Which Of The Following Is A Non-renewable Source Of Energy
News Leon
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
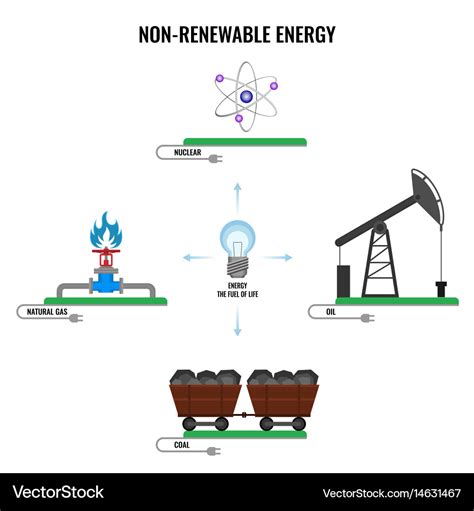
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Is A Non-renewable Source Of Energy
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following is a Non-Renewable Source of Energy? Understanding Finite Resources
- What are Non-Renewable Energy Sources?
- Major Types of Non-Renewable Energy Sources
- 1. Fossil Fuels: The Pillars of Non-Renewable Energy
- 2. Nuclear Energy: A Controversial Non-Renewable Source
- Environmental Impact of Non-Renewable Energy Sources
- The Urgent Need for Transition to Renewable Energy
- Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Look at Non-Renewable Resource Management
- Conclusion: A Sustainable Energy Future
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following is a Non-Renewable Source of Energy? Understanding Finite Resources
The world's energy consumption is constantly increasing, driven by population growth, industrialization, and rising living standards. Understanding the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy sources is crucial for addressing our future energy needs sustainably. This article dives deep into the definition of non-renewable energy, explores various examples, and discusses their environmental impact and the importance of transitioning to cleaner alternatives.
What are Non-Renewable Energy Sources?
Non-renewable energy sources are those that are finite; meaning they exist in limited quantities and will eventually be depleted. Unlike renewable resources which replenish naturally, non-renewable sources take millions of years to form, making them unsustainable for long-term use at current consumption rates. Their extraction and use often have significant environmental consequences.
The key characteristic distinguishing non-renewable from renewable sources is their rate of replenishment. Renewable resources, like solar, wind, and hydro, are replenished faster than they are consumed. Non-renewable resources, however, are consumed at a much faster rate than nature can replace them.
Major Types of Non-Renewable Energy Sources
Several types of energy fall under the umbrella of non-renewable resources. Let's explore some of the most prominent ones:
1. Fossil Fuels: The Pillars of Non-Renewable Energy
Fossil fuels – coal, oil (crude oil and petroleum), and natural gas – are the most widely used non-renewable energy sources globally. They are formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals, compressed and heated over millions of years under the Earth's surface. Their energy is released through combustion, a process that generates heat to produce electricity or power vehicles.
-
Coal: A solid fossil fuel, coal is primarily used for electricity generation in power plants. Its extraction is often environmentally damaging, leading to habitat destruction and water pollution. Burning coal releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases, contributing significantly to climate change.
-
Oil (Petroleum): A liquid fossil fuel, oil is a versatile energy source used for transportation (gasoline, diesel), heating, and the production of plastics and other petrochemicals. Oil extraction, particularly offshore drilling, poses environmental risks, including oil spills and habitat disruption. Burning oil also contributes heavily to greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Natural Gas: A gaseous fossil fuel, natural gas is cleaner-burning than coal and oil, emitting less carbon dioxide per unit of energy produced. However, it still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and its extraction (fracking) can contaminate groundwater and cause seismic activity.
2. Nuclear Energy: A Controversial Non-Renewable Source
Nuclear energy is derived from the splitting of uranium atoms in a process called nuclear fission. This process generates immense heat used to produce electricity in nuclear power plants. While nuclear energy doesn't directly emit greenhouse gases during electricity generation, it presents other significant challenges.
-
Nuclear Waste: The radioactive waste produced by nuclear power plants remains dangerous for thousands of years, requiring secure and long-term storage solutions. Finding safe and permanent disposal sites remains a major global challenge.
-
Nuclear Accidents: Accidents at nuclear power plants, such as Chernobyl and Fukushima, have highlighted the potential for catastrophic consequences, leading to widespread environmental contamination and health problems.
-
Uranium Mining: The process of uranium mining and processing itself can lead to environmental damage and health risks for workers and surrounding communities.
Environmental Impact of Non-Renewable Energy Sources
The environmental consequences of using non-renewable energy sources are substantial and far-reaching. The most significant impacts include:
-
Climate Change: The combustion of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases (GHGs) like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trapping heat in the atmosphere and causing global warming. This leads to a cascade of effects, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
-
Air Pollution: The burning of fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants into the air, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. These pollutants contribute to respiratory illnesses, acid rain, and smog.
-
Water Pollution: Oil spills, coal mining runoff, and fracking wastewater can contaminate water sources, harming aquatic life and posing risks to human health.
-
Land Degradation: Extraction of fossil fuels can cause significant land degradation, including habitat destruction, deforestation, and soil erosion.
-
Resource Depletion: The finite nature of non-renewable energy sources means that they will eventually be depleted, requiring a transition to alternative energy sources.
The Urgent Need for Transition to Renewable Energy
The environmental and social costs associated with non-renewable energy are unsustainable. The overwhelming scientific consensus points to the urgent need for a transition towards renewable energy sources. Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, offer cleaner, sustainable alternatives.
While transitioning entirely to renewable energy will require significant investment and technological advancements, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. The transition will:
-
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Renewable energy sources produce significantly fewer greenhouse gas emissions, helping mitigate climate change.
-
Improve Air and Water Quality: Switching to renewable energy will lead to cleaner air and water, improving public health.
-
Enhance Energy Security: Reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels will improve energy security and reduce vulnerability to price fluctuations.
-
Create Economic Opportunities: The renewable energy sector is a growing industry, creating numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Look at Non-Renewable Resource Management
While transitioning to renewable energy is paramount, responsible management of remaining non-renewable resources is also crucial during the transition period. This includes:
-
Improving Extraction Techniques: Developing cleaner and more efficient methods of extracting fossil fuels to minimize environmental damage.
-
Carbon Capture and Storage: Implementing technologies to capture carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and industrial facilities and store them underground.
-
Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry to reduce overall energy consumption.
-
Nuclear Waste Management: Developing safe and sustainable methods for managing nuclear waste.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Energy Future
The choice between renewable and non-renewable energy sources is not merely an economic one; it's a crucial decision with far-reaching environmental and societal implications. While non-renewable sources have powered much of our progress, their finite nature and environmental consequences necessitate a swift and decisive shift towards renewable energy. By investing in renewable energy technologies, improving energy efficiency, and implementing responsible management strategies for remaining non-renewable resources, we can pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable, and secure energy future for generations to come. The transition will require collaboration between governments, industries, and individuals, but the long-term benefits are undeniable. Our future depends on making informed choices today about how we power our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Most Abundant Gas On Earth
Apr 13, 2025
-
An Organism That Feeds On Dead And Decomposing Matter
Apr 13, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Characteristic Of Shifting Cultivation
Apr 13, 2025
-
A Cross That Involves Two Traits Is Called A
Apr 13, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Organisms Are Prokaryotes
Apr 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Non-renewable Source Of Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.