In The Carbon Cycle The Role Of Plants Is To
News Leon
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
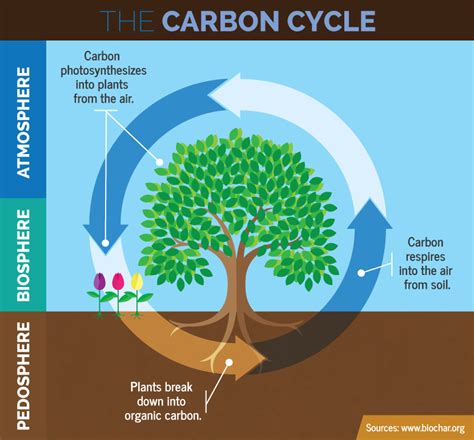
Table of Contents
In the Carbon Cycle, the Role of Plants Is to… Be the Lungs of the Earth
Plants are the unsung heroes of our planet's carbon cycle. While often overshadowed by discussions of fossil fuels and industrial emissions, their role is absolutely critical to maintaining the delicate balance of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) and supporting life as we know it. Understanding their multifaceted contribution is key to appreciating the intricacies of the carbon cycle and devising effective strategies to combat climate change.
The Carbon Cycle: A Brief Overview
Before delving into the specific role of plants, let's establish a basic understanding of the carbon cycle itself. This biogeochemical cycle describes the continuous movement of carbon atoms through various reservoirs on Earth, including:
- The Atmosphere: The primary reservoir of carbon in the form of CO2.
- The Oceans: Carbon dissolves in seawater, forming carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions. Marine organisms incorporate carbon into their shells and skeletons.
- The Land: Carbon is stored in soil, plants, and animals. Fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) represent ancient, concentrated forms of carbon from past life.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Carbonates (like limestone) represent a significant long-term carbon sink.
The carbon cycle involves a complex interplay of processes that transfer carbon between these reservoirs. These include:
- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic matter (sugars) using sunlight.
- Respiration: Plants, animals, and microorganisms release CO2 back into the atmosphere as they break down organic matter for energy.
- Decomposition: Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) break down dead organic matter, releasing CO2 into the atmosphere or the soil.
- Combustion: Burning of fossil fuels and biomass releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Ocean Uptake: The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, but this process is becoming saturated due to increasing atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Weathering and Erosion: The slow breakdown of rocks releases carbon into the environment.
Plants: The Primary Carbon Sinks
The most significant role of plants in the carbon cycle is their role as primary producers and carbon sinks. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic compounds, effectively sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. This process can be summarized as follows:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation shows how plants use sunlight, water, and CO2 to create glucose (a simple sugar), which serves as the building block for all plant tissues. This glucose is then used for growth, reproduction, and other metabolic processes. The more plants grow, the more carbon they absorb and store.
Different Types of Carbon Storage in Plants
Plants store carbon in various ways:
- Biomass: This includes the aboveground parts (leaves, stems, branches) and belowground parts (roots). The larger the plant, the more carbon it stores in its biomass. Forests, in particular, act as massive carbon sinks due to the large amount of biomass they contain.
- Soil Carbon: Plant roots release organic compounds into the soil, which are then decomposed by microbes. This process contributes significantly to soil organic carbon, enriching the soil and increasing its carbon storage capacity. Healthy soils are crucial for maintaining the carbon cycle's balance.
- Dead Organic Matter: When plants die, their biomass decomposes, releasing CO2 back into the atmosphere. However, a significant portion of this carbon can remain stored in the soil as organic matter for extended periods, especially in environments with low decomposition rates (e.g., cold climates).
The Impact of Deforestation and Land Use Change
The removal of forests and other vegetation through deforestation and land use change significantly disrupts the carbon cycle. When forests are cleared, the stored carbon in trees and soil is released back into the atmosphere as CO2, contributing to global warming. This release is further amplified by the loss of photosynthetic capacity, reducing the planet's ability to absorb atmospheric CO2.
This highlights the crucial need for sustainable forestry practices that balance the demand for timber and other forest products with the need to maintain forest carbon stocks. Reforestation and afforestation (planting new forests) are also critical strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration and mitigating climate change.
Oceanic Plants: A Crucial Role Often Overlooked
While terrestrial plants receive considerable attention in discussions of the carbon cycle, phytoplankton, microscopic marine plants, play an equally vital role. These tiny organisms are responsible for a significant portion of the Earth's primary productivity, absorbing CO2 through photosynthesis and forming the base of the marine food web. Their contribution to carbon sequestration is vast, and their health is directly impacted by ocean acidification, a consequence of increased atmospheric CO2.
Beyond Carbon Sequestration: Other Plant Roles in the Carbon Cycle
The role of plants extends beyond carbon sequestration. They are also involved in:
- Nutrient Cycling: Plants play a crucial role in nutrient cycling, which influences soil carbon storage. Nutrient availability influences plant growth and thus carbon uptake.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Plants influence the water cycle through transpiration (release of water vapor from leaves), affecting rainfall patterns and soil moisture. This, in turn, indirectly impacts carbon cycling.
- Biodiversity Support: Plants support a diverse range of organisms that are involved in the carbon cycle, including decomposers, herbivores, and other trophic levels. Loss of biodiversity can negatively affect the efficiency of carbon cycling.
The Future of Plants in a Changing Climate
Climate change poses a significant threat to the planet's plant life, impacting their ability to absorb and store carbon. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can stress plants, reducing their growth and photosynthetic capacity. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to enhance plant resilience and protect their crucial role in the carbon cycle.
Strategies to Enhance Plant's Role in Carbon Sequestration
Numerous strategies can be implemented to enhance the role of plants in mitigating climate change by increasing carbon sequestration:
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees on a large scale is crucial for restoring forests and increasing carbon uptake.
- Sustainable Forestry Practices: Implementing sustainable forestry practices helps maintain forest carbon stocks and ensures the long-term health of forests.
- Improved Agricultural Practices: Implementing practices like no-till farming, cover cropping, and crop rotation can enhance soil carbon storage in agricultural lands.
- Urban Greening: Increasing the number of trees and green spaces in urban areas can help absorb CO2 and improve air quality.
- Protecting and Restoring Wetlands: Wetlands are highly effective carbon sinks, and their protection and restoration are crucial for mitigating climate change.
- Promoting Biodiversity: Maintaining biodiversity helps ensure the health and resilience of ecosystems, enhancing their capacity for carbon sequestration.
Conclusion: Plants—Our Planetary Allies
In conclusion, the role of plants in the carbon cycle is multifaceted and indispensable. They act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis and storing carbon in their biomass and the soil. Their health and abundance are vital for maintaining the balance of the carbon cycle and mitigating climate change. Protecting and enhancing plant life through various strategies is crucial for securing a sustainable future for our planet. Understanding the intricate mechanisms by which plants participate in the carbon cycle is not just an academic pursuit but a critical step toward addressing the urgent challenge of climate change. By embracing sustainable practices and investing in research and conservation efforts, we can harness the power of plants to create a healthier and more resilient planet for future generations. The future of the planet's carbon balance, and indeed, the future of life itself, is intrinsically linked to the health and well-being of the plant kingdom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percentage Of 32 Is 4
Apr 06, 2025
-
Are Glucose And Fructose Structural Isomers
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Are Interest Groups Different From Political Parties
Apr 06, 2025
-
Quotient Of A Number And 3
Apr 06, 2025
-
Write The Complete Nuclear Equation For The Bombardment
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In The Carbon Cycle The Role Of Plants Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
