practicing with diverse examples, you can confidently solve even complex problems. Remember to review your work, check for common mistakes, and embrace the challenge of unraveling the mysteries of geometry. The ability to confidently solve for 'x' not only improves your mathematical abilities but also enhances your problem-solving skills across various disciplines. Keep practicing, and soon you'll master the art of decoding the mystery of 'x' in any geometric figure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Layer Of Earth Possesses The Greatest Thickness
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is Air A Mixture Of
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Protein Is The Most Important Buffer In Blood Plasma
Mar 20, 2025
-
Dsl Is An Example Of What Type Of Internet Access
Mar 20, 2025
-
In A Nuclear Experiment A Proton With Kinetic Energy
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In The Figure Below Find X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
