How Many Watts Equal One Horse Power
News Leon
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
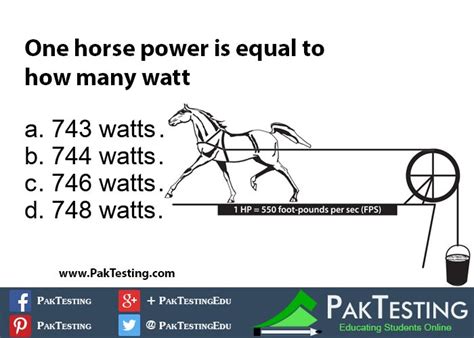
Table of Contents
How Many Watts Equal One Horsepower? Unpacking the Power Conversion
Understanding the relationship between watts and horsepower is crucial for anyone working with engines, motors, or power systems. While seemingly simple, the conversion isn't just a matter of plugging numbers into a formula; it involves delving into the history, context, and nuances of these two distinct units of power measurement. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of converting watts to horsepower and vice-versa, addressing common misconceptions and providing practical examples.
The Genesis of Horsepower: A Measure of Muscle
Before delving into the numerical conversion, let's understand the origins of horsepower. Invented by James Watt, a Scottish engineer instrumental in the development of the steam engine, horsepower wasn't a scientifically precise unit initially. Watt, needing a way to market his improved steam engines, devised a comparison to a familiar, relatable power source – the horse.
His method involved observing the rate at which strong horses could lift water from mines using a system of pulleys and ropes. Through observation and calculation, he estimated that a strong horse could lift a 550-pound weight one foot in one second. This became the foundation of the imperial horsepower (hp).
The Imperial Horsepower: A Practical, but Imperfect, Standard
It's vital to recognize that Watt's observation was an approximation. The actual power output of horses varies considerably based on factors like breed, age, health, and workload. Thus, horsepower, as originally defined, wasn't a highly precise scientific unit but rather a practical measure for comparing the power of steam engines to that of working animals.
Watts: The Metric Standard of Power
In contrast to horsepower's somewhat ad-hoc origins, the watt is a rigorously defined unit within the International System of Units (SI). It represents the rate of energy transfer or work done. One watt is equal to one joule of energy expended per second. This provides a much more precise and universally understood basis for power measurement.
The Joule: The Foundation of the Watt
The joule (J) is the SI unit of energy. Understanding the joule is key to grasping the watt. One joule is the energy transferred when a force of one newton is applied over a distance of one meter. Because a watt is one joule per second, it neatly ties power (rate of energy transfer) to energy itself. This provides a consistent and scientific framework for measuring power.
The Conversion: Watts to Horsepower and Vice Versa
The conversion factor between watts and horsepower is derived from the original definition of horsepower. Since one horsepower is equivalent to 550 foot-pounds per second, and the foot-pound is a unit of energy (work), we can use established conversion factors to arrive at the equivalent in watts.
The commonly accepted conversion is:
- 1 horsepower (hp) ≈ 746 watts (W)
This means that one horsepower is approximately equal to 746 watts. The "≈" symbol indicates an approximation, reflecting the inherent imprecision in the original definition of horsepower.
Calculating Power Conversions: Practical Examples
Let's illustrate with a few examples:
Example 1: Converting Horsepower to Watts
A motor has a power rating of 10 horsepower. How many watts is this?
10 hp * 746 W/hp = 7460 W
Therefore, a 10 horsepower motor is equivalent to approximately 7460 watts.
Example 2: Converting Watts to Horsepower
An electrical appliance consumes 1500 watts of power. What is its equivalent horsepower?
1500 W / 746 W/hp ≈ 2.01 hp
Therefore, a 1500-watt appliance is approximately equivalent to 2.01 horsepower.
Different Types of Horsepower: Metric vs. Imperial
While the conversion factor of 746 W/hp is widely used, it's crucial to acknowledge that variations exist in horsepower definitions.
- Mechanical Horsepower (hp): This is the most common type of horsepower and is based on the original definition of 550 ft-lb/s. This is often used in automotive and mechanical engineering.
- Electrical Horsepower (hp): Used primarily in electrical engineering and relates electrical power (watts) directly to horsepower. The conversion may differ slightly based on specific standards used.
- Metric Horsepower (PS or cv): This is used in some European countries and is defined as 735.49875 watts. It is slightly less than the mechanical horsepower.
The differences between these types of horsepower are relatively small, but understanding these subtle variations ensures precision when dealing with highly sensitive power calculations.
Beyond the Numbers: Context Matters
The conversion between watts and horsepower is more than just a mathematical equation. Understanding the context in which these units are used is crucial. Horsepower is often used in mechanical applications, especially those involving internal combustion engines (cars, trucks, etc.), while watts are more commonly used for electrical systems.
Practical Applications and Considerations
- Automotive Engineering: Horsepower is commonly used to describe the power output of internal combustion engines in vehicles. Knowing the conversion allows engineers to compare the performance of engines with different specifications.
- Electrical Motors: The power output of electric motors is typically expressed in watts or kilowatts. The conversion is necessary when comparing electric motors to those with internal combustion engines.
- Industrial Machinery: Heavy industrial machinery might use both watts and horsepower in its specifications, depending on the components and their origin.
Understanding the conversion isn't just about numbers; it's about comparing and contrasting the capabilities of various power systems.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
- Horsepower isn't a constant: Remember, Watt's original measurement was an approximation. The actual power a horse can produce is highly variable.
- The conversion isn't perfectly precise: The 746 W/hp conversion is an approximation due to the inherent variability in the original horsepower definition.
- Different horsepower types exist: Be aware of the variations in horsepower definitions (mechanical, electrical, metric) to avoid misinterpretations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Watts-Horsepower Equation
The conversion between watts and horsepower, while seemingly straightforward, involves understanding the historical context, the different types of horsepower, and the inherent imprecision in the original definition of horsepower. Mastering this conversion empowers you to effectively compare power outputs of various systems, whether mechanical or electrical, fostering a more nuanced understanding of power and energy. Remember to always consider the context and potential variations in horsepower definitions for accurate calculations and comparisons. The information provided here serves as a valuable resource for anyone involved in engineering, mechanics, or any field dealing with power measurements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Containing Two Different Alleles For A Trait
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Non Renewable Source Of Energy
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Binds To The Exposed Cross Bridges On Actin
Apr 04, 2025
-
All Squares Are Rectangles And Rhombuses
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Role Of Toothpaste In Preventing Cavities
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Watts Equal One Horse Power . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
